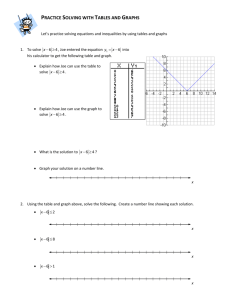
Page 1 Section 1.2: Lines Points: (3, 4), (7, 16) − y
advertisement

Math 141-copyright Joe Kahlig, 15A Page 1 Section 1.2: Lines Points: (3, 4), (7, 16) Slope: y2 − y1 x2 − x1 Equation of a line: Section 1.3 and 1.4: Linear Functions and Modeling Example: The percent of people with an iPad was at 6% at the beginning of 2010 and is projected to grow linearly so that at the beginning of 2014 the percent of people with an iPad is projected to be 26%. A) Derive an equation of the line that represents this information. B) In what year will the percentage of people with ipads be 49%? Math 141-copyright Joe Kahlig, 15A Page 2 Example: The Monde Company makes a wine cooler with a capacity of 24 bottles. Each wine cooler sells for $245. The monthly fixed cost incurred by the company are $381,300, and the variable cost of producing each wine cooler is $90. A) Find the Cost, Revenue, and Profit functions. B) How many coolers should be made and sold when the company breaks even? C) What is the break even point? Example: Paul manages a t-shirt store which has a monthly rent of $805. If Paul needs to sell 46 shirts each month to break even and he sells the shirts for $28.50, what does Paul pay for each shirt? Math 141-copyright Joe Kahlig, 15A Page 3 Supply and Demand functions: The supply function is a formula that relates the number of items being supplied by manufacturers, x, to the price of the items, p. The demand function is a formula that relates the number of items being demanded by consumers, x, to the price of the items, p. Note: All points for supply and demand formulas are given as (x, p). Market equilibrium is the point where the supply and demand functions intersect. Example: When a coffee maker is priced at $40, 200 sell. If the price increases by $10, then 150 sell. The producer is willing to provide 240 coffee makers when the price is $160 and are willing to provide 120 coffee makers when the price is $88. Find the supply and demand equations and then find the equilibrium point.