Dimensional Analysis
advertisement

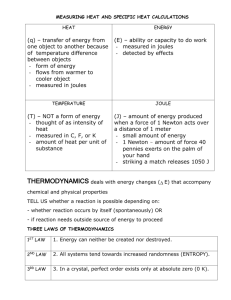
Dimensional Analysis In class you were asked to prove that Pascal X meter3 = Joules. It was demonstrated that a Pascal = Newton/m2 (which was a hint on how to approach this). From Physics you should recall Pressure = Force/Area, Force = Mass x Acceleration, Using the MKS or (SI) units Force Newton = kg-m sec 2 E = mc2 (or any definition of energy) acceleration is meters/sec2 and mass is the kilogram. = mass x acceleration Newton = kg x and meter second 2 force area Newton = meter 2 kg-m/sec 2 kg = = 2 m m-sec 2 Pressure = Pascal Pascal Recalling Einstein’s equation E = m c2 Since energy is measured in Joules, m stands for mass (kg) and c is the speed of light (m/sec), then a Joule must be the same thing as kg-m2/sec2. Finally: ! Newton $ Pressure times volume = Pascals x meters 3 = # meters 3 = Newton-meters " meter 2 &% ( ) ! kg-m $ N-m = # ( m ) = kg-m 2 /sec 2 which is the same things as a Joule " sec 2 &% Thus it has been shown that Pa x m3 is the same thing as a Joule Lastly: Since 1000 Liters = 1 m3 and 1 kiloPascal = 1000 Pascal " 1 % Pascal ! meter 3 = $ kPa ' ! (1000 L ) = KiloPascal ! Liter = Joules # 1000 & For example: R = 8.31447 Pascals-meters 3 /mole-Kelvin = 8.31447 kPa-L/mol-K = 8.31447 Joule/mol-K All of this should have been covered in General Chemistry I and/or University (or College) Physics I. You are expected to know ALL of this