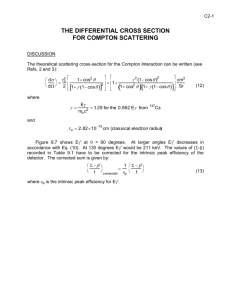
Proton Compton Scattering In Unified Proton- Theory
advertisement

Outline Background and Motivation The Model Proton Compton Scattering Vertex Structure Summary 2011 Cross Strait Meeting on Particle Physics and Cosmology Proton Compton Scattering In Unified Proton-∆+ Theory ZHANG Yun (Collaboration With Konstantin G. Savvidy) Physics Department, Nanjing University April 1, 2011 Outline Background and Motivation The Model Proton Compton Scattering 1 Background and Motivation 2 The Model 3 Proton Compton Scattering 4 Vertex Structure 5 Summary Vertex Structure Summary Outline Background and Motivation The Model + Proton Compton Scattering Vertex Structure ∆+ (1232MeV, J P = 32 ) freedom must be taken into account in proton Compton scattering Summary Outline Background and Motivation The Model Proton Compton Scattering Vertex Structure Summary + ∆+ (1232MeV, J P = 32 ) freedom must be taken into account in proton Compton scattering Previously p is treated as spin 1/2 Dirac spinor and ∆+ in a different theory Outline Background and Motivation The Model Proton Compton Scattering Vertex Structure Summary + ∆+ (1232MeV, J P = 32 ) freedom must be taken into account in proton Compton scattering Previously p is treated as spin 1/2 Dirac spinor and ∆+ in a different theory Our innovation: We treat p and ∆+ in a unified spin 3/2 field theory Outline Background and Motivation The Model Proton Compton Scattering Vertex Structure Summary + ∆+ (1232MeV, J P = 32 ) freedom must be taken into account in proton Compton scattering Previously p is treated as spin 1/2 Dirac spinor and ∆+ in a different theory Our innovation: We treat p and ∆+ in a unified spin 3/2 field theory How Motivated Outline Background and Motivation The Model Proton Compton Scattering Vertex Structure Summary + ∆+ (1232MeV, J P = 32 ) freedom must be taken into account in proton Compton scattering Previously p is treated as spin 1/2 Dirac spinor and ∆+ in a different theory Our innovation: We treat p and ∆+ in a unified spin 3/2 field theory How Motivated Proton and ∆+ are both comprised of the same quarks. Outline Background and Motivation The Model Proton Compton Scattering Vertex Structure Summary + ∆+ (1232MeV, J P = 32 ) freedom must be taken into account in proton Compton scattering Previously p is treated as spin 1/2 Dirac spinor and ∆+ in a different theory Our innovation: We treat p and ∆+ in a unified spin 3/2 field theory How Motivated Proton and ∆+ are both comprised of the same quarks. Three spin 1/2 particles results in 8 spin states, that for a spin 3/2 particle and two spin 1/2 particles. Outline Background and Motivation The Model Proton Compton Scattering Generalized Rarita-Schwinger Theory The Lagrangian Konstantin G. Savvidy, arXiv:1005.3455: L = ψ̄µ [D µ ν − mΘµ ν ]ψ ν , D µ ν = γ ρ pρ δ µ ν + ξ(γ µ pν + γν pµ ) + ζγ µ γ ρ pρ γν , 2 Θµ ν = δ µ ν − zγ ν γν ,ζ = 3ξ +2ξ+1 2 Vertex Structure Summary Outline Background and Motivation The Model Proton Compton Scattering Generalized Rarita-Schwinger Theory The Lagrangian Konstantin G. Savvidy, arXiv:1005.3455: L = ψ̄µ [D µ ν − mΘµ ν ]ψ ν , D µ ν = γ ρ pρ δ µ ν + ξ(γ µ pν + γν pµ ) + ζγ µ γ ρ pρ γν , 2 Θµ ν = δ µ ν − zγ ν γν ,ζ = 3ξ +2ξ+1 2 L invariant under point transformation: ψ µ → ψ µ + λγ µ γν ψ ν ξ 0 = ξ(1 − 4λ) − 2λ Vertex Structure Summary Outline Background and Motivation The Model Proton Compton Scattering Generalized Rarita-Schwinger Theory The Lagrangian Konstantin G. Savvidy, arXiv:1005.3455: L = ψ̄µ [D µ ν − mΘµ ν ]ψ ν , D µ ν = γ ρ pρ δ µ ν + ξ(γ µ pν + γν pµ ) + ζγ µ γ ρ pρ γν , 2 Θµ ν = δ µ ν − zγ ν γν ,ζ = 3ξ +2ξ+1 2 L invariant under point transformation: ψ µ → ψ µ + λγ µ γν ψ ν ξ 0 = ξ(1 − 4λ) − 2λ ξ = 2z − 1 =⇒ pµ ψ µ (p) = 0. Vertex Structure Summary Outline Background and Motivation The Model Proton Compton Scattering Generalized Rarita-Schwinger Theory The Lagrangian Konstantin G. Savvidy, arXiv:1005.3455: L = ψ̄µ [D µ ν − mΘµ ν ]ψ ν , D µ ν = γ ρ pρ δ µ ν + ξ(γ µ pν + γν pµ ) + ζγ µ γ ρ pρ γν , 2 Θµ ν = δ µ ν − zγ ν γν ,ζ = 3ξ +2ξ+1 2 L invariant under point transformation: ψ µ → ψ µ + λγ µ γν ψ ν ξ 0 = ξ(1 − 4λ) − 2λ ξ = 2z − 1 =⇒ pµ ψ µ (p) = 0. mass spectrum: m3/2 = m,m1/2 = m 6z−2 . Vertex Structure Summary Outline Background and Motivation The Model Proton Compton Scattering Vertex Structure Summary Generalized Rarita-Schwinger Theory The Lagrangian Konstantin G. Savvidy, arXiv:1005.3455: L = ψ̄µ [D µ ν − mΘµ ν ]ψ ν , D µ ν = γ ρ pρ δ µ ν + ξ(γ µ pν + γν pµ ) + ζγ µ γ ρ pρ γν , 2 Θµ ν = δ µ ν − zγ ν γν ,ζ = 3ξ +2ξ+1 2 L invariant under point transformation: ψ µ → ψ µ + λγ µ γν ψ ν ξ 0 = ξ(1 − 4λ) − 2λ ξ = 2z − 1 =⇒ pµ ψ µ (p) = 0. mass spectrum: m3/2 = m,m1/2 = m 6z−2 . Original Rarita-Schwinger Theory: z= (1+3ξ)2 +3(1+ξ)2 . 4 Outline Background and Motivation The Model Proton Compton Scattering Vertex Structure Summary Generalized Rarita-Schwinger Theory The Lagrangian Konstantin G. Savvidy, arXiv:1005.3455: L = ψ̄µ [D µ ν − mΘµ ν ]ψ ν , D µ ν = γ ρ pρ δ µ ν + ξ(γ µ pν + γν pµ ) + ζγ µ γ ρ pρ γν , 2 Θµ ν = δ µ ν − zγ ν γν ,ζ = 3ξ +2ξ+1 2 L invariant under point transformation: ψ µ → ψ µ + λγ µ γν ψ ν ξ 0 = ξ(1 − 4λ) − 2λ ξ = 2z − 1 =⇒ pµ ψ µ (p) = 0. mass spectrum: m3/2 = m,m1/2 = m 6z−2 . Original Rarita-Schwinger Theory: z= (1+3ξ)2 +3(1+ξ)2 . 4 no spin 1/2 on shell component. Outline Background and Motivation The Model Proton Compton Scattering Vertex Structure Summary Generalized Rarita-Schwinger Theory The Lagrangian Konstantin G. Savvidy, arXiv:1005.3455: L = ψ̄µ [D µ ν − mΘµ ν ]ψ ν , D µ ν = γ ρ pρ δ µ ν + ξ(γ µ pν + γν pµ ) + ζγ µ γ ρ pρ γν , 2 Θµ ν = δ µ ν − zγ ν γν ,ζ = 3ξ +2ξ+1 2 L invariant under point transformation: ψ µ → ψ µ + λγ µ γν ψ ν ξ 0 = ξ(1 − 4λ) − 2λ ξ = 2z − 1 =⇒ pµ ψ µ (p) = 0. mass spectrum: m3/2 = m,m1/2 = Original Rarita-Schwinger Theory: z= (1+3ξ)2 +3(1+ξ)2 . 4 no spin 1/2 on shell component. superluminal propagation m 6z−2 . Outline Background and Motivation The Model Proton Compton Scattering L = ψ̄µ [D µ ν − mΘµ ν ]ψ ν , D µ ν = γ ρ pρ δ µ ν + ξ(γ µ pν + γν pµ ) + ζγ µ γ ρ pρ γν , Θµ ν = δ µ ν − zγ ν γν Vertex Structure Summary Outline Background and Motivation The Model Proton Compton Scattering Vertex Structure L = ψ̄µ [D µ ν − mΘµ ν ]ψ ν , D µ ν = γ ρ pρ δ µ ν + ξ(γ µ pν + γν pµ ) + ζγ µ γ ρ pρ γν , Θµ ν = δ µ ν − zγ ν γν Spin 1/2 component wave function: u2 (0, + 21 ) = 1 1 1 i i 1 1 T √ √ √ √ √ √ 3z−1 (0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 2 3 , 0, − 2 3 , 0, 2 3 , 0, − 2 3 , 2 3 , 0, − 2 3 , 0) u2 (0, − 12 ) = 1 1 1 i i 1 1 T √ √ √ √ √ √ 3z−1 (0, 0, 0, 0, 2 3 , 0, − 2 3 , 0, − 2 3 , 0, 2 3 , 0, 0, − 2 3 , 0, 2 3 ) u2µ α (k , σ) = Lµ ναβ (k , M)u2ν β (0, σ) Lµ ν αβ = LV µ ν ⊗ LSαβ LV , LS: boost matrix for vector and dirac spinor fields respectively. Summary Outline Background and Motivation The Model Proton Compton Scattering Vertex Structure Summary L = ψ̄µ [D µ ν − mΘµ ν ]ψ ν , D µ ν = γ ρ pρ δ µ ν + ξ(γ µ pν + γν pµ ) + ζγ µ γ ρ pρ γν , Θµ ν = δ µ ν − zγ ν γν LV = LS = √ E M k1 M k1 M k2 E 1 + (M − 1) ~12 k2 M E (M k3 M E (M 1 2M(E+M) − − |k | k2 k1 1) ~ 2 |k | k3 k1 1) ~ 2 |k | E (M − 1) k~1 k22 |k | 1+ E (M E (M − k3 M k2 M k2 − 1) ~22 |k | k3 k2 1) ~ 2 |k | E (M − 1) k~1 k23 |k | k2 k3 E ( M − 1) ~ 2 |k | k2 E ( M − 1) ~32 E + M − ~k · ~σ 0 0 E + M + ~k · ~σ |k | ! Outline Background and Motivation The Model Proton Compton Scattering Vertex Structure L = ψ̄µ [D µ ν − mΘµ ν ]ψ ν , D µ ν = γ ρ pρ δ µ ν + ξ(γ µ pν + γν pµ ) + ζγ µ γ ρ pρ γν , Θµ ν = δ µ ν − zγ ν γν Electrodynamic Interaction pµ → pµ − Aµ ⇒ LI = Aµ J µ = eψ̄ν Γµν ρ ψ ρ Aµ , pµ J µ = 0 Γµν ρ = γ µ δ ν ρ + ξ(γ ν δ µ ρ + γρ η νµ ) + ζγ ν γ µ γρ Summary Outline Background and Motivation The Model Proton Compton Scattering Vertex Structure L = ψ̄µ [D µ ν − mΘµ ν ]ψ ν , D µ ν = γ ρ pρ δ µ ν + ξ(γ µ pν + γν pµ ) + ζγ µ γ ρ pρ γν , Θµ ν = δ µ ν − zγ ν γν Electrodynamic Interaction pµ → pµ − Aµ ⇒ LI = Aµ J µ = eψ̄ν Γµν ρ ψ ρ Aµ , pµ J µ = 0 Γµν ρ = γ µ δ ν ρ + ξ(γ ν δ µ ρ + γρ η νµ ) + ζγ ν γ µ γρ Comparison V. Pascalutsa and O. Scholten, Nucl. Phys. A591, 658 (1995) α νµ + h.c. 1 L1I = iG 2m ψ̄ Θαµ (zf )γν γ5 T3 NF −G L2I = (2m)22 ψ̄ α Θαµ (zf )γ5 T3 ∂µ NF νµ + h.c. L3I = −G3 α ψ̄ Θαµ (zf )γ5 T3 N∂ν F νµ (2m)2 + h.c. Summary Outline Background and Motivation The Model Proton Compton Scattering Vertex Structure In L = ψ̄µ [D µ ν − mΘµ ν ]ψ ν ,we identify spin 3/2 component as ∆+ and spin 1/2 component as proton. Proton Compton Scattering Feynman Diagrams Summary Outline Background and Motivation The Model Proton Compton Scattering Vertex Structure In L = ψ̄µ [D µ ν − mΘµ ν ]ψ ν ,we identify spin 3/2 component as ∆+ and spin 1/2 component as proton. Feynman Rules Out line: u2 (k1 ), ū2 (k4 ) Vertex: Γµν ρ = γ µ δ ν ρ + ξ(γ ν δ µ ρ + γρ η νµ ) + ζγ ν γ µ γρ Propogator: [D µ ν − mΘµ ν ]−1 Summary Outline Background and Motivation The Model Proton Compton Scattering Vertex Structure In L = ψ̄µ [D µ ν − mΘµ ν ]ψ ν ,we identify spin 3/2 component as ∆+ and spin 1/2 component as proton. Feynman Rules Out line: u2 (k1 ), ū2 (k4 ) Vertex: Γµν ρ = γ µ δ ν ρ + ξ(γ ν δ µ ρ + γρ η νµ ) + ζγ ν γ µ γρ Propogator: [D µ ν − mΘµ ν ]−1 Two poles in propogator: p2 = m2 : ∆+ pole p2 = M 2 : proton pole(M = m 6z−2 ) Summary Outline Background and Motivation The Model Proton Compton Scattering Vertex Structure In L = ψ̄µ [D µ ν − mΘµ ν ]ψ ν ,we identify spin 3/2 component as ∆+ and spin 1/2 component as proton. Summary Outline Background and Motivation The Model Proton Compton Scattering Vertex Structure Summary In L = ψ̄µ [D µ ν − mΘµ ν ]ψ ν ,we identify spin 3/2 component as ∆+ and spin 1/2 component as proton. Amplitude and Differential Cross Section Mσ1 ,σ4 ,λ2 ,λ3 = ie2 (ū2η (k4 , σ4 )Γµη ρ S ρ γ (k1 − k3 )Γνγ κ u2 κ (k1 , σ1 ) +ū2η (k4 , σ4 )Γνη ρ S ρ γ (k1 + k2 )Γµγ κ u2 κ (k1 , σ1 )) dσ = dΩ µ (k2 , λ2 )∗ν (k3 , λ3 ) 1 ω0 2 X ( ) |M|2 64π 2 ω σ1 ,σ4 ,λ2 ,λ3 Outline Background and Motivation The Model Proton Compton Scattering Vertex Structure Low energy expansion agrees with F.E.Low,PR96,1428(1954): dσ = α2 (1+cos2 θ) − α2 (1−cos θ)(1+cos2 θ) ω + O(ω 2 ) 2M 2 M3 dΩ Summary Outline Background and Motivation The Model Proton Compton Scattering Vertex Structure Low energy expansion agrees with F.E.Low,PR96,1428(1954): dσ = α2 (1+cos2 θ) − α2 (1−cos θ)(1+cos2 θ) ω + O(ω 2 ) 2M 2 M3 dΩ Difference at O(ω 2 ) from Dirac theory affects the extraction of polarizability parameters(ᾱ,β̄) from experiment(δ ᾱ,δ β̄ = O(1)) dσ = ( dσ ) − αω2 ( ᾱ+β̄ (1 + cos θ)2 + ᾱ−β̄ (1 − cos θ)2 ) M 2 2 dΩ dΩ Born Summary Outline Background and Motivation The Model Proton Compton Scattering Vertex Structure Low energy expansion agrees with F.E.Low,PR96,1428(1954): dσ = α2 (1+cos2 θ) − α2 (1−cos θ)(1+cos2 θ) ω + O(ω 2 ) 2M 2 M3 dΩ Difference at O(ω 2 ) from Dirac theory affects the extraction of polarizability parameters(ᾱ,β̄) from experiment(δ ᾱ,δ β̄ = O(1)) dσ = ( dσ ) − αω2 ( ᾱ+β̄ (1 + cos θ)2 + ᾱ−β̄ (1 − cos θ)2 ) M 2 2 dΩ dΩ Born 8. ´ 10-11 6. ´ 10-11 θ=0 4. ´ 10-11 Blue: current theory 2. ´ 10-11 Red: Dirac theory 50 100 150 200 250 Ω Summary Outline Background and Motivation The Model Proton Compton Scattering Vertex Structure Low energy expansion agrees with F.E.Low,PR96,1428(1954): dσ = α2 (1+cos2 θ) − α2 (1−cos θ)(1+cos2 θ) ω + O(ω 2 ) 2M 2 M3 dΩ Difference at O(ω 2 ) from Dirac theory affects the extraction of polarizability parameters(ᾱ,β̄) from experiment(δ ᾱ,δ β̄ = O(1)) dσ = ( dσ ) − αω2 ( ᾱ+β̄ (1 + cos θ)2 + ᾱ−β̄ (1 − cos θ)2 ) M 2 2 dΩ dΩ Born 3.5 ´ 10-11 3. ´ 10-11 2.5 ´ 10-11 θ= 2. ´ 10-11 π 2 Blue: current theory 1.5 ´ 10-11 1. ´ 10-11 Red: Dirac theory 5. ´ 10-12 50 100 150 200 250 Ω Summary Outline Background and Motivation The Model Proton Compton Scattering Vertex Structure Low energy expansion agrees with F.E.Low,PR96,1428(1954): dσ = α2 (1+cos2 θ) − α2 (1−cos θ)(1+cos2 θ) ω + O(ω 2 ) 2M 2 M3 dΩ Difference at O(ω 2 ) from Dirac theory affects the extraction of polarizability parameters(ᾱ,β̄) from experiment(δ ᾱ,δ β̄ = O(1)) dσ = ( dσ ) − αω2 ( ᾱ+β̄ (1 + cos θ)2 + ᾱ−β̄ (1 − cos θ)2 ) M 2 2 dΩ dΩ Born 6. ´ 10-11 5. ´ 10-11 4. ´ 10-11 θ=π 3. ´ 10-11 Blue: current theory 2. ´ 10-11 Red: Dirac theory 1. ´ 10-11 50 100 150 200 250 Ω Summary Outline Background and Motivation The Model Proton Compton Scattering Vertex Structure Low energy expansion agrees with F.E.Low,PR96,1428(1954): dσ = α2 (1+cos2 θ) − α2 (1−cos θ)(1+cos2 θ) ω + O(ω 2 ) 2M 2 M3 dΩ Difference at O(ω 2 ) from Dirac theory affects the extraction of polarizability parameters(ᾱ,β̄) from experiment(δ ᾱ,δ β̄ = O(1)) dσ = ( dσ ) − αω2 ( ᾱ+β̄ (1 + cos θ)2 + ᾱ−β̄ (1 − cos θ)2 ) M 2 2 dΩ dΩ Born 6. ´ 10-11 5. ´ 10-11 We are not ready to fit experimental data yet, since proton is not a fundamental particle. 4. ´ 10-11 -11 3. ´ 10 2. ´ 10-11 1. ´ 10-11 50 100 150 200 250 Ω Summary Outline Background and Motivation The Model Proton Compton Scattering Vertex Structure Vertex Structure Reminiscence Dirac spinor electrodynamic interaction: 0 )µ iσ µν qν 2 2 ū(p0 )[ (p+p 2m F1 (q ) + 2m F2 (q )]u(p)Aµ F1 , F2 : form factors. q = p0 − p Summary Outline Background and Motivation The Model Proton Compton Scattering Reminiscence Dirac spinor electrodynamic interaction: 0 )µ iσ µν qν 2 2 ū(p0 )[ (p+p 2m F1 (q ) + 2m F2 (q )]u(p)Aµ F1 , F2 : form factors. Vertex Structure q = p0 − p Our Task Find (all) possible Γµν ρ (p, p0 ) in ψ̄ν (p0 )Γµν ρ (p, p0 )ψ ρ (p)Aµ Gauge Invariance: qµ ψ̄ν (p0 )Γµν ρ (p, p0 )ψ ρ (p) = 0 Summary Outline Background and Motivation The Model Proton Compton Scattering Vertex Structure Our Task Find (all) possible Γµν ρ (p, p0 ) in ψ̄ν (p0 )Γµν ρ (p, p0 )ψ ρ (p)Aµ Gauge Invariance: qµ ψ̄ν (p0 )Γµν ρ (p, p0 )ψ ρ (p) = 0 Structures We Have Found Γµν ρ (p, p0 ) = Scalar Type η ν ρ (p + p0 )µ γ ν γρ (p + p0 )µ × η ν ρ γ 5 (p + p0 )µ × γ ν γρ γ 5 (p + p0 )µ Summary Outline Background and Motivation The Model Proton Compton Scattering Vertex Structure Our Task Find (all) possible Γµν ρ (p, p0 ) in ψ̄ν (p0 )Γµν ρ (p, p0 )ψ ρ (p)Aµ Gauge Invariance: qµ ψ̄ν (p0 )Γµν ρ (p, p0 )ψ ρ (p) = 0 Structures We Have Found Γµν ρ (p, p0 ) = Vector Type ην ργ µ γ ν γ µ γρ γ ν η µ ρ + γρ η µν × γ ν η µ ρ − γρ η µν × γ 5 (· · · ) Summary Outline Background and Motivation The Model Proton Compton Scattering Vertex Structure Our Task Find (all) possible Γµν ρ (p, p0 ) in ψ̄ν (p0 )Γµν ρ (p, p0 )ψ ρ (p)Aµ Gauge Invariance: qµ ψ̄ν (p0 )Γµν ρ (p, p0 )ψ ρ (p) = 0 Structures We Have Found Γµν ρ (p, p0 ) = Tensor Type τ µλν ρ qλ σ µλ η ν ρ qλ σ µλ σ ν ρ qλ τ µλν κ σ κ ρ qλ τ µλκ ρ σ ν κ qλ × γ 5 (· · · ) Summary Outline Background and Motivation The Model Proton Compton Scattering Structures We Have Found Scalar Type: Vector Type: η ν ρ (p + p0 )µ ην ργ µ ν 0 µ γ γρ (p + p ) γ ν γ µ γρ γ ν η µ ρ + γρ η µν Vertex Structure Summary Tensor Type: τ µλν ρ qλ σ µλ η ν ρ qλ σ µλ σ ν ρ qλ τ µλν κ σ κ ρ qλ τ µλκ ρ σ ν κ qλ Our Claim The scalar, vector and tensor type vertexes we have found comprise the most general set of vertexes that are at most first order in q, and dominate the low energy Compton scattering amplitude. Outline Background and Motivation The Model Proton Compton Scattering Vertex Structure Summary Summary Motivation for unifying proton and ∆+ in a generalized Rarita-Schwinger theory, and the model Summary Outline Background and Motivation The Model Proton Compton Scattering Vertex Structure Summary Summary Motivation for unifying proton and ∆+ in a generalized Rarita-Schwinger theory, and the model * Lagrangian; Summary Outline Background and Motivation The Model Proton Compton Scattering Vertex Structure Summary Summary Motivation for unifying proton and ∆+ in a generalized Rarita-Schwinger theory, and the model * Lagrangian; * spin 1/2 solution; Summary Outline Background and Motivation The Model Proton Compton Scattering Vertex Structure Summary Summary Motivation for unifying proton and ∆+ in a generalized Rarita-Schwinger theory, and the model * Lagrangian; * spin 1/2 solution; * electrodynamic interaction Summary Outline Background and Motivation The Model Proton Compton Scattering Vertex Structure Summary Summary Motivation for unifying proton and ∆+ in a generalized Rarita-Schwinger theory, and the model * Lagrangian; * spin 1/2 solution; * electrodynamic interaction Proton Compton scattering amplitude and cross section Summary Outline Background and Motivation The Model Proton Compton Scattering Vertex Structure Summary Summary Motivation for unifying proton and ∆+ in a generalized Rarita-Schwinger theory, and the model * Lagrangian; * spin 1/2 solution; * electrodynamic interaction Proton Compton scattering amplitude and cross section * Low energy limit; Summary Outline Background and Motivation The Model Proton Compton Scattering Vertex Structure Summary Summary Motivation for unifying proton and ∆+ in a generalized Rarita-Schwinger theory, and the model * Lagrangian; * spin 1/2 solution; * electrodynamic interaction Proton Compton scattering amplitude and cross section * Low energy limit; * comparison with Dirac theory calculation Summary Outline Background and Motivation The Model Proton Compton Scattering Vertex Structure Summary Summary Motivation for unifying proton and ∆+ in a generalized Rarita-Schwinger theory, and the model * Lagrangian; * spin 1/2 solution; * electrodynamic interaction Proton Compton scattering amplitude and cross section * Low energy limit; * comparison with Dirac theory calculation Constructing general electrodynamic interaction vertexes Summary Outline Background and Motivation The Model Proton Compton Scattering Vertex Structure Summary Summary Motivation for unifying proton and ∆+ in a generalized Rarita-Schwinger theory, and the model * Lagrangian; * spin 1/2 solution; * electrodynamic interaction Proton Compton scattering amplitude and cross section * Low energy limit; * comparison with Dirac theory calculation Constructing general electrodynamic interaction vertexes * Scalar, vector and tensor type vertexes; Summary Outline Background and Motivation The Model Proton Compton Scattering Vertex Structure Summary Summary Motivation for unifying proton and ∆+ in a generalized Rarita-Schwinger theory, and the model * Lagrangian; * spin 1/2 solution; * electrodynamic interaction Proton Compton scattering amplitude and cross section * Low energy limit; * comparison with Dirac theory calculation Constructing general electrodynamic interaction vertexes * Scalar, vector and tensor type vertexes; * claiming that other vertexes are higher order in q Summary Outline Background and Motivation The Model Thank you all! Proton Compton Scattering Vertex Structure Summary