Solutions to Quiz2
advertisement

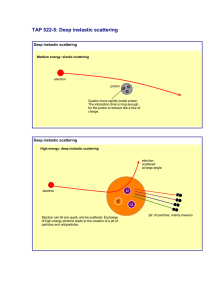
Solutions to Quiz 2 : PHYS: 1411, Dec 3 2015, Thurs Each question carries equal credit (50 points total) 1. In electron-proton scattering, the differential cross-section is given by: where, E1 and E3 are the incident and the scattered electron energies, respectively, and is the scattering angle. i) Does this represent elastic or inelastic scattering? Elastic ii) What does M represent? Mass of proton iii) Is the proton treated as a complex or a point object? Yes (no form factor) iv) What do the cos2 and the sin2 terms represent? electron spin; e and p magnetic moment interaction from e,p spins v) Does it take into account any of the proton/electron spins, both the spins or neither? both 2. In electron-positron high energy colliders, the ratio R is represented by This value was used to measure the search for new quarks. What is qq and what is the summation over? Is this formula missing any factor? If so, what factor. qq is the charge of the quark under consideration, and the sum is over all quark flavors which can be pair produced at the CM energy. The equation is missing a factor of 3 due to color. 3. The equation F2 = 2xF1 is known as the Callan-Gross relationship. Which of the following statements are applicable to the above relationship? Mark the ones correctly applicable. a) It refers to “scaling-violation” in deep inelastic scattering. No b) It refers to spin-zero point particles only. No c) It is related to “scaling” in deep inelastic scattering. Yes d) It refers to scattering off gluons. No e) It refers to scattering off quarks. Yes f) It is related to e-p elastic scattering. No g) It only works in the infinite momentum scale. No 4. What is the source of “scaling”? And of “scaling violation” ? At high energies the highly virtual photon (from the electron) penetrates deeply into the proton and “sees” individual partons, valence and sea quarks (and anti-quarks), and behaves as if it scatters off elastically from individual partons. Thus the form factor depends only on one variable (x) and not on Q2. This is called scaling behavior. However, as soon as the scattered parton attempts to leave the proton, QCD forces acts on it and the elastic scattering behavior is lost. Also as x decreases, the gluon momentum density increases sharply. (about half the momentum of the proton is carried by gluons.) This is known as scaling violation, primarily the gluons are responsible for this. 5. A) What kind of “current/s” is/are present in the EM interactions? Charged vector current at each vertex, the photon itself is neutral. B) What kind of “current/s” is/are represented in the weak interactions? Both charged and neutral weak currents, vector and axial vector type. The exchange particles are W and Z0.