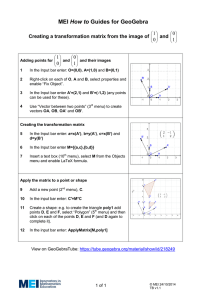
MEI Tasks for Casio Graphical Calculators

MEI Tasks for Casio Graphical Calculators
Using the Casio fx-9750G Plus
1. Drawing lines of the form x
c :
From the main menu: select option 5 (GRAPH): then F3 (TYPE): followed by F4 (X=C):
Now enter 2: then EXE followed by F6 (DRAW): showing the graph of x
2
Page 1 of 13 © MEI 2005
MEI Tasks for Casio Graphical Calculators
2. Drawing inequalities such as y
x
2
1 :
From the main menu: select option 5 (GRAPH): then F3 (TYPE): followed by F6 (more options): and F1 (Y>): x
2
1 and EXE: followed by F6 (DRAW): showing the region satisfying y
x
2
1 .
Page 2 of 13 © MEI 2005
MEI Tasks for Casio Graphical Calculators
3. Summing an AP given the general term and the number of terms.
From the main menu: select option 1 (RUN) followed by the OPTN key: then F4 (CALC) and F6(more options) and then F3 ( ):
To sum the AP (with 8 terms) k
8
1
3 k
1
Page 3 of 13 © MEI 2005
MEI Tasks for Casio Graphical Calculators
4. Evaluating d
2 y d x 2
at a point on curve.
From the main menu: select option 1 (RUN) followed by the OPTN key: then F4 (CALC) and F3 ( d
2 y d x
2
):
Now to evaluate d
2 y d x
2
at the point x
2 on the curve y
x
3
2 x
2 :
Similarly to find
1
3
2 d , choose F4 (
d x ):
Page 4 of 13 © MEI 2005
MEI Tasks for Casio Graphical Calculators
5. Plotting a family of curves dynamically.
To plot y
Ax
2 for A
1, 2,3, 4 :
From the main menu: select option 6 (DYNA): and (using the ALPHA button to access the variable A) enter y
Ax
2 followed by EXE:
To set the range for A press F4 (VAR) then 1 (for the initial value of A ): followed by F2 (RANGE) and set End to 4 and Pitch to 1:
EXIT followed by F6 ( DYNA) and after “One moment please” the graphs will be drawn in sequence a total of 10 times.
Page 5 of 13 © MEI 2005
MEI Tasks for Casio Graphical Calculators
6. Given the y co-ordinate of a point on a graph determining the corresponding x co-ordinate
From the main menu: select option 5 (GRAPH): then y
2
4
and EXE: and F6 (DRAW):
SHIFT F5 (G-SLV) followed by F6 (more options) and F2 (XCAL) prompts you for the y coordinate you are interested in:
Try y
1.5
and EXE:
Press the right cursor ► to get the next point with y coordinate 1.5: and ► again:
Page 6 of 13 © MEI 2005
MEI Tasks for Casio Graphical Calculators
7. Drawing a line that is the tangent or the normal to a point on a graph.
From the main menu: select option 5 (GRAPH): then, say, y
x
3
4 x
4 : and F6 (DRAW):
To draw a tangent to the curve at a chosen point select the Sketch menu
(SHIFT and F4) followed by F2 (Tang) and then you are prompted to move the cursor to your chosen point: and EXE draws the tangent:
F3 rather than F2 would draw the normal. Due to the scales on the graph, the tangent and normal do not look perpendicular – a good discussion point:
Page 7 of 13 © MEI 2005
MEI Tasks for Casio Graphical Calculators
8. Using the dual graph to view the graph of a function alongside an enlarged region.
From the main menu: select option 5 (GRAPH): then enter, say, y
x
2 and y x 3 : followed by F6 (DRAW):
SHIFT and SET UP and ▼▼ followed by F1 (Grph): then EXIT and F6 (DRAW):
SHIFT F2 (Zoom), F1 (Box) and using the cursors and EXE to select a region to enlarge:
Page 8 of 13 © MEI 2005
MEI Tasks for Casio Graphical Calculators
9. Drawing a dynamic graph using the built-in functions.
From the main menu: select option 6 (DYNA): and then F5 (B-IN): followed by ▼ and F1 (Select):
You will need to give values to two of these and choose a range of values for the third. First using the cursor ▼ and EXE choose values for A, B and C:
Now highlight B=-2 (you might need to use EXE) and press F1 (Select) and this will be the dynamic coefficient:
F2 (Range) allows you to select the range of values for B:
F3 (Speed) allows you to change the speed at which the graphs are plotted and F6 (DYNA) shows the family of curves plotted in sequence:
Page 9 of 13 © MEI 2005
MEI Tasks for Casio Graphical Calculators
10. Graphing circles
From the main menu: select option 9 (Conics): and ▼to circles:
EXE then allows you to choose values for the coordinates of the centre (H,K) and the radius:
F6 (DRAW): looks like an ellipse so a combination of
SHIFT F2 (Zoom), F6, F2 (SQR) and SHIFT F3 (V-Window) results in a circular circle!
Page 10 of 13 © MEI 2005
MEI Tasks for Casio Graphical Calculators
11. Solving equations
From the main menu: select option 1 (RUN) and then OPTN F4 (CALC):
Press F1 (Solve) and then input the expression. For example, if you want to solve the equation x
3
4 x
1 finding the root near 2:
You can also find the root near 0 by pressing the
◄ key and editing: and similarly the root near
–2:
Page 11 of 13 © MEI 2005
MEI Tasks for Casio Graphical Calculators
12. Recursive functions
From the main menu: select option 8 (RECUR): and then F3 ( a n
2
):
Example 1. The Fibonacci sequence.
Press key F4: then enter a n
2
a n
1
a n
You could use F1 to generate
A.P.s such as a n
3 n
1
then F5(Range) and EXE
using F3 and F2 and EXE: the following values
EXE twice at the end takes F6(Table) gives the Fibonacci sequence, you back to the previous screen: using the ▼ key to see further values.
Example 2. Adding the terms of a GP
Following the instructions above… and this generates the GP
1
,
2
,
3
,...
with first term 2 and common ratio 1.5 and the sum of this GP: b n
r n
1 a r
Page 12 of 13 © MEI 2005
MEI Tasks for Casio Graphical Calculators
13. Dealing with derivative functions.
From the main menu: select option 5 (GRAPH) along with the graph shown:
OPTN F2 (CALC) VARS, F4(GRAPH) and F1 (Y) followed by 1,X) EXE: followed by F1(d/dx):
SHIFT F3 (V-Window) and these settings: and EXE takes you back to the previous screen :
Finally F6 (DRAW): showing the graph of y
2
x
2
x
3
4 x and the derivative function
Y 2
3 x
2
4 . d x
Lots of interesting questions can be asked here:
What is special about the three points where the graph of Y2 crosses the axes?
What happens to the two graphs as x
?
Is y
x
3
4 x an odd function? Does this mean that d y d x even function? must be an
Is there anything special about the points where the two graphs intersect? In how many places do they intersect?
Page 13 of 13 © MEI 2005