Classical Mechanics vs Electricity and Magnetism
advertisement
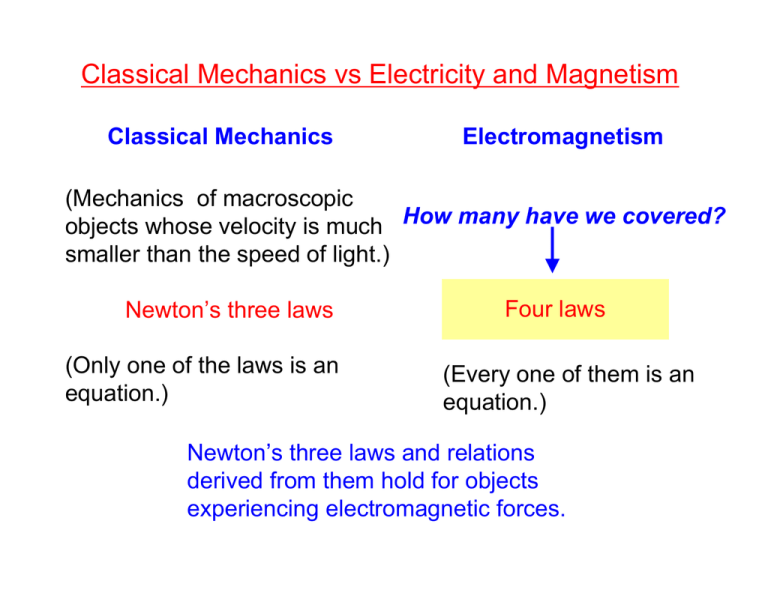
Classical Mechanics vs Electricity and Magnetism Classical Mechanics Electromagnetism (Mechanics of macroscopic objects whose velocity is much How many have we covered? smaller than the speed of light.) Newton’s three laws (Only one of the laws is an equation.) Four laws (Every one of them is an equation.) Newton’s three laws and relations derived from them hold for objects experiencing electromagnetic forces. Electricity vs Magnetism Electricity Magnetism The one law No “magnetic charges” (monopoles) have been found. Coulomb’s law Ù Gauss’ law • • About the force between two point charges. (Dependence of the electric field on the source charge and distance.) Alternatively, about the property of the electric field. Everything else is derived from this law, which completely agrees with all observed electrical phenomena. (Talked about situations in which this law alone is insufficient.) The equation about the force between two small bar magnets turns out to be not fundamental. What are fundamental? 1. Dependence of the magnetic field on the strength of the source (a current) and distance. Chapter 29 2. The force due to a magnetic field. The force on what? Chapter 28 Force on a charge due to magnetic field r Magnetic Field B At this point, we do no get into the question of how it is produced by a current or by a bar magnet, etc. and how its strength is varied. Fundamental relation based on a large number of experimental observations: r r r Fm ∝ qv × B Magnetism is inseparable from electricity. Choose the unit (tesla) for magnetic field such that this relation is written in the simplest form: r r r Fm = qv × B