Announcements
advertisement

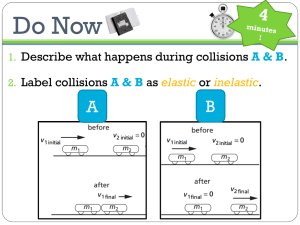
Announcements • Exam 1 is being graded. • Solutions will be available before end of today. • Hope to post grades on e-learning by Friday. • You will get back your exam on March 2nd. • If you forgot to bring ID during exam, you must see Prof. Chan with your ID or your exam will not be graded. Momentum of an object Momentum r ∆p m(v f − v i ) r = = Fnet ∆t ∆t alternative statement of Newton’s second law The time rate of change of momentum of an object is equal to the net force acting on it p t Impulse When a single, constant force F acts on the objectr for time ∆t, there is an impulse I delivered to the object: r r I = F∆t Using F = area under F-t curve r r ∆p F= ∆t Impulse r r r r r I = ∆p = m(v f − vi ) = F∆t t Average Force in Impulse Definition: The average force = the constant force that would give the same impulse to the object in the time interval as the actual time-varying force gives in the interval r r r I = ∆p = Fav ∆t 20. A pitcher throws a 0.15-kg baseball so that it crosses home plate horizontally with a speed of 20 m/s. The ball is hit straight back at the pitcher with a final speed of 22 m/s. (a) What is the impulse delivered to the ball? (b) Find the average force exerted by the bat on the ball if the two are in contact for 2.0 × 10–3 s. pitcher 20 m/s positive batter 22 m/s Collision of 2 objects Conservation of Momentum Momentum in an isolated system in which a collision occurs is conserved An “ isolated” system: no external forces the total momentum before the collision equals the total momentum after the collision Conservation of Momentum Momentum is conserved for the system of objects. You must define the isolated system Assumes only internal forces are acting during the collision Can be generalized to any number of objects Types of Collisions Momentum is conserved in any collision Inelastic collisions Kinetic energy is not conserved Some of the kinetic energy is converted into other types of energy such as heat, sound, work to permanently deform an object Perfectly inelastic collisions occur when the objects stick together Not all of the KE is necessarily lost Types of Collisions Elastic collision both momentum and kinetic energy are conserved Actual collisions Most collisions fall between elastic and perfectly inelastic collisions