m ra g ro
advertisement

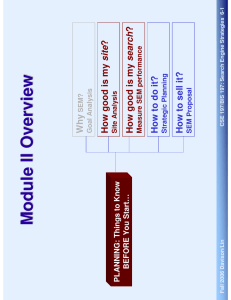
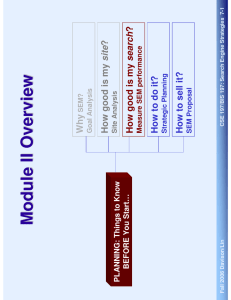
Paid Search Optimization step-by-step guide to implement a paid − CSE 197/BIS 197: Search Engine Strategies 14-1 Planning Paid Search − search campaign Types of Paid Search − In this section, we discuss: Fall 2006 Davison/Lin Optimize Your Paid Search Program Customer segmentation Cost Timing − − − Unlimited keywords Flexibility Customer oriented design − − − Technical advantages Customer quality − Economic advantages CSE 197/BIS 197: Search Engine Strategies 14-2 Compare to SEM, what are the advantages of paid search? Fall 2006 Davison/Lin Why Paid Search? CSE 197/BIS 197: Search Engine Strategies 14-3 Paid search can be expensive if not executed properly − Fall 2006 Davison/Lin Remember the click frauds? Show me the money! − What’s the catch? Why Paid Search? The price is usually also fixed Pay – per – impression Long contract time − − − Not flexible Bottom line: be VERY SURE about what you are pursuing − − CSE 197/BIS 197: Search Engine Strategies 14-4 Place guaranteed. Price predictable & fixed − Pros & Cons The place your ad appears remains fixed − Fixed Placement Fall 2006 Davison/Lin Types of Paid Search Google & Yahoo still own 97% market Small players: GoClick.com & msn AdCenter − − Pay by bidding in keyword auction − CSE 197/BIS 197: Search Engine Strategies 14-5 Pay-per-click − Characteristics The one we’ve been discussing the whole semester − “Traditional” Paid Placement Fall 2006 Davison/Lin Types of Paid Search − − − CSE 197/BIS 197: Search Engine Strategies 14-6 This makes estimation of final keyword cost difficult Both Google and Yahoo now use a combination of price and click-through to determine the winner for a bid Keyword bidding is a complicated process “Traditional” Paid Placement Fall 2006 Davison/Lin Types of Paid Search − − − − CSE 197/BIS 197: Search Engine Strategies 14-7 Google: same as AdWord; Yahoo: separated Google’s AdSense & Yahoo’s Content Match network are examples of contextual Ad. Vendors It is a more sophisticated form of affiliated marketing Contextual ad system scans the text of a Web site for keywords and returns ads based on what the user is viewing Contextual Ads. Fall 2006 Davison/Lin Types of Paid Search CSE 197/BIS 197: Search Engine Strategies 14-8 Cost: should contextual ad. Cost the same as paid placement? Control: You cannot choose the site, the place or the ad. − − Audience: very specific customer groups − Contextual Ads: Pros & Cons Fall 2006 Davison/Lin Types of Paid Search CSE 197/BIS 197: Search Engine Strategies 14-9 70% had used the Internet to search for a local service business at any point, and 46% had used the Internet to search one or more times for a local service in 2005 More than ¼ searches in 2004 are near home or work − − At infancy stage online Used to be mainly offline (think yellow page and local newspapers) Local search is deemed as the holy grail of advertising − − − Local Ads Fall 2006 Davison/Lin Types of Paid Search Yahoo is the biggest vendor Free listing − − Local Ads Fall 2006 Davison/Lin CSE 197/BIS 197: Search Engine Strategies 14-10 Types of Paid Search CSE 197/BIS 197: Search Engine Strategies 14-11 Competitors in the same product category are charged the same per-click fee Major players − − 1% of all Internet traffic, 22% growth rate (2004) Customers: transactional searchers ready to buy (twice as likely to buy and buy twice as much) Specifically designed search engines that offer one-stop shopping for particular products − − − Shopping Search Fall 2006 Davison/Lin Types of Paid Search Remember to measure them! − 80% of the lower demand keywords show higher conversion rates for lower slots! Top position attracts 40% more traffic than 2nd position CSE 197/BIS 197: Search Engine Strategies 14-12 STEP 3: Don’t forget local search! − − STEP 2: Paid Placement Search – Position What do you want? Traffic or conversion? − STEP 1: Don’t forget your GOALS! Fall 2006 Davison/Lin Planning Paid Search − − In paid placement – more bidders = higher fees In shopping search -- product categories with more competitors cost more CSE 197/BIS 197: Search Engine Strategies 14-13 In paid placement – better understanding of your keyword value is the key to higher efficiency In the real world, no market is totally efficient – information asymmetry In other words, the market price is an unbiased estimate of the true value of the product Efficiency: sellers will maximize the price based on the value to the buyers Scarcity: scarce items cost more (less supply, more demand) Marketing Basics (and how they relate to SEM) Fall 2006 Davison/Lin Planning Paid Search − CSE 197/BIS 197: Search Engine Strategies 14-14 In other words, why would the value of a keyword be higher for your competitors? Why could someone outbid you? Efficiency: sellers will maximize the price based on the value to the buyers Marketing Basics (and how they relate to SEM) Fall 2006 Davison/Lin Planning Paid Search Optimize the list Iterate! − − CSE 197/BIS 197: Search Engine Strategies 14-15 Monitor closely: collect traffic, conversion, profit…. As much data as you could get Start broad: choose a collection of keywords, collect data − − Start small: don’t expect it to work at the beginning − Starting your paid placement campaign Fall 2006 Davison/Lin Planning Paid Search And google only shows you the AVERAGE bid And MORE THAN that! CSE 197/BIS 197: Search Engine Strategies 14-16 Very difficult task, since cost is dependent on click-through Decide your media cost Media costs − Management costs Budget to build : handed a budget to do everything Creative costs Build to budget: add up all your costs and ask for the budget − − 1. Decide your budget Fall 2006 Davison/Lin Step-by-step Paid Search − − Don’t estimate Use the average Second price auction Conversion affects fee Auction is an ever-changing game CSE 197/BIS 197: Search Engine Strategies 14-17 Media cost could not be estimated accurately Test using both yahoo and google Decide your media cost 1. Decide your budget Fall 2006 Davison/Lin Step-by-step Paid Search Gap surfing, bid jamming & dayparting No longer useful $0.99 $0.25 $0.5 $0.51 $1 CSE 197/BIS 197: Search Engine Strategies 14-18 Used to have different style Google vs. Yahoo − Focus on one vendor to begin − 2. Set Up Your Account Fall 2006 Davison/Lin Step-by-step Paid Search Market leap performics The search works CSE 197/BIS 197: Search Engine Strategies 14-19 Other tools are: − To start, google or yahoo tools are fine (and free!) − 3. Select Bid Management Tool Fall 2006 Davison/Lin Step-by-step Paid Search − − − CSE 197/BIS 197: Search Engine Strategies 14-20 For paid placement, refer to our discussion before regarding keyword selection For shopping search engines, set up trust-feed and pay a fixed fee Keywords or products 4. Select Targets Fall 2006 Davison/Lin Step-by-step Paid Search Google refers to them as ad groups campaign − Negative match Exact match (google) / standard match (yahoo default): only the exact phrase Phrase match (google): must contain the exact phrase! Broad match (google default) / advanced match (Yahoo): include variation of keywords CSE 197/BIS 197: Search Engine Strategies 14-21 7. Geographic targeting of keywords − − − − 6. Match Type for Keywords Yahoo divide keywords into categories − 5. Manage Keywords Fall 2006 Davison/Lin Step-by-step Paid Search − ROAS: revenue / ad cost (maximize returns) ROI: profit / ad cost (maximize returns) Allowable: highest CPA CSE 197/BIS 197: Search Engine Strategies 14-22 Different optimization strategy leads to different performances You cannot optimize ALL metrics! Profit Margin: profit per unit / revenue per unit (maximize profit) Metrics useful for bid management − CPA: ad cost / number of ACTIONS (minimize costs) The key is to use metrics to drive your bids – objective bidding − Three focuses: maximize returns, minimize costs, maximize profit − 8. Select Bidding Strategy Fall 2006 Davison/Lin Step-by-step Paid Search Every bid must be at least 1 cent higher than the bid below You can set budget maximums, bid maximums, and cap for your campaign Bidding is usually an iterative process – trial and error! − − − CSE 197/BIS 197: Search Engine Strategies 14-23 Bids start at 1 to 10 cents − 9. Make your bid Fall 2006 Davison/Lin Step-by-step Paid Search − − Don’t hype it up, but try to draw attention Call to action Create urgency Complete and correct metadata Price Merchant rating CSE 197/BIS 197: Search Engine Strategies 14-24 Sell your uniqueness For shopping search Use the keywords Optimize the copy 10. Attract the searchers Fall 2006 Davison/Lin Step-by-step Paid Search − Reinforce your offer Do NOT use pop-ups and visitor traps CSE 197/BIS 197: Search Engine Strategies 14-25 Include the keywords – reinforce the message Optimize the landing pages 10. Attract the searchers Fall 2006 Davison/Lin Step-by-step Paid Search CSE 197/BIS 197: Search Engine Strategies 14-26 “Maintenance” -- Measure and Adjust! Fall 2006 Davison/Lin Step-by-step Paid Search Fall 2006 Davison/Lin CSE 197/BIS 197: Search Engine Strategies 14-27 What’s Next?