Document 10282858
advertisement

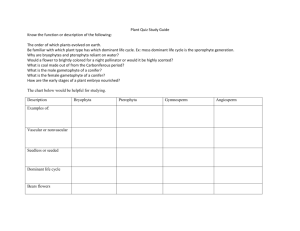
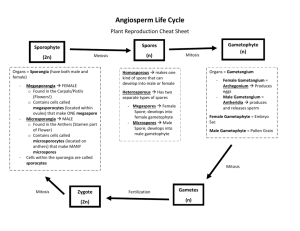
Bio20B (Plants), Lecture 6 outline Thurs, 1/20/2011 Plant of the day Common name: Latin name: Phyllotaxy: Notes: Taxonomy: 1. Floral morphology a. Four whorls: S, P, S, C b. Incomplete flowers i. Pistillate ii. Staminate c. Monoecious Leaf form: Bio20B (Plants), Lecture 6 outline Thurs, 1/20/2011 d. Dioecious e. Monocot f. Dicot 2. Function of Flowers a. Pollination syndromes 1. Wind 2. Bee 3. Bird 4. Bat 5. Fly 3. Angiosperm Life Cycle a. Alternation of generations Fern example: How are angiosperms different from ferns? Bio20B (Plants), Lecture 6 outline Thurs, 1/20/2011 b. Angiosperm Life Cycle c. Gamete formation i. Female gametophyte ii. Male gametophyte d. Pollination i. Self-­‐ Incompatibility ii. Double Fertilization: One sperm fuses with _______________________ and develops into the ___________________________. The other sperm fuses with _______________________ and develops into the ___________________________. Bio20B (Plants), Lecture 6 outline Thurs, 1/20/2011 4. Fruits develop from flowers a. The ovary wall develops into the ________________________. Ovules develop into the __________________________. b. What is a fruit? c. Major divisions within fruit types. i. Simple fruits 1. Fleshy fruits a. drupe b. pome c. berry 2. Dry fruits a. Indehiscent i. Achene d. Aggregate fruits e. Multiple fruits f. The function of fruit is seed dispersal: wind, water, animal Bio20B (Plants), Lecture 6 outline Thurs, 1/20/2011 1. Homoeotic genes of floral development When A is missing? When B is missing? When C is missing? 2. Function of Flowers a. Pollination syndromes 1. Wind 2. Bee 3. Bird Bio20B (Plants), Lecture 6 outline Thurs, 1/20/2011 4. Bat 5. Fly 3. Angiosperm Life Cycle a. Alternation of generations Fern example: How are angiosperms different from ferns? b. Angiosperm Life Cycle c. Gamete formation i. Female gametophyte Bio20B (Plants), Lecture 6 outline Thurs, 1/20/2011 ii. Male gametophyte d. Pollination i. Tube growth ii. Self-­‐ Incompatibility iii. Double Fertilization: One sperm fuses with _______________________ and develops into the ___________________________. The other sperm fuses with _______________________ and develops into the ___________________________. 4. Fruits develop from flowers a. The ovary wall develops into the ________________________. Ovules develop into the __________________________. b. What is a fruit? c. The function of fruit is seed dispersal: wind, water, animal Bio20B (Plants), Lecture 6 outline Thurs, 1/20/2011 Homework: Use the text to explain these experiments. What are the main result from each of these experiments. 5. Environmental cues initiate flower formation i. Exp: Do short day plants measure day length? ii. Exp: Do plant measure the length of night? iii. Exp: Does phytochrome participate in the timing mechanism? iv. Exp: Do leaves detect the dark period? v. Exp: Can the signal be passed from plant to plant?