Production and Costs Short-Run vs. Long-Run
advertisement

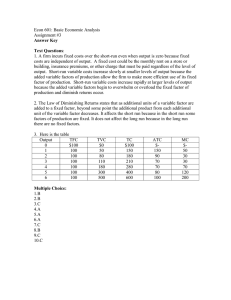
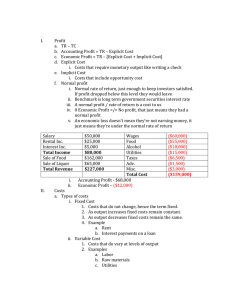
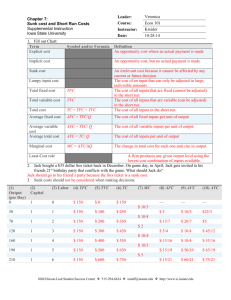
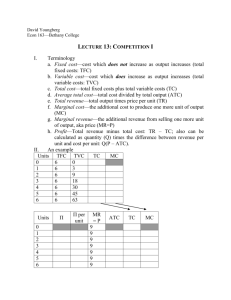
Production and Costs Production Short-Run Costs Short-Run vs. Long-Run • Technically, time does not determine the difference between “short-run” and “longrun” The Short Run is defined by the presence of a factor of production that is fixed in quantity –typically, this is capital (K). In the short-run, firms can only change the amount of non-capital inputs (e.g. Labor) The Long Run is defined by the ability for firms to vary the quantities of all factors of production. The time in which this takes a firm to do so may depend upon the firm as well as the industry. SHORT-RUN PRODUCTION • Graphically, we can analyze short-run production Total Product (TP) (Q): describes how output varies in the SR as more of any variable input is used with the fixed input, under current technology Marginal Product (MP): the increase in output from one more unit of an input when the quantity of all other inputs are unchanged Average Product (AP): the total output produced divided by the number of units of the input used 1 Marginal/Average Product • Formulas for MP and AP • Since Kapital is fixed in quantity, we are concerned with Marginal and Average products of labor MPL: ∆TP/ ∆L APL: TP/L What do the TP, MPL and APL curves look like? What is the relationship between MPL and APL? Law of Diminishing Marginal Produce • As a firm uses more a variable input, with a given quantity of fixed inputs, the MP of a variable input eventually diminishes. Short Run Costs • Short-run costs can be separated according to the nature of the input: Fixed Costs (Total Fixed Costs) (TFC): total cost to all the fixed inputs (Overhead costs) - must be incurred in the short-run even if don't produce anything Total Variable Cost (TVC): total cost to the variable inputs Total Cost (TC): sum of all the costs of all inputs in the production process SO, TC=TFC+TVC 2 Marginal Costs • However, when firms are choosing to maximize profit, they are more concerned with Marginal Costs – the cost of producing 1 more unit of output. MC = ∆TC/∆ ∆Q What do we know about the relationship between MC and MP? Average Costs • Firms are also concerned with Average Costs. In the short-run, there are 3 average costs: Average Fixed Costs: AFC= TFC/Q Average Variable Costs: AVC=TVC/Q Average Costs: AC=TC/Q Thus, AC=AVC + AFC What do these curves look like? Why are these curves important? GRAPHICAL ANALYSIS OF SR COST Graph 1: TC, TVC, TFC 1) Why is TVC upward sloping ? 2) Why does TC slope upward ? Graph 2: MC, ATC, AFC, AVC 1) Why is AFC downward sloping ? 2) Why is AVC "U-shaped" ? 3) Why is ATC "U-shaped" ? 4) Why does MC curve slope upward ? 5 ) Where does the MC curve intersect AVC ? ATC ? 3