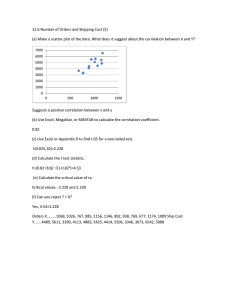
2011 Palisade Risk Conference, Las Vegas, NV
advertisement

2011 Palisade Risk Conference, Las Vegas, NV
Integrated Cost and Schedule Risk Analysis for
Engineering Projects Using a Custom @RISK Solution
Mark Brumer, MBA
11 November 2011
Integrated Cost and Schedule Risk Analysis for
Engineering Projects Using a Custom @RISK Solution
Reasons for Integration
Design Considerations
Consequences of Normality
Assembly of Data Set
Construction of Model
Interpretation of Results
Demonstration
Questions
2
11 November 2011
Reasons for Integration
Limitations of schedule software
Relies on additive algorithms
Impedes incorporation of capital costs
Limits choice of risk functions
Restricts introduction of correlated risks
Dominance of labor costs
Comprise 60 to 80% of phase cost
Inversely related under acceleration
Nature of potential solutions
Comprises a complex surface
Risks overlooking behavior at peaks
Utilize @RISK v. 6.0
3
11 November 2011
Design Considerations
Define purpose and role of the risk analysis
Incorporate natural phases of the Project
Design, Construction, Systemization, Pilot Testing, et al.
Timing of capital expenditures
Transitions during the evolution of a phase
Recognize inherent bias of estimate
Precision of estimate
Tendency towards conservatism
Establish conditions for risk identification
4
Discretely defined
Distributed impacts (vice acute)
Relatively small, multiplicative impacts
11 November 2011
Consequences of Normality
Project schedules are by definition not normal distributed
Consider the consequences of “central limit theorem”
Sum of a large number of risks tends to be normally distributed
While the product of a large number of risks tends to be
log-normally distributed
Quantify risks in terms of relative perturbations
Calculate product of multiple risks impacting a single activity
Include correlations between related risks
5
11 November 2011
Assembly of Data Set:
Project Schedules
Provide the model foundation
Import MS Project files into
@RISK v.6.0 directly as *.mpp
Establish linkage of risks to
activities automatically using
customized VBA scripts
Require critical analysis before use
6
Let the duration and logic drive
milestone dates
Verify the validity of critical path
Eliminate unnecessary constraints
or artificial lags
Ensure most activities start
“As soon as possible”
Avoid dangling activities
11 November 2011
Assembly of Data Set:
Cost Estimates
Constructed historically using
Microsoft Excel
Exploit standardized cost
breakdown structures
Clone existing cost estimates to
facilitate data entry
7
11 November 2011
Assembly of Data Set:
Risk Quantification
Quantify risk events employing an
iterative process
Develop an aggregated risk
function
RiskDiscrete({x1,x2,x3}, {p1,p2,p3})
Where pi is the probability of
Negative impact
Opportunity benefit
Status quo
Where x1 and x2 are negative and
positive consequence distributions
bounded at the P10 and P90
Recognize that the consequence at
the status quo equals one
Generate parameters utilizing a
variation of the Delphi method
Value creative dissonance
8
11 November 2011
Construction of Model:
Overview
Integrated Risk Analysis
Save Model
Project Phases
Group Activities
Codes
Units Managment
Update Model
Structure
Project Cost
Project Cost
Schedule
Schedule
Risk Register
Risk Register With
Weights
Periods by Phase
Risk Register With
Weights
Cost Model Creation
Cost Categories
Cost Elements
Risk Events
Allocation
Risk Correlation
Matrix
Units Cost and Quantities
Cost Categories
Period Resources
Risk Simulation
Settings
Cost Subcategories
Cost Elements
Probability Impact
Matrix Definition
Risk Definition and
Allocation
Risk Category
PALISADE.COM
9
Risk Events
Start Simulation
Mitigate Model
Correlation Matrix
powered by
11 November 2011
Construction of Model:
Project Model
10
11 November 2011
Construction of Model:
Cost Breakdown Structure
11
11 November 2011
Construction of Model:
Risk Definition
12
11 November 2011
Construction of Model:
Risk Allocation
13
11 November 2011
Construction of Model:
Correlation Matrix
14
11 November 2011
Construction of Model:
Integration of Schedule and Cost
15
11 November 2011
Interpretation of Results:
Project End Date
CL(15 Feb 13) ≈ 30%
1. Availability of Constr. Labor
2. Availability of System. Labor
3. Errors in Design
…
16
11 November 2011
Interpretation of Results:
Total Project Cost
CL($176 mil) ≈ 30%
1. Constr. Labor Costs
…
6. Throughput of WRS
8. Throughput of 2nd Rx
17
11 November 2011
Interpretation of Results:
Correlation and Phase End Dates
Correlation < 30%
σ(Con) < σ(Sys) < σ(Pil)
18
11 November 2011
Interpretation of Results:
Discussion
Allowance for contingency
Select confidence level appropriate with risk tolerance
Subtract deterministic cost from cost at confidence level
Prioritize risk mitigations
19
Evaluate most serious risks
Price mitigation measures
Rerun mitigated scenario
Analyze cost vs. benefit
11 November 2011
Demonstration
20
11 November 2011
Questions
21
11 November 2011
Acknowledgements
Richard R. Lunt, PhD †
Javier F. Ordóñez, PhD
22
11 November 2011
Contact
Mark P. Brumer
mark@brumer.org
(603) 498-6072
23
11 November 2011