Test 1 solutions Phz 3113 Fall 2007 x/ x ¿
advertisement
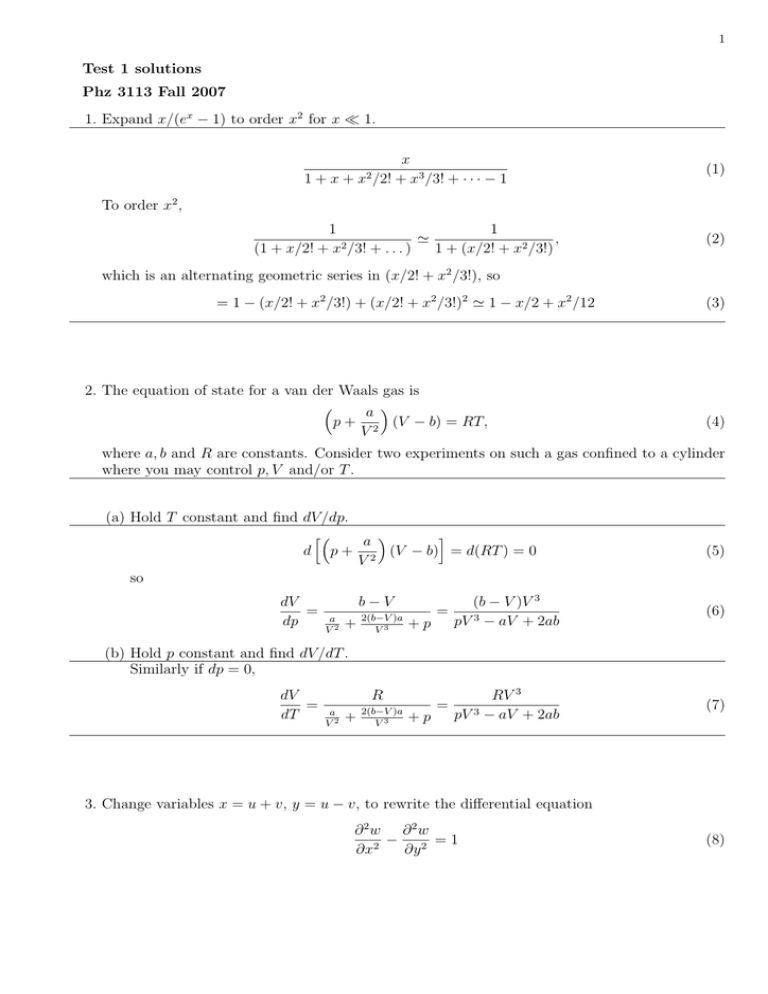
1 Test 1 solutions Phz 3113 Fall 2007 1. Expand x/(ex − 1) to order x2 for x ¿ 1. x2 /2! 1+x+ x + x3 /3! + · · · − 1 (1) To order x2 , 1 1 ' , 2 (1 + x/2! + x /3! + . . . ) 1 + (x/2! + x2 /3!) (2) which is an alternating geometric series in (x/2! + x2 /3!), so = 1 − (x/2! + x2 /3!) + (x/2! + x2 /3!)2 ' 1 − x/2 + x2 /12 2. The equation of state for a van der Waals gas is ³ a ´ p + 2 (V − b) = RT, V (3) (4) where a, b and R are constants. Consider two experiments on such a gas confined to a cylinder where you may control p, V and/or T . (a) Hold T constant and find dV /dp. h³ i a ´ d p + 2 (V − b) = d(RT ) = 0 V so dV = dp b−V a V2 + 2(b−V )a V3 +p (5) = (b − V )V 3 pV 3 − aV + 2ab (6) = RV 3 pV 3 − aV + 2ab (7) (b) Hold p constant and find dV /dT . Similarly if dp = 0, dV = dT R a V2 + 2(b−V )a V3 +p 3. Change variables x = u + v, y = u − v, to rewrite the differential equation ∂ 2w ∂ 2w − =1 ∂x2 ∂y 2 (8) 2 in terms of u and v (no need to solve the equation). Sketch solution. First invert u = (x + y)/2, v = (x − y)/2. calculate partial derivatives: · ¸ ∂w ∂u ∂w ∂v 1 ∂w ∂w ∂w = + = + ∂x ∂u ∂x ∂v ∂x 2 ∂u ∂v µ ¶ ∂ 1 ∂ ∂ ⇒ = + ∂x 2 ∂u ∂v (9) and similarly for y ∂ 1 = ∂y 2 µ ∂ ∂ − ∂u ∂v ¶ (10) The 2nd partials are e.g. µ ¶µ ¶ ∂2w 1 ∂ ∂ ∂ ∂ = + + w ∂x2 4 ∂u ∂v ∂u ∂v · ¸ 1 ∂ 2w ∂ 2w ∂ 2w = + +2 4 ∂u2 ∂v 2 ∂u∂v (11) and similarly for y except the coefficient of the mixed partial derivative is negative. Constructing 2 ∂2w − ∂∂yw2 = 1, we find ∂x2 ∂ 2w = 1. ∂u∂v (12) 4. Evaluate the integral Z Z π π dy y=0 dx x=y sin x . x Reverse order of integrations: Z π Z Z π sin x x dx dy = dx sin x = − cos x|π0 = 2. x 0 0 0 (13) (14) ~ ·A ~ = 0 and ∇ ~ ·B ~ = 0, show that 5. If ∇ ~ × (A ~ × B) ~ = (B ~ · ∇) ~ A ~ − (A ~ · ∇) ~ B. ~ ∇ [Hint: ²ijk ²i`m = δj` δkm − δjm δk` ] (15) 3 ~ × (A ~ × B)] ~ i = ²ijk ∇j (A ~ × B) ~ k = ²ijk ²kmn Am Bn = ²kij ²kmn ∇j Am Bn [∇ = (δim δjn − δin δjm )∇j Am Bn = ∇j Ai Bj − ∇j Aj Bi ~ · B) + (B ~ · ∇)A ~ i − Bi (∇ ~ · A) ~ − (A ~ · ∇)B ~ i = (B ~ · ∇)A ~ i − (A ~ · ∇)B ~ i, = Ai (∇ where in the last step I used the info given that both vectors had zero divergence, and the product rule of differentiation. 6. Look for a minimum of the function 1/x + 4/y + 9/z for x, y, z > 0 and x + y + z = 12. Lagrange multipliers: F = 1/x + 4/y + 9/z + λ(x + y + z − 12), (16) so minimize: ∂F 1 =− 2 +λ=0 ; ∂x x ∂F 4 =− 2 +λ=0 ; ∂y y ∂F 9 = − 2 + λ = 0. ∂z z (17) Together with the constraint equation x + y + z = 12 this system can be easily solved by noting that the solutions should be positive. Therefore by eliminating λ we find x = y/2 = z/3. The constraint equation is then x + 2x + 3x = 6, so x = 2, y = 4, z = 6 is a solution. Function takes minimum value of 3 here. ~ 7. (Extra p credit) Consider the vector V = 4y î + xĵ + 2z k̂ and the scalar field ψ(x, y, z) = 1/ x2 + y 2 + z 2 . ~ × V~ = −3k̂ (a) show ∇ ²ijk ∇j vk For i = 1, ²1jk ∇j vk = ∇2 v3 − ∇3 v2 = 0; for i = 2, ²2jk ∇j vk = ∇3 v1 − ∇1 v3 = 0; for i = 3, ²3jk ∇j vk = ∇1 v2 − ∇2 v1 = 1 − 4 = −3. So answer is −3ẑ. (b) evaluate R V~ · d~r from the origin (0,0,0) to (1,1,1) along the line x = t, y = t2 , z = t3 . Since curl ~v 6= 0, integral depends on path in general. Z Z Z 1,1,1 Z 1 (4y î + xĵ + 2z k̂) · (dxî + dy ĵ + dz k̂) = (4t2 dt + t · 2tdt + 2t3 · 3t2 dt) 0,0,0 0 · 1 1 = 6 t3 + t6 3 6 ¸1 =3 0 (18) 4 ~ and ∇ ~ × ∇ψ. ~ (c) evaluate ∇ψ ~ = −(x, y, z)/(x2 + y 2 + z 2 )3/2 = − ~r ∇ψ r3 (19) ¯ ¯ ¯ ¯ x̂ ŷ ẑ ¯ ¯ ~ ~ ¯ ∇ × ∇ψ = ¯ ∂x ∂y ∂z ¯¯ , ¯ ∂ x ψ ∂ y ψ ∂z ψ ¯ (20) and which vanishes by equality of mixed partial derivatives. You can also do this problem with ²ijk notation if you like. 8. (Extra credit.) Calculate the radii of convergence of the following series: (a) ∞ X (nx)n n=1 Use ratio test: n! ¯ ¯ ¯ ¯ ¯ an+1 ¯ ¯ (n + 1)n+1 xn+1 n! ¯ ¯ ¯ ¯ ¯ ρn = ¯ = an ¯ ¯ (n + 1)! nn xn ¯ µ ¶n 1 |x|(n + 1)n = |x| 1 + = nn n µ ¶n 1 ρ = lim ρn = |x| lim 1 + = |x|e n→∞ n→∞ n (21) (22) (23) (24) (b) ∞ X n=1 Use ratio test: xn n2 + 1 ¯ ¯ ¯ ¯ n+1 2 2 ¯ ¯ an+1 ¯ ¯ x n + 1 ¯=¯ ¯ = |x| n + 1 ρn = ¯¯ an ¯ ¯ n2 + 2n + 2 x2 ¯ n2 + 2n + 2 ρ = lim ρn = |x| < 1 n→∞ (25) (26) (27)











