Motivation "Motivation" Motivation and Performance
advertisement
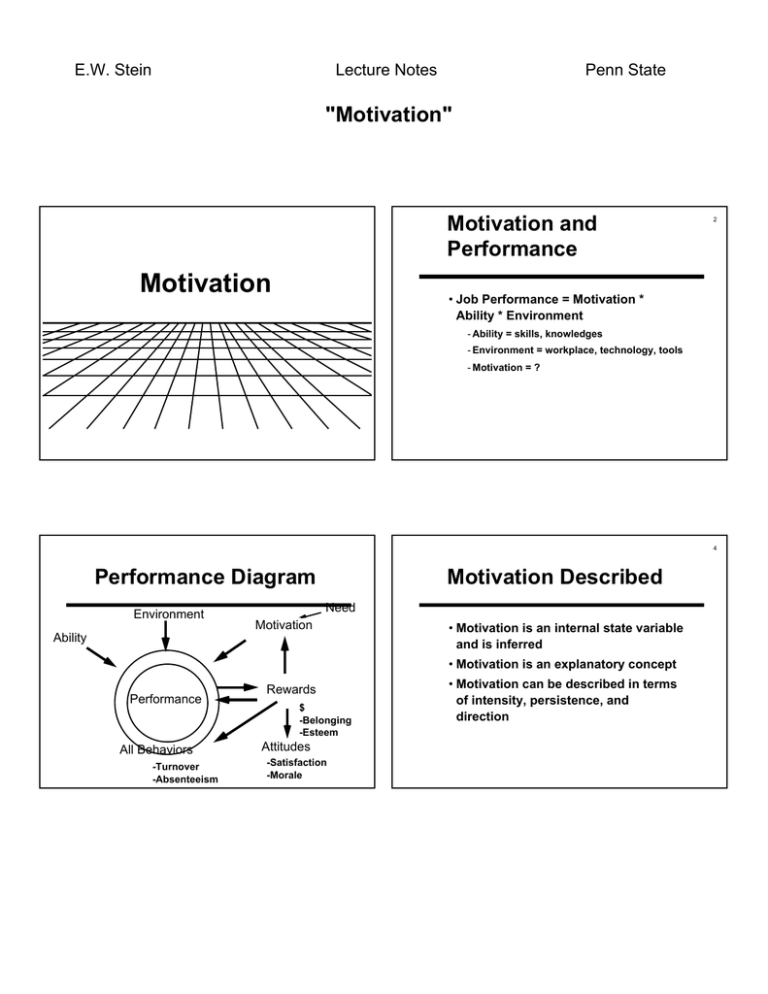
E.W. Stein Lecture Notes Penn State "Motivation" Motivation and Performance Motivation 2 • Job Performance = Motivation * Ability * Environment - Ability = skills, knowledges - Environment = workplace, technology, tools - Motivation = ? 4 Performance Diagram Environment Motivation Described Need Motivation Ability • Motivation is an internal state variable and is inferred • Motivation is an explanatory concept Performance All Behaviors -Turnover -Absenteeism Rewards $ -Belonging -Esteem Attitudes -Satisfaction -Morale • Motivation can be described in terms of intensity, persistence, and direction E.W. Stein Lecture Notes Penn State "Motivation" Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs Content Models of Motivation Self-actualization 6 10% • Hierarchy of Needs • ERG Theory Belongingness • Two Factor Theory Security 40% 50% 70% Physiological Needs 85% Esteem 7 ERG theory (Alderfer) Two Factor Theory (Herzberg) • Two scales: Pursue each Growth Relatedness Existence - Satisfaction-----no satisfaction - Dissatisfaction---no dissatisfaction • Can be satisfied and dissatisfied at same time • Managers can influence motivation by addressing "Hygiene Factors" and "Motivation Factors" 8 E.W. Stein Lecture Notes Penn State "Motivation" 9 Two Factor Diagram Satisfaction -Achievement -Recognition -Work itself -Responsibility -Achievement Dissatisfaction Process Models of Motivation No satisfaction • Expectancy theory • Equity theory No dissatisfaction -Supervisors -Working conditions -Interpersonal relations -Pay and security Expectancy Theory (Vroom) Expectancy Theory (Vroom) 11 • Assumes a relationship between motivation, effort, performance, and outcomes • Motivation is a function of: - Expectations about effort and performance - Expectations about performance and outcomes - Individual valuation of outcomes e1 Effort e2 Perform. (0-1) (0-1) Outcome 1 (V1) Outcome 2 (V2) ..... Outcome n (Vn) 12 E.W. Stein Lecture Notes Penn State "Motivation" 13 Equity Theory 14 Equity Theory Diagram • Argues that we compare ourselves to the efforts and outcomes of others • When equivalent, we are satisfied and motivated Outcomes (self) • When out of balance, we are dissatisfied and lose motivation Inputs (self) ? Outcomes (other) = Inputs (other) R2 R1 15 Equity Situations • Ratio (self) = Ratio (other) Motivating Employees - State of equity exists. Person is satisfied. • Ratio (self) < Ratio (other) - State of INequity exists. Person is not satisfied. Becomes jeolous of others. Loses motivation. • Ratio (self) > Ratio (other) - State of INequity exists. Person may or may not be satisfied. In some cases may reduce performance to others level. Relates to need to belong. • Reinforcement • Positive • Avoidance • Extinction • Punishment • Rewards E.W. Stein Lecture Notes Penn State "Motivation" 17 Reinforcement 18 Rewards • Positive • A formal mechanism by which employee performance is defined, evaluated, and rewarded - Strengthens behavior by providing desirable outcome • Avoidance • Rewards impact: - Strengthens behavior by removing undesirable outcome - Attitudes • Extinction - Behaviors - Weakens behavior by not responding to performance - Motivation • Punishment - Weakens behavior by providing undesirable 19 Performance Diagram Environment Motivation end... Need Ability Performance All Behaviors -Turnover -Absenteeism Rewards $ -Belonging -Esteem Attitudes -Satisfaction -Morale 20