(The Spirit of Laws) as they affect our concept of government
advertisement

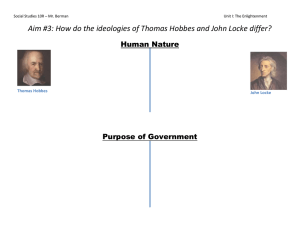
• SSCG1 The student will demonstrate knowledge of the political philosophies that shaped the development of United States constitutional government. • a. Analyze key ideas of limited government and the rule of law as seen in the Magna Carta, the Petition of Rights, and the English Bill of Rights. • b. Analyze the writings of Hobbes (Leviathan), Locke (Second Treatise on Government), and Montesquieu (The Spirit of Laws) as they affect our concept of government. Essential Features of a State 1. Population - people 2. Territory - established boundaries 3. Sovereignty - absolute authority within its boundaries (threatened by globalization today) 4. Government - institution through which the state maintains social order, provides public services, and enforces decisions that are binding on all people living within the state Purposes of Government 1. Maintain social order Laws, courts, police 2. Provide public services Roads, schools, programs 3. Provide national security Military 4. Make economic decisions What, how much, for whom 3 Values Pursued by Government 1. Freedom •Freedom of : absence of constraints on behavior •Freedom from: Fight against exploitation and oppression; equality 4 Values Pursued by Government 2. Order •Preserving life and protecting property •Preserving social order –Police power –authority to safeguard residents’ safety, health, welfare, and morals Values Pursued by Government 3. Equality • Political equality: one person, one vote • Social equality: wealth, education, and status • Equality of opportunity: each person has the same chance to succeed • Equality of outcome: society must ensure people are equal socially and economically –Government-supported rights • Models of Democratic Government – Majoritarian Democracy • Type of democracy interpreted as government by the majority of the people. – Pluralist Democracy • Type of democracy interpreted as government by the people operating through competing interest groups. Liberals and Conservatives: The Narrow Middle • Liberals –Favor more government spending, programs and regulation • Conservatives –Favor less government spending, programs and regulation American Political Ideologies 1. Liberals – Favor freedom and equality over order 2. Conservatives – Favor freedom and order over equality 3. Libertarians – Favor freedom over order or equality 4. Communitarians – Favor order and equality over freedom Ideologies: A TwoDimensional Framework Copyright © 2014 Cengage Learning 10 • a. Analyze key ideas of limited government and the rule of law as seen in the Magna Carta, the Petition of Rights, and the English Bill of Rights. What is Limited Government? • A system of power in which the power of the government is not absolute. What is rule of law? • The principle that all people and institutions are subject to and accountable to law that is fairly applied and enforced. –Including the king • Where do the ideas of limited government and the rule of law come from? –3 English Documents • Magna Carta (1215) • Petition of Right (1628) • English Bill of Rights (1689) Magna Carta (1215) • Nobles forced King John to sign –Provided the basis for limited gov’t – Only applied to nobles – Certain basic rights may not be denied by government – Representatives of the people should take part in government Petition of Right (1628) • Signed by King Charles I –Monarch could no longer: • Collect taxes without Parliament consent • Imprison people without just cause • House troops in private homes without owner permission • Declare martial law except in times of war English Bill of Rights (1689) • Accepted by William III and Mary II –Established a constitutional monarchy and set clear limits on what king could do: • It established Parliamentary supremacy • It established a balance of powers between the executive and legislative branches Our English Heritage • Rule of Law – not even the ruler is above the law • Representative Government – people should have a voice in government • Limited Government – citizens have basic rights that are protected by law • b. Analyze the writings of Hobbes (Leviathan), Locke (Second Treatise on Government), and Montesquieu (The Spirit of Laws) as they affect our concept of government. Thomas Hobbes • Thomas Hobbes - one of the first to theorize on the social contract. • Social contract - people gave up to the state the power needed to maintain order and state agreed to protect the citizens. • He wrote the book Leviathan, Hobbes set out his doctrine of social contract theories. John Locke • John Locke took social contract a step further. • People were born with natural rights: life, liberty, and property. • People give power to a governing authority. When government failed to preserve the rights of the people, the people had the right to break the contract. • He influenced the American Declaration of Independence. John Locke • People need government to keep social order because they have not figured out a way to live in groups without conflict. • The Second Treatise outlines a theory of political or civil society based on natural rights and contract theory. Baron de Montesquieu • The Spirit of Laws was published anonymously by Montesquieu. • Montesquieu stressed the separation of powers, three branches of gov’t, and the rule of law. • Many of his ideas are in our Constitution. • SSCG19 The student will compare and contrast governments that are unitary, confederal, and federal; autocratic, oligarchic and democratic; and presidential and parliamentary. 3 Government Systems 1. Unitary system – all key powers given to national gov’t 2. Federal system – powers shared between state and national gov’t 3. Confederacy – loose union of independent states Major Types of Government (Aristotle) 1. Autocracy Power to rule in the hands of a single individual Two forms of autocracy: Dictatorship monarchy 2. Oligarchy Gov’t in which a small group holds power Power comes from wealth, military power, social position, or religion China has this 3. Democracy Rule by the people Two forms direct democracy – people rule themselves by voting on issues individually representative democracy – people elect representatives to make laws and run gov’t USA has this • Two Types of Democracy –Parliamentary »Legislative and executive powers both belong to an elected legislature »Legislature chooses the cabinet and head executive –Presidential »Executive branch independent of the legislative branch »President heads executive branch and chooses his cabinet 3 Economic Systems in World 1. Capitalism –Free choice or free enterprise –Developed by Adam Smith –Economic decisions are made buy buyers (consumers) and sellers (producers) –USA actually has a mixed-market economy 2. Socialism – Government owns the basic means of production, determines the use of resources, distributes products and wages, and provides social services. 3. Communism –Central government directs all major economic decisions –Developed by Karl Marx • Believed one class would evolve where property belonged to everyone and no government would be needed