Topic 10-Labor, Wages, & Outsourcing
advertisement

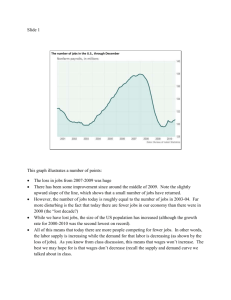
Topic 10: The Work Force & Wages Day 1 Notes Textbook Chapters-Chapters 9 & 13 Labor Force All non military people age 16-65 who are employed or seeking it What it means to be Employed •16 yrs.+ working for pay at least 1 hr./wk. •15 yrs.+ w/o pay for family business •Held jobs but didn’t work due to illness, vacation, strike, weather The US Labor Force Population and labor force, 1998, 2008, and projected 2018, in millions Numeric change in labor force by age, projected 2008–18, in thousands The baby-boom generation— those born between 1946 and 1964—is expected to remain in the labor force longer than previous generations. As this group ages, the number of people in the labor force aged 55 to 64 is expected to increase by more than 7 million during the projections decade, and the number of people aged 65 and older is projected to increase by almost 5 million. The numbers of 45- to 54-year-olds and 35- to 44-year-olds are expected to shrink as baby boomers age and shift into older groups. Labor force participation rates for men and women, 1958–2008 and projected 2018, in percents The labor force participation rates for both men and women are expected to decline slightly over the projections decade. By 2018, about 71 percent of men and 59 percent of women are expected to be in the labor force.The aging of the population will be a factor driving down labor force participation rates. Despite working longer than previous generations, baby boomers will still have lower levels of labor force participation than those in younger age groups. The baby-boom generation is becoming a larger segment of the total population, driving down overall participation in the labor force. Percent distribution of labor force by race, projected 2018 Although whites will continue to be the largest racial category in the labor force, other racial groups are projected to make up 21 percent of the labor force by 2018. Percent growth in labor force by race, projected 2008–18 Although Asians will remain a small part of the labor force, they—along with the "all other races" category—will have the fastest rate of labor force growth between 2008 and 2018. This growth is due to increased immigration and both groups' very high labor force participation rates. The "all other races" category includes American Indians and Alaska Natives, Native Hawaiians and other Pacific Islanders, multiracial individuals, and any other people who do not identify themselves as white, black, or Asian. Occupational Trends 1800-1900’s: shift from agriculture to Industrial Revolution which created factory jobs 1900’s-1960’s: heavy manufacturing 1970’s- present: boom in electronics led to new factory jobs; revolution in computers created new jobs Future: Shift from manufacturing to service economy Implications for the Younger Segment of the Population (18-24 Year Olds) Must have skills, education, training and experience Manufacturing jobs disappearing Most work several jobs before settling How are wages determined? Supply & demand…AGAIN Demand for product changes, so does demand for the labor that produces it Factors that Affect Wages Education Opportunity Initiative Discrimination ◦ Women/minorities ◦ Glass ceiling Laws Employers Region Labor Unions Education Highly educated jobs have High Demand, Low supply Higher salaries Impact: education increases productivity & results in higher wages Opportunity Isolated geography Job safety Impact: These factors hinder chances to improve salary May take dangerous job Initiative Lack of motivation Impact: No effort means no high salary Discrimination Women & minorities Glass ceiling: allow women to rise to a particular place in the company’s hierarchy & then stop the promotions no matter how deserving the employee is Race & gender keep you from getting a promotion Impact: Pay gap exists between male & females Legislation to Prevent Discrimination (Laws) Affirmative action programs-insure the equitable recruitment of workers Civil Rights Act of 1964, Equal Pay Act of 1963, & U.S. Code 1963 prevent gender discrimination Rehabilitation Act of 1973: prohibits discrimination based on handicap Age Discrimination in Employment Act of 1967 protects those between 40 & 70 Laws Against wage discrimination Impact: Prevent unfair practices Minimum wage laws Fair Labor Standards Act Employers Impact: Outsource Impact: Results in lay offs & lower wages Region Where you live Impact: Cost of living determines pay differences NYC vs Ballston Spa Labor Unions Impact: Fight for higher wages and better working conditions Tend to produce higher wages than non-union workers Strength in Numbers Outsourcing and Globalization Topic 10 Day 2 Key Terms Outsourcing-Sending jobs from one nation to another to decrease costs for the business either through manufacturing costs, wages, taxes, etc.) Globalization-Inter-consecutiveness of the world’s nations through economic, social, and political means. Idea merges theories of cultural diffusion with interdependence. Outsourcing Advantages & Disadvantages for the Outsourcing Nation: Advantages Disadvantages Provides jobs to people in Loss of domestic jobs other countries Weakens strength of Lower prices for consumers domestic economy Bigger profit margins Less tax revenue for country Lower costs of production Loss of power/ #’s in unions Better, higher paying corp. Plant Closings jobs in US Impact of Outsourcing Skilled workers & professionals: increased demand, wages increase Unskilled/lower skilled: Lowered Demand, Increased Supply Lower Pay Surplus of unskilled workers Temporary/Contingent workers: People working free lance; as contracted ex. Engineers, attorneys Increased Demand- can adjust for peak seasons, fewer rights, paid less, flexible Directions: In your notebook make a t-chart of the Advantages and Disadvantages that outsourcing has for India. (The Other Side of Outsourcing 44:20) Advantages Disadvantages Topic 10 Day 3 I wish I was in school!!! Avondale mine disaster Exploitation, long hours, low pay, faulty equipment, dirty, poor ventilation, poor lighting, dull/repetitive tasks, substandard conditions 12 hours a day, 6 days a week 1 in 300 killed in Railroad work Organized Labor Types of Laborers Unskilled: requires no Skilled: requires specialized skills, specialized abilities & education, & training; training hrly wage Professional: demands Semi Skilled: requires advanced skills & minimal specialized education skills & education The Labor Movement: Strength in Numbers Labor Unions project that no one creates change alone. Better chances for change come with more people. Types of Unions Craft Industrial Craft Union Association of skilled workers who perform the same kind of work Ex. NYSUT-teachers Industrial Union All workers in a given industry regardless of what job they perform Ex. UAW: any worker in the auto industry Types of Union Activities Types of Union Activities Purpose of Union Activity Strike: Most common; refusal to work until demands are met slows efficiency; tool used to increase bargaining power Pickett: Parade vocalize disputed issues; cut off patrons, supplies; intimidate; inform Boycott Mass refusal to buy product or service from a target Hurts income and reputation Roles of Labor Unions Roles Collectively Bargain Use strength in numbers Union and company reps meet to negotiate a new labor contract 1st steps unions take Get favorable legislation passed Endorse candidates that will support the unions cause Secure better working conditions Wages Hours Seniority Rights (LIFO) Safety and Comfort Job Security Resolving Differences Conciliation 3rd party brought in to encourage talks between mgmt. And workers Role is to bring two sides together Arbitration Binding decision Union and mgmt. Turn case over to a 3rd party to resolve dispute Seldom used Mediation Union and mgmt. Help settle dispute Mediator is neutral and knows concessions to agree on Non binding Major Issues in Contract Disputes Wages and Fringe Benefits Working Conditions Job Security Right to Work Laws Ban mandatory union membership. Unemployment & Poverty Topic 10 Day 4 Unemployment One who is actively seeking but not finding a job. How do we figure out the unemployment rate? The total number unemployed in proportion to the total civilian labor force (16-65) (Percentage) Problems with Unemployment Doesn’t count “drop outs” People are “employed” even with part time jobs (doesn’t give a true measure) Types of Unemployment Frictional Unemployment ◦ Unemployment that comes from moving between careers, jobs and/or relocation. Types of Unemployment Seasonal Unemployment ◦ Unemployment that occurs when industries slow or shut down for a season or make seasonal changes in production. Types of Unemployment Structural Unemployment ◦ Occurs when a worker’s skills do not match the jobs that are available; often occurs because of technological advances. Types of Unemployment Cyclical Unemployment ◦ Unemployment that rises during economic downturns and falls during periods of economic growth. Technological Unemployment Replacement by machines Full Employment Lowest possible unemployment rate with growth & all factors of production used efficiently ECO. GOAL- between 4 & 6 % Causes of Income Inequality & Poverty Education Ability Wealth Location Discrimination Family Structure Income Distribution Problem Richest 20% have 13x’s the income as the 20% poorest Uneven Distribution of Wealth Poverty Those living on or below the poverty line or threshold. (Annual dollar amount needed to sustain life with basic needs.) Poverty Rate % of people who live below the poverty threshold Differs by race and ethnic origin, type of family, age, residence Welfare Programs Income Assistance Direct Cash Comes with guidelines General Assistance Food Stamps Medicaid Based on Income Social Service Family Planning Daycare Child Welfare Job Training Workfare Exchange labor for benefits Community service, build skills TANF: Temporary Assistance for Needy Families Eliminated abuses of the system (got rid of cash abuses) Limited time to receive benefits to 5 years The poverty line is an annual dollar amount needed to sustain life with basic needs. Poverty Line in 2003 for: Single adult: $9,393 Family of 2: $12,490 Family of 4: $18,850 Add $3180 for each additional person (less for persons over 65 years old) Some Interesting Stats: A Closer Look at WHO is in poverty: RACESTATUSAGE Blacks=22.7% Single Women =26.4% Under 18=16.3% Hispanics=21.4% Single Men =13.1% Whites9.9%Married=4.9% Asians=10.2% Black and Hispanic, Female-headed households = 35+% The 2009 Poverty Guidelines for the48 Contiguous States and the District of Columbia Persons in family Poverty guideline 1 $10,830 2 14,570 3 18,310 4 22,050 5 25,790 6 29,530 7 33,270 8 37,010 For families with more than 8 persons, add $3,740 for each additional person. http://www.irp.wisc.edu/ Worldwide Demographics Source:www.globalissues.org/print/article/26 Poverty Almost half the world-over three billion people-live on less than $2.50 a day At least 80% of humanity lives on less than $10 a day Poverty line-$1.25 a day Children 2.2 billion children in the world 1 billion children in poverty 10.6 million died in 2003 before age 5 15 million children orphaned due to HIV/AIDS25,000 children each day die due to poverty 72 million children of primary school age in the developing world were not in school in 2005 Less than one percent of what the world spent every year on weapons was needed to put every child into school by the year 2000 and yet it didn’t happen Health An estimated 40 million people are living with HIV/AIDS, with 3 million deaths in 2004 Every year 1 million people die from Malaria Life expectancy-Reduced for 4 out of 5 groups of countries except for the highest group (69-76 years) Urbanization-the movement of people from the rural countryside into cities Half of the world’s population lives in cities or towns 1 billion live in slums Wealth 2005-wealthiest 20% accounted for 76.6% total consumption 2005-Poorest 5% accounted for just 1.5% The GDP (Gross Domestic Product) Measures a countries wealth through imports, exports, spending, investments, etc.-of the 41 heavily indebted poor countries (567 million people) is less than the wealth of the world’s 7 richest people combined. The wealthiest nation on Earth (US) has the widest gap between rich and poor of any industrialized nation Consumerism: Definition 1 Organized-efforts by individuals, groups, and governments to help protect consumers from policies and practices that infringe consumer rights to fair business practices. Definition 2 Doctrine that ever-increasing consumption of goods and services forms the basis of a sound economy. Definition 3 Continual expansion of one's wants and needs for goods and services. Global Priority Cosmetics in the United States Ice cream in Europe Perfumes in Europe and the United States Pet foods in Europe and the United States Business entertainment in Japan Cigarettes in Europe Alcoholic drinks in Europe Narcotics drugs in the world Military spending in the world $U.S. Billions 8 11 12 17 35 50 105 400 780 Global Priority Basic education for all Water and sanitation for all Reproductive health for all women Basic health and nutrition $U.S. Billions 6 9 12 13 Resources 12 percent of the world uses 85% of the world’s water-none of the 12% live in a third world nation Water problems affect half of humanity 1.1 billion people have inadequate access to water 2.6 billion lack basic sanitation 1.6 billion (25% of humanity) live without electricity Number of people living without electricity Region South Asia Sub-Saharan Africa Millions without electricity 706 547 East Asia Other 224 101 Growth in goods components of personal consumption expenditures, projected 2008–18, in billions Consumerism http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hGaOQKJik-s http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_nk2_rk0FLw http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2N0NHu2GJm8