CHEMISTRY 2.4 An assessment for AS90308
advertisement

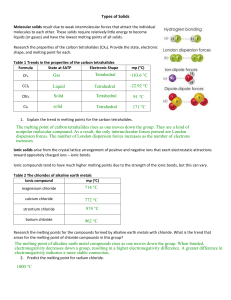
CHEMISTRY 2.4 An assessment for AS90308 Describe the nature of structure and bonding in different substances. Credits: Four INSTRUCTIONS Answer ALL questions. © New Zealand Institute of Chemistry 2005 2 You should spend 40 minutes answering the questions in this booklet QUESTION ONE 1 (a) Lewis diagrams Complete the table below by: • drawing the Lewis structures • naming the shape • stating whether the compound is polar or non-polar Molecule hydrogen chloride HCl (b) beryllium chloride BeCl2 (c) sulfur dichloride SCl2 (d) Carbon disulfide CS2 (e) phosphorus trichloride PCl3 (f) methane CH4 Lewis structure Name of shape Polar or non-polar Turn over 3 QUESTION TWO: 1 Shapes of molecules Using HCl as an example, explain what is meant by the term 'polar bond'. _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ 2 Explain why the shape of the ammonia molecule, NH3, is trigonal pyrimidal rather than triangular. _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ 3 Explain why water, H2O, and carbon dioxide, CO2 have different shapes, even though both molecules contain three atoms. _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ 4 Discuss the effect the shape of the molecules PCl3 and CCl4 have on their polarity and relate this effect to the solubility of each molecule in water. _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ Turn over 4 QUESTION THREE: 1 Structures of solids The table below supplies information about the oxides of some of the third-row elements. Complete the following table by stating the type of solid the type of particle(s) in the solid crystal the name of the bond or force broken when the solid melts Name and formula of solid Melting point °C 2 sodium oxide, Na2O 1275 silicon dioxide SiO2 1710 sulfur trioxide SO3 27 chlorine dioxide ClO2 –75 Type of solid (covalent network, ionic, metallic, or molecular) Type of particle(s) in crystal (atoms, ions or molecules) Name of bond broken when the solid melts (covalent, ionic, metallic or weak molecular) The table in Question 1 shows both Na2O and SiO2 have high melting points while SO3 and ClO2 have low melting points. For each of the following, state whether their melting points will be high or low and explain your choice. Oxide Relative Melting Point (high/low) Explanation MgO P4O6 Turn over 5 QUESTION 4: 1 Properties of solids Explain, in terms of structure and bonding within the solid, why each of the following has the property described. Property Explanation Gold is very malleable and can be shaped into many items of jewellery. Solid sodium chloride is a poor conductor of electricity. However, when molten, sodium chloride is a good electrical conductor. Iodine crystals are easily changed into a gas when warmed gently. 2 Diamond and graphite are allotropes of carbon, yet graphite is soft enough to be used as the 'lead' in pencils, while diamond is so hard that it can cut glass. Discuss these properties in terms of the structure and bonding in these solids. _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ End of Assessment Turn over