Economics 001 Principles of Microeconomics Price discrimination What makes price discrimination
advertisement

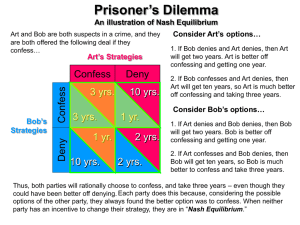
Price discrimination Economics 001 Principles of Microeconomics Professor Arik Levinson •Lecture 16 – price discrimination – cartels and oligopolies – monopolistic competition – game theory Definition: charging different prices for the same product (with the same marginal cost). • 1) Among buyers • 2) Among units • 3) Among markets What makes price discrimination possible? Figure 11-6 Price Discrimination • 1) Need to keep track of buyers • 2) No resale market • 3) Market power (monopoly power) Thinking like an Economist 1. Why do dry cleaner charge more to clean a woman's shirt than a man's? Cartels • "Seldom do members of the same trade meet together but conversation turns to conspiring to raise prices" • Adam Smith • "Any time 30 of the wealthiest and most influential individuals get together behind closed doors and agree to reduce output, that cannot be a good thing for anyone but the monopolists." • Rep. John Conyers (D, MI) 1 Three problems facing cartels Figure 11-5 A Cartel Member’s Incentive to Cheat • 1) Illegal in U.S. • 2) Restricting entry • 3) Enforcing output restriction Game Theory • DN: Game = strategies and payoffs • DN: Best response = highest payoff given other players' strategies • DN: Dominant strategy = best response always • Nash Equilibrium = all players playing their best responses Prisoner's Dilemma 20 yrs Don’t talk Life Free Free Life 5 yrs 5 yrs Compete 20 yrs Rat Braniff Airlines Collude Compete Collude Prisoner #1 Rat Don’t talk American Prisoner #2 Nash Equilibrium An application $1 M $2 M $0.2 M $5 M $1.5 M $0.5 M $0.5 M $1.5 M Nash Equilibrium 2