Dougherty Valley High School AP Chemistry
advertisement

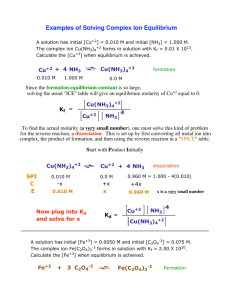
Dougherty Valley High School AP Chemistry Chapters 14 and 15 Test - Acid-Base Equilibria This is a PRACTICE TEST. Complete ALL questions. Answers will be provided so that you may check your work. I strongly suggest that you complete ALL of these problems. 1. For the equilibrium that exists in an aqueous solution of nitrous acid (HNO2, a weak acid), the equilibrium constant expression is: A) [ H ][ NO2 ] K= [ HNO2 ] B) [ H ][ N ][O]2 K= [ HNO2 ] C) K = [H+][NO2–] D) [ H ]2 [ NO2 ] K= [ HNO2 ] E) none of these 2. What is the equilibrium constant for the following reaction? N3– + H3O+ value for HN3 = 1.9 x 10–5. A) 5.3 x 10–10 B) 1.9 x 10–9 C) 1.9 x 10–5 D) 5.3 x 104 E) 1.9 x 109 HN3 + H2O The Ka 3. The equilibrium constants (Ka) for HCN and HF in H2O at 25°C are 6.2 x 10–10 and 7.2 x 10–4, respectively. The relative order of base strengths is: A) F– > H2O > CN– B) H2O > F– > CN– C) CN– > F– > H2O D) F– > CN– > H2O E) none of these 4. Calculate the [H+] in a solution that has a pH of 11.05. A) 2.9 M B) 11.1 M C) 1.1 x 10–3 M D) 8.9 x 10–12 M E) none of these 5. Solid calcium hydroxide is dissolved in water until the pH of the solution is 10.29. The hydroxide ion concentration [OH-] of the solution is: A) 5.1 x 10–11 M B) 3.9 x 10–4 M C) 1.9 x 10–4 M D) 9.7 x 10–5 M E) none of these 6. The pKa of HOCl is 7.5. Calculate the pH of a 0.50 M solution of HOCl. A) 7.5 B) 6.5 C) 3.9 D) 10.1 E) 0.3 7. Calculate the pOH of a 0.20 M solution of Ba(OH)2. A) 0.70 B) 0.40 C) 13.60 D) 13.30 E) none of these 8. Determine the pH of a 0.037 M solution of H2SO4. The dissociation occurs in two steps. Ka1 is extremely large; Ka2 is 1.2 x 10-2. A) 12.69 B) 1.43 C) 1.92 D) 1.31 E) 1.00 9. The [OH-] in a 0.68 M pyridine (C5H5N; Kb = 1.7 x 10-9) solution is A) 1.2 x 10–9 M B) 3.4 x 10–5 M C) 0.68 M D) 5.0 x 10–5 M E) none of these 10. The conjugate acid and conjugate base of bicarbonate ion, HCO3–, are, respectively: A) H3O+ and OH– B) H3O+ and CO32– C) H2CO3 and OH– D) H2CO3 and CO32– E) CO32– and OH– 11. Which of the following species is present in the greatest concentration in a 0.100 M H2SO4 solution in H2O? A) H3O+ B) HSO4– C) H2SO4 D) All species are in equilibrium and therefore have the same concentration. E) SO42– 12. Which of the following is the correct order for increasing pHs for HNO3, KCl, NH4Cl, KOH, and NaC2H3O2? (Ka for HC2H3O2 is 1.80 x 10–5, Ka for NH4+ is 5.56 x 10–10). A) KCl, NH4Cl, HNO3, KOH, NaC2H3O2 B) HNO3, KCl, NH4Cl, KOH, NaC2H3O2 C) NH4Cl, HNO3, KCl, KOH, NaC2H3O2 D) HNO3, NH4Cl, KCl, NaC2H3O2, KOH E) none of these 13. If Ka for HCN is 6.16 x 10–10, what is Kb for CN-? Note: CN H 2O HCN OH A) B) C) D) E) Kb [ HCN ][OH ] [CN ] 6.16 x 10–24 6.16 x 104 1.62 x 10–5 1.23 x 10–9 none of these 14. The hydrogen halides (HF, HCl, HBr, and HI) are all polar molecules. The strength of the acid each forms in water is based on which of the following? A) the polarity of the molecule B) the size of the molecule C) the strength of the bond D) two of these E) none of these 15. Calculate the [H+] in a solution that is 0.10 M in NaF and 0.20 M in HF. (Ka = 7.2 x 10-4) A) 7.2 x 10–4 M B) 2.0 M C) 1.4 x 10–3 M D) 0.20 M E) none of these 16. For a solution equimolar in HCN and NaCN, which statement is false? A) This is an example of the common ion effect. B) The [H+] is larger than it would be if only the HCN was in solution. C) The [H+] is equal to the Ka. D) Addition of more NaCN will shift the acid dissociation equilibrium of HCN to the left. E) Addition of NaOH will increase [CN–] and decrease [HCN]. 17. Calculate the pH of a solution made by mixing 100.0 mL of 0.268 M NH3 with 100.0 mL of 0.100 M HCl. (Kb for NH3 = 1.8 x 10-5.) A) 9.48 B) 4.52 C) 9.03 D) 9.26 E) none of these 18. A titration of 200.0 mL of 1.00 M H2A was done with 1.12 M NaOH. For the diprotic acid H2A, Ka1 = 2.5 x 10-5, Ka2 = 3.1 x 10-9. Calculate the pH after 100.0 mL of 1.12 M NaOH have been added. A) 9.29 B) 8.61 C) 5.39 D) 9.41 E) 4.71 19. The pH at the equivalence point of a titration of a weak acid with a strong base will be A) less than 7.00. B) equal to 7.00. C) greater than 7.00. D) More data is needed to answer this question. Use the following to answer questions 20-23: The following questions refer to the following system: 3.5 x 102 mL of 3.2 M Pb(NO3)2 and 2.0 x 102 mL of 0.020 M NaCl are added together. Ksp for the lead chloride is 1.6 x 10–5. 20. Determine Q, or the ion product. A) 1.1 x 10–4 B) 1.5 x 10–2 C) 7.8 x 10–3 D) 8.1 x 10–4 E) none of these 21. Will precipitation occur? A) Yes B) No C) Maybe, it depends on the temperature. D) Maybe, it depends on the limiting reagent concentration. E) None of these. 22. What is the limiting reagent in the formation of the lead chloride? A) Pb2+ B) Cl– C) (NO3)– D) PbCl2 E) Pb(NO3)2 23. Determine the equilibrium concentration of the chloride ion. A) 3.9 x 10–4 B) 8.0 x 10–6 C) 2.8 x 10–3 D) 6.1 x 10–2 E) none of these 24. How many moles of HCl(g) must be added to 1.0 L of 1.6 M NaOH to achieve a pH of 0.00? (Neglect any volume change.) A) 0.6 moles B) 3.6 moles C) 2.6 moles D) 4.6 moles E) none of these Use the following to answer questions 25-26: Consider a solution made by mixing 500.0 mL of 4.0 M NH3 and 500.0 mL of 0.40 M AgNO3. Ag+ reacts with NH3 to form AgNH3+ and Ag(NH3)2+: Ag+ + NH3 25. The concentration of Ag(NH3)2+ at equilibrium is: A) 2.0 M B) 0.40 M C) 0.20 M D) 1.0 x 10–3 M E) none of these 26. The concentration of Ag+ at equilibrium is: A) 2.0 M B) 1.2 x 10–8 M C) 4.5 x 10–9 M D) 1.6 M E) none of these 27. The Kf for the complex ion Ag(NH3)2+ is 1.7 x 107. The Ksp for AgCl is 1.6 x 10–10. Calculate the molar solubility of AgCl in 1.0 M NH3. A) 5.2 x 10–2 B) 4.7 x 10–2 C) 2.9 x 10–3 D) 1.3 x 10–5 E) 1.7 x 10–10 28. Find the solubility (in mol/L) of lead(II) chloride (PbCl2) at 25oC. Ksp = 1.56 x 10–5. A) 1.57 x 10–2 B) 2.50 x 10–2 C) 5.93 x 10–17 D) 1.97 x 10–3 E) 1.98 x 10–2 29. It is observed that 7.50 mmol of BaF2 will dissolve in 1.0 L of water. Use these data to calculate the value of Ksp for barium fluoride. A) 1.1 x 10–4 B) 4.2 x 10–7 C) 1.7 x 10–6 D) 2.3 x 10–4 E) 5.6 x 10–5 30. The Ksp for PbF2 is 4.0 x 10-8. If a 0.071 M NaF solution is saturated with PbF2, what is the [Pb2+] in solution? A) 5.6 x 10–7 M B) 2.0 x 10–10 M C) 1.1 x 10–4 M D) 7.9 x 10–6 M E) 2.8 x 10–9 M