w ie rv e
advertisement

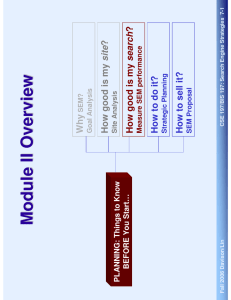
Fall 2006 Davison/Lin PLANNING: Things to Know BEFORE You Start… CSE 197/BIS 197: Search Engine Strategies 6-1 SEM Proposal How to sell it? Strategic Planning How to do it? Measure SEM performance How good is my search? Site Analysis How good is my site? Goal Analysis Why SEM? Module II Overview − − − Conversion Rate Counting dollars And more… CSE 197/BIS 197: Search Engine Strategies 6-2 Tools that help your web analytical needs How to measure web site performance based on your goals Counting visitors How to diagnose a web site’s well being using multiple performance metrics [notice not just HOW, but HOW WELL!!] In this section, we discuss: Fall 2006 Davison/Lin If you can’t measure, you can’t manage By using cookie, servers store the state of your machine Often session = visit in SEM context − session-id-time 1159167600l amazon.com/ Technically, hard to accurately measure − CSE 197/BIS 197: Search Engine Strategies 6-3 Session: theoretically, one visit paid by the customer to your web site − disk. The pieces of information are stored as name-value pairs Cookie: a piece of text that a Web server can store on a user's hard Fall 2006 Davison/Lin Metric 1: # of Visits / Visitors CSE 197/BIS 197: Search Engine Strategies 6-4 Both were actively used to measure site performance around 2000 Number of unique visitors: the number of unique machine IDs that visited the server Number of visits: the number of unique sessions as counted by the server Fall 2006 Davison/Lin Metric 1: # of Visits / Visitors How unique is “unique”? − CSE 197/BIS 197: Search Engine Strategies 6-5 Financial analysts have become increasingly skeptical of nonfinancial metrics [Gupta et al. 2004] Issue with session − Issues with visits / unique visitor Fall 2006 Davison/Lin Metric 1: # of Visits / Visitors Heuristics to solve the problem (but distributed environment!) Single pixel tracking − − CSE 197/BIS 197: Search Engine Strategies 6-6 Stickiness = average duration / page view Simple log for each requested file (but file != page) − Textbook (as well as Brian ☺) explains in detail how page views are counted Visit duration / page views Fall 2006 Davison/Lin Metric 2: Stickiness - Related Implicates higher likelihood to purchase − CSE 197/BIS 197: Search Engine Strategies 6-7 Stickiness is capable of explaining the share price of Internet firms [Demers and Lev 2001] Page views offer some explanatory power but do not appear affecting firms’ net incomes [Trueman et al 2000] Reflects high loyalty − Conventional wisdom suggests stickiness to be a valuable metrics Fall 2006 Davison/Lin Metric 2: Stickiness - Related Page views significant for search goods − CSE 197/BIS 197: Search Engine Strategies 6-8 Duration significant for experience goods − Positive relationship between stickiness and conversion [Lin et al, 2006] Positive relationship between stickiness and purchase [Wu et al. 2005] Fall 2006 Davison/Lin Metric 2: Stickiness - Related 330 Number of websites in shopping category that offer direct sales services CSE 197/BIS 197: Search Engine Strategies 6-9 601 Total number of websites that offer direct sales services 1,392,713 Total number of websites visited 46,942 174,990 Total number of online purchases made in shopping websites Total number of websites belonging to shopping category 342,706 213,356,003 Total number of online purchases made Total number of website visits 100,000 Or they could buy service from companies such as comScore to get client-side monitoring capability Companies could invest in technology and build stronger server side monitoring programs (limitations exist) Total number of participating households − − Server – side solution vs. Client – side solution Fall 2006 Davison/Lin Solving Measurement Issues Poisson Poisson with variation BG/NBD (Fader et al 1004) Dynamic NBD (Moe and Fader 2004b) Fall 2006 Davison/Lin Dynamic Model (Allenby et al 1999) Inter-purchase time: Gamma Inter-purchase time: Poisson Poisson Pareto/NBD (Schmittlein 1987) ** Poisson NBD (Gupta and Morrison 1997) Joint Model (Boatwright, et al) Purchase Rate Assumption Models * None *** None None Geometric Exponential None None None None Beta Gamma None Death Events Heterogeneity Death Rate Assumption in death rate CSE 197/BIS 197: Search Engine Strategies 6-10 Inverse Generalized Gamma Gamma Gamma Gamma Gamma Gamma Heterogeneity in purchase rate Purchase Behavior Metric 3: Stochastic Models Mostly academic research, no industry adoption yet CSE 197/BIS 197: Search Engine Strategies 6-11 Hard to implement Fall 2006 Davison/Lin Enables individualized prediction Metric 3: Stochastic Models − CSE 197/BIS 197: Search Engine Strategies 6-12 Average conversion is at 5% and decreasing [Moe 2004] Conversion = number of actions / number of visitors Fall 2006 Davison/Lin Metric 4: Conversion Average conversion is at 5% and decreasing [Moe 2004] CSE 197/BIS 197: Search Engine Strategies 6-13 Depending on the goal of the web site (remember last chapter?), the meaning of “action” might differ A relatively well-accepted metric for measuring web site performance − Conversion = number of actions / number of visitors Fall 2006 Davison/Lin Metric 4: Conversion Use web analysis program to find number of visits Purchase / visits − − CSE 197/BIS 197: Search Engine Strategies 6-14 Use e-commerce system to find number of transactions − Simplest to calculate Fall 2006 Davison/Lin Revenue Generation Metric 4: Conversion CSE 197/BIS 197: Search Engine Strategies 6-15 You can also continue to track these visitors and capture their purchase events as well That means connect the form with lead management system − − Count each visitor who fills in web contact form as an action − For lead generation with the goal of acquire new customer information Fall 2006 Davison/Lin Lead Generation Metric 4: Conversion “Call Me” button Questionnaires at the offline locations − − CSE 197/BIS 197: Search Engine Strategies 6-16 Special phone number, special coupon, etc Need innovative methods for the offline channel to identify traffic re-directed from online − − For lead generation with the goal of offline sales: Fall 2006 Davison/Lin Lead Generation Metric 4: Conversion − ? CSE 197/BIS 197: Search Engine Strategies 6-17 Measuring the lead is only the first step… For lead generation with the goal of offline sales: Fall 2006 Davison/Lin Lead Generation Metric 4: Conversion − − CSE 197/BIS 197: Search Engine Strategies 6-18 Then implement possible mechanism to capture conversion behaviour First, define what is a conversion based on the goal of your campaign Abstract and hard to measure Fall 2006 Davison/Lin Brand Image Metric 4: Conversion For example, 1,000 visitors, $ 1 per visitor, 20 end up purchasing, then cost per purchase = ? Advertising Cost / Total Completed Actions CSE 197/BIS 197: Search Engine Strategies 6-19 For example, last month you spent $1,000 on advertising to generate 2,000 visitors and 20 bought at an average of $100 per sale with a gross profit margin of 90. Average Action Value = revenue / action − − Average Action Value x Gross Profit as % of Sales − completed action Value of a Buyer: the average gross profit you earn from a − − completed action Cost per Action: the advertising cost you pay for one Fall 2006 Davison/Lin Metric 5: Monetary Measurements − CSE 197/BIS 197: Search Engine Strategies 6-20 number of visitors to the site, unique/return visitors traffic referrers search engine referrers search keywords used page views visit paths average number of page views per visitor entry and exit pages Basic Level: Tools that help analyzing the web site performance Fall 2006 Davison/Lin Web Analysis Tools CSE 197/BIS 197: Search Engine Strategies 6-21 Conversion stats. Dividing the website into logical categories and monitoring each separately Bounce rates- the percentage of visitors who leave the website within the first x seconds of the visit. Advanced Level: Example − Tools that help analyzing the web site performance Fall 2006 Davison/Lin Web Analysis Tools