Name ID 1 /10
advertisement

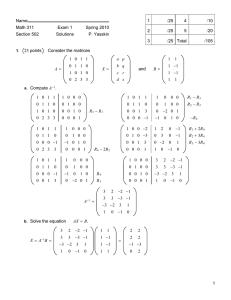
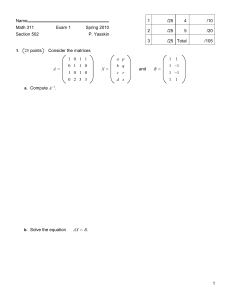
Name ID Math 311 Exam 1 Spring 2002 Section 503 P. Yasskin Solutions 1. 10 points 1 /10 2 /10 3 /30 4 /25 5 /25 A matrix A satisfies E 3 E 2 E 1 A = U where 1 0 0 0 1 0 2 0 0 1 0 1 0 E1 = E2 = 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 E3 = 0 1 0 0 2 1 ∗ 0 −3 ∗ 0 0 −1 2 U= 5 and the ∗’s represent unknown non-zero numbers. Find det A. det E 1 = −1 det A = 2. det E 2 = 1 2 det E 3 = 1 det U = det E 1 det E 2 det E 3 6 1 2 −1 1 det U = 2 −3 −1 = 6 = −12 10 points If c is a scalar, A is a 50 × 60 matrix and B is a 60 × 80 matrix, prove AcB = cAB . HINT: Write out the ij-component of each side. ∑A 60 AcB ij = cAB ij = cAB ij = c k=1 ik cB kj = ∑ A cB 60 k=1 ∑A B ik 60 k=1 ik kj These are equal. So AcB = cAB kj =c ∑A B 60 k=1 ik kj 3. 30 points Consider the triangle with vertices A = 2, 4, 0 B = 4, 2, 1 C = 2, 7, 4 a. Find cos θ where θ is the angle at vertex A. AB = B − A = 2, −2, 1 cos θ = AB ⋅ AC AB AC = AC = C − A = 0, 3, 4 −6 + 4 = −2 15 4 + 4 + 1 9 + 16 b. Find the area of the triangle ΔABC. i AB × AC = j k 2 −2 1 0 3 = i−8 − 3 − j8 + k6 = −11, −8, 6 4 Area = 1 AB × AC = 1 121 + 64 + 36 = 1 221 2 2 2 c. Find a set of parametric equations for the line containing A and C. x X = A + t AC 2 = y +t 4 z 0 0 x=2 3 y = 4 + 3t 4 z = 4t d. Find a set of parametric equations for the plane containing A, B and C. x X = A + s AB + t AC y z 2 = 4 2 +s 0 −2 +t 1 0 x = 2 + 2s 3 y = 4 − 2s + 3t 4 z = s + 4t e. Find a non-parametric equation for the plane containing A, B and C. N = AB × AC = −11, −8, 6 N⋅X = N⋅A −11x − 8y + 6z = −11 ⋅ 2 − 8 ⋅ 4 + 6 ⋅ 0 = −54 11x + 8y − 6z = 54 4. 25 points Consider the system of equations: 2 AX = B A= where 0 1 1 −2 1 0 −1 3 x p X= y q z r Compute A −1 . (Give reasons for each step.) 2 0 1 1 0 0 R2 1 −2 1 0 1 0 R1 0 3 −1 0 0 1 1 −2 1 0 1 0 2 0 1 1 0 0 0 3 −1 0 0 1 1 −2 1 0 1 R 2 − 2R 1 0 −1 0 3 −1 0 0 1 1 −2 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 −2 −1 0 3 −1 0 0 1 −2 0 4 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 −3 −2 1 −2 −1 −3 6 4 2 0 0 −1 1 0 0 0 R2 − R3 R 1 + 2R 2 R 3 − 3R 2 R1 + R3 −R 3 −1 3 2 1 −2 −1 3 −6 −4 A −1 = −1 3 2 1 −2 −1 3 −6 −4 Solve AX = B. X= A −1 B = −1 3 2 1 −2 −1 3 −6 −4 1 0 0 1 1 −1 1 = 1 −1 −1 −2 0 B= 1 0 0 1 1 −1 5. 25 points Consider the system of equations: 3w + 6x + y = y − 3z = w + 2x + y − 2z = −2w − 4x + y − 5z = 5 2 3 b Find the value(s) of b for which there exist solutions. (Give reasons for each step.) 3 6 1 0 5 0 0 1 −3 2 1 2 1 −2 3 −2 −4 1 −5 b R3 R1 1 2 1 −2 3 0 0 1 −3 2 3 6 1 0 5 R 3 − 3R 1 −2 −4 1 −5 b R 4 + 2R 1 −2 0 0 1 −3 0 0 −2 6 0 0 3 −9 3 1 2 1 1 2 0 R1 − R2 2 −4 b+6 1 1 0 0 1 −3 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 b R 3 + 2R 2 R 4 − 3R 2 To have solutions we must have b = 0. For that value (those values) of b what is the solution set? w = 1 − 2s − t x=s y = 2 + 3t z=t Give a geometrical description of the solution set. Plane in R 4 .