The Coordinate Plane
advertisement

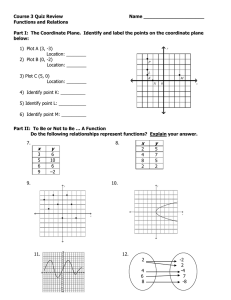
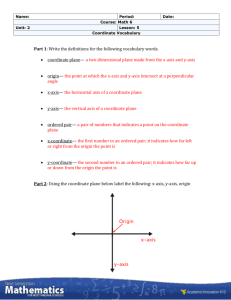
The Coordinate Plane You will learn to name and graph ordered pairs on a coordinate plane. In coordinate geometry, grid paper is used to locate points. The plane of the grid is called the coordinate plane. The Coordinate Plane You will learn to name and graph ordered pairs on a coordinate plane. In coordinate geometry, grid paper is used to locate points. The plane of the grid is called the coordinate plane. y 5 4 3 2 1 x -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 -1 -2 -3 -4 -5 2 3 4 5 The Coordinate Plane The horizontal number line is called the ______. y 5 4 3 2 1 O x -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 -1 -2 -3 -4 -5 2 3 4 5 The Coordinate Plane The horizontal number line is called the ______. x-axis y 5 4 3 2 1 O x -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 -1 -2 -3 -4 -5 2 3 4 5 The Coordinate Plane The horizontal number line is called the ______. x-axis y 5 4 3 The vertical number line is called the ______. 2 1 O x -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 -1 -2 -3 -4 -5 2 3 4 5 The Coordinate Plane The horizontal number line is called the ______. x-axis y 5 4 3 The vertical number line is called the ______. y-axis 2 1 O x -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 -1 -2 -3 -4 -5 2 3 4 5 The Coordinate Plane The horizontal number line is called the ______. x-axis y 5 4 3 The vertical number line is called the ______. y-axis 2 1 O x The point of intersection of the two axes is called the _____. -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 -1 -2 -3 -4 -5 2 3 4 5 The Coordinate Plane The horizontal number line is called the ______. x-axis y 5 4 3 The vertical number line is called the ______. y-axis 2 1 O x The point of intersection of the two origin axes is called the _____. -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 -1 -2 -3 -4 -5 2 3 4 5 The Coordinate Plane The horizontal number line is called the ______. x-axis y 5 4 3 The vertical number line is called the ______. y-axis 2 1 x The point of intersection of the two origin axes is called the _____. -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 -1 -2 -3 -4 The two axes separate the plane into four regions called _________. -5 2 3 4 5 The Coordinate Plane The horizontal number line is called the ______. x-axis y 5 4 Quadrant II (–, +) The vertical number line is called the ______. y-axis 3 2 Quadrant I (+, +) 1 x The point of intersection of the two origin axes is called the _____. -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 3 4 -1 Quadrant III-2 (–, –) -3 -4 The two axes separate the plane into quadrants four regions called _________. 2 -5 Quadrant IV (+, –) 5 The Coordinate Plane An ordered pair of real numbers, called coordinates of a point, locates a point in the coordinate plane. The Coordinate Plane An ordered pair of real numbers, called coordinates of a point, locates a point in the coordinate plane. Each ordered pair corresponds to EXACTLY ________ in the coordinate plane. The Coordinate Plane An ordered pair of real numbers, called coordinates of a point, locates a point in the coordinate plane. one point in the Each ordered pair corresponds to EXACTLY ________ coordinate plane. The Coordinate Plane An ordered pair of real numbers, called coordinates of a point, locates a point in the coordinate plane. one point in the Each ordered pair corresponds to EXACTLY ________ coordinate plane. The point in the coordinate plane is called the graph of the ordered pair. The Coordinate Plane An ordered pair of real numbers, called coordinates of a point, locates a point in the coordinate plane. one point in the Each ordered pair corresponds to EXACTLY ________ coordinate plane. The point in the coordinate plane is called the graph of the ordered pair. Locating a point on the coordinate plane is called _______ the ordered pair. The Coordinate Plane An ordered pair of real numbers, called coordinates of a point, locates a point in the coordinate plane. one point in the Each ordered pair corresponds to EXACTLY ________ coordinate plane. The point in the coordinate plane is called the graph of the ordered pair. graphing the ordered pair. Locating a point on the coordinate plane is called _______ The Coordinate Plane An ordered pair of real numbers, called coordinates of a point, locates a point in the coordinate plane. one point in the Each ordered pair corresponds to EXACTLY ________ coordinate plane. The point in the coordinate plane is called the graph of the ordered pair. graphing the ordered pair. Locating a point on the coordinate plane is called _______ Postulate 2 – 4 Completeness Property for Points in the Plane Each point in a coordinate plane corresponds to exactly one __________________________. Each ordered pair of real numbers corresponds to exactly one __________________________. The Coordinate Plane An ordered pair of real numbers, called coordinates of a point, locates a point in the coordinate plane. one point in the Each ordered pair corresponds to EXACTLY ________ coordinate plane. The point in the coordinate plane is called the graph of the ordered pair. graphing the ordered pair. Locating a point on the coordinate plane is called _______ Postulate 2 – 4 Completeness Property for Points in the Plane Each point in a coordinate plane corresponds to exactly one __________________________. ordered pair of real numbers Each ordered pair of real numbers corresponds to exactly one __________________________. The Coordinate Plane An ordered pair of real numbers, called coordinates of a point, locates a point in the coordinate plane. one point in the Each ordered pair corresponds to EXACTLY ________ coordinate plane. The point in the coordinate plane is called the graph of the ordered pair. graphing the ordered pair. Locating a point on the coordinate plane is called _______ Postulate 2 – 4 Completeness Property for Points in the Plane Each point in a coordinate plane corresponds to exactly one __________________________. ordered pair of real numbers Each ordered pair of real numbers corresponds to exactly one point in the coordinate plane __________________________. The Coordinate Plane Graphing an ordered pair, (point): (x, y) Graph point A at (4, 3) y The first number, 4, is called the x-coordinate ___________. 5 4 3 It tells the number of units the point lies to the __________ of the origin. 2 1 x -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 -1 -2 -3 -4 -5 2 3 4 5 The Coordinate Plane Graphing an ordered pair, (point): (x, y) Graph point A at (4, 3) y The first number, 4, is called the x-coordinate ___________. 5 4 3 It tells the number of units the point lies to left or right of the origin. the __________ 2 1 x -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 -1 -2 -3 -4 -5 2 3 4 5 The Coordinate Plane Graphing an ordered pair, (point): (x, y) Graph point A at (4, 3) y The first number, 4, is called the x-coordinate ___________. 5 4 3 It tells the number of units the point lies to left or right of the origin. the __________ 2 1 x -5 The second number, 3, is called the y-coordinate ___________. It tells the number of units the point lies _____________ the origin. -4 -3 -2 -1 1 -1 -2 -3 -4 -5 2 3 4 5 The Coordinate Plane Graphing an ordered pair, (point): (x, y) Graph point A at (4, 3) y The first number, 4, is called the x-coordinate ___________. 5 4 (4, 3) 3 It tells the number of units the point lies to left or right of the origin. the __________ 2 1 x -5 The second number, 3, is called the y-coordinate ___________. It tells the number of units the point lies _____________ above or below the origin. -4 -3 -2 -1 1 -1 -2 -3 -4 -5 2 3 4 5 The Coordinate Plane Graphing an ordered pair, (point): (x, y) Graph point A at (4, 3) y The first number, 4, is called the x-coordinate ___________. 5 4 (4, 3) 3 It tells the number of units the point lies to left or right of the origin. the __________ 2 1 x -5 The second number, 3, is called the y-coordinate ___________. It tells the number of units the point lies _____________ above or below the origin. What is the coordinate of the origin? -4 -3 -2 -1 1 -1 -2 -3 -4 -5 2 3 4 5 The Coordinate Plane Graphing an ordered pair, (point): (x, y) Graph point A at (4, 3) y The first number, 4, is called the x-coordinate ___________. 5 4 (4, 3) 3 It tells the number of units the point lies to left or right of the origin. the __________ 2 (0, 0) 1 x -5 The second number, 3, is called the y-coordinate ___________. It tells the number of units the point lies _____________ above or below the origin. What is the coordinate of the origin? -4 -3 -2 -1 1 -1 -2 -3 -4 -5 2 3 4 5 The Coordinate Plane Graphing an ordered pair, (point): (x, y) Graph point B at (2, –3) y 5 4 3 2 1 x -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 -1 -2 -3 -4 -5 2 3 4 5 The Coordinate Plane Graphing an ordered pair, (point): (x, y) Graph point B at (2, –3) y The first number, 2, is called the x-coordinate ___________. 5 4 3 It tells the number of units the point lies to the __________ of the origin. 2 1 x -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 -1 -2 -3 -4 -5 2 3 4 5 The Coordinate Plane Graphing an ordered pair, (point): (x, y) Graph point B at (2, –3) y The first number, 2, is called the x-coordinate ___________. 5 4 3 It tells the number of units the point lies to left or right of the origin. the __________ 2 1 x -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 -1 -2 -3 -4 -5 2 3 4 5 The Coordinate Plane Graphing an ordered pair, (point): (x, y) Graph point B at (2, –3) y The first number, 2, is called the x-coordinate ___________. 5 4 3 It tells the number of units the point lies to left or right of the origin. the __________ 2 1 x -5 The second number, –3, is called the y-coordinate ___________. It tells the number of units the point lies _____________ the origin. -4 -3 -2 -1 1 -1 -2 -3 -4 -5 2 3 4 5 The Coordinate Plane Graphing an ordered pair, (point): (x, y) Graph point B at (2, –3) y The first number, 2, is called the x-coordinate ___________. 5 4 3 It tells the number of units the point lies to left or right of the origin. the __________ 2 1 x -5 The second number, –3, is called the y-coordinate ___________. It tells the number of units the point lies _____________ above or below the origin. -4 -3 -2 -1 1 2 3 4 -1 -2 -3 -4 -5 (2, –3) 5 The Coordinate Plane Give the coordinates of the points A, B, C, & D y 5 4 3 B Point A(x, y) = A 2 Point B(x, y) = 1 x Point C(x, y) = Point D(x, y) = -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 2 3 4 -1 -2 C -3 -4 -5 D 5 The Coordinate Plane Name the points A, B, C, & D y 5 4 Point A(x, y) = (3, 2) 3 B (–3, 2) 2 Point B(x, y) = (–3, 2) Point C(x, y) = (–3, –2) Point D(x, y) = (3, –2) A (3, 2) 1 x -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 2 3 4 5 -1 -2 C (–3, –2) -3 -4 -5 D (3, –2) The Coordinate Plane On a piece of grid paper draw lines representing the x-axis and the y-axis. y 5 4 Graph : Point A(x, y) = A(2, 4) 3 2 Point B(x, y) = B(2, 0) Point C(x, y) = C(2, –3) 1 x -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 -1 Point D(x, y) = D(2, –5) -2 -3 -4 -5 2 3 4 5 The Coordinate Plane On a piece of grid paper draw lines representing the x-axis and the y-axis. y 5 4 Graph : Point A(x, y) = A(2, 4) 3 2 Point B(x, y) = B(2, 0) Point C(x, y) = C(2, –3) 1 x -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 2 -1 Point D(x, y) = D(2, –5) -2 -3 Consider these questions: -4 -5 x=2 1) What do you notice about the graphs of these points? 3 4 5 The Coordinate Plane On a piece of grid paper draw lines representing the x-axis and the y-axis. y 5 4 Graph : Point A(x, y) = A(2, 4) 3 2 Point B(x, y) = B(2, 0) Point C(x, y) = C(2, –3) 1 x -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 2 -1 Point D(x, y) = D(2, –5) -2 -3 Consider these questions: -4 -5 x=2 1) What do you notice about the graphs of these points? They lie on a vertical line. 3 4 5 The Coordinate Plane On a piece of grid paper draw lines representing the x-axis and the y-axis. y 5 4 Graph : Point A(x, y) = A(2, 4) 3 2 Point B(x, y) = B(2, 0) Point C(x, y) = C(2, –3) 1 x -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 2 -1 Point D(x, y) = D(2, –5) -2 -3 Consider these questions: -4 -5 x=2 1) What do you notice about the graphs of these points? They lie on a vertical line. 2) What do you notice about the x-coordinates of these points? 3 4 5 The Coordinate Plane On a piece of grid paper draw lines representing the x-axis and the y-axis. y 5 4 Graph : Point A(x, y) = A(2, 4) 3 2 Point B(x, y) = B(2, 0) Point C(x, y) = C(2, –3) 1 x -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 2 -1 Point D(x, y) = D(2, –5) -2 -3 Consider these questions: -4 -5 x=2 1) What do you notice about the graphs of these points? They lie on a vertical line. 2) What do you notice about the x-coordinates of these points? They are the same number. 3 4 5 The Coordinate Plane On a piece of grid paper draw lines representing the x-axis and the y-axis. y 5 4 Graph : Point A(x, y) = A(2, 4) 3 2 Point B(x, y) = B(2, 0) Point C(x, y) = C(2, –3) 1 x -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 -1 Point D(x, y) = D(2, –5) -2 -3 -4 -5 Write a general statement about ordered pairs that have the same x-coordinate. 2 3 4 5 The Coordinate Plane On a piece of grid paper draw lines representing the x-axis and the y-axis. y 5 4 Graph : Point A(x, y) = A(2, 4) 3 2 Point B(x, y) = B(2, 0) Point C(x, y) = C(2, –3) 1 x -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 2 -1 Point D(x, y) = D(2, –5) -2 -3 -4 -5 x=2 Write a general statement about ordered pairs that have the same x-coordinate. 3 4 5 The Coordinate Plane On the same coordinate plane y 5 4 Graph : Point W(x, y) = W(–4, –4) 3 2 Point X(x, y) = X(–2, –4) Point Y(x, y) = Y(0, –4) 1 x -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 -1 Point Z(x, y) = Z(3, –4) -2 -3 -4 -5 2 3 4 5 The Coordinate Plane On the same coordinate plane y 5 4 Graph : Point W(x, y) = W(–4, –4) 3 2 Point X(x, y) = X(–2, –4) Point Y(x, y) = Y(0, –4) 1 x -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 -1 Point Z(x, y) = Z(3, –4) -2 -3 -4 -5 2 3 4 5 The Coordinate Plane On the same coordinate plane y 5 4 Graph : Point W(x, y) = W(–4, –4) 3 2 Point X(x, y) = X(–2, –4) Point Y(x, y) = Y(0, –4) 1 x -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 -1 Point Z(x, y) = Z(3, –4) -2 -3 Consider these questions: 1) What do you notice about the graphs of these points? -4 -5 2 3 4 5 The Coordinate Plane On the same coordinate plane y 5 4 Graph : Point W(x, y) = W(–4, –4) 3 2 Point X(x, y) = X(–2, –4) Point Y(x, y) = Y(0, –4) 1 x -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 -1 Point Z(x, y) = Z(3, –4) -2 -3 Consider these questions: 1) What do you notice about the graphs of these points? They lie on a horizontal line. -4 -5 2 3 4 5 The Coordinate Plane On the same coordinate plane y 5 4 Graph : Point W(x, y) = W(–4, –4) 3 2 Point X(x, y) = X(–2, –4) Point Y(x, y) = Y(0, –4) 1 x -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 -1 Point Z(x, y) = Z(3, –4) -2 -3 Consider these questions: -4 -5 1) What do you notice about the graphs of these points? They lie on a horizontal line. 2) What do you notice about the y-coordinates of these points? 2 3 4 5 The Coordinate Plane On the same coordinate plane y 5 4 Graph : Point W(x, y) = W(–4, –4) 3 2 Point X(x, y) = X(–2, –4) Point Y(x, y) = Y(0, –4) 1 x -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 -1 Point Z(x, y) = Z(3, –4) -2 -3 Consider these questions: -4 -5 1) What do you notice about the graphs of these points? They lie on a horizontal line. 2) What do you notice about the y-coordinates of these points? They are the same number. 2 3 4 5 The Coordinate Plane On the same coordinate plane y 5 4 Graph : Point W(x, y) = W(–4, –4) 3 2 Point X(x, y) = X(–2, –4) Point Y(x, y) = Y(0, –4) 1 x -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 -1 Point Z(x, y) = Z(3, –4) -2 -3 -4 -5 Write a general statement about ordered pairs that have the same y-coordinate. 2 3 4 5 The Coordinate Plane On the same coordinate plane y 5 4 Graph : Point W(x, y) = W(–4, –4) 3 2 Point X(x, y) = X(–2, –4) 1 Point Y(x, y) = Y(0, –4) x -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 -1 Point Z(x, y) = Z(3, –4) -2 -3 y=–4 -4 -5 Write a general statement about ordered pairs that have the same y-coordinate. 2 3 4 5 The Coordinate Plane If a and b are real numbers, a vertical line contains all points (x, y) such that _____ Theorem 2 – 4 and a horizontal line contains all points (x, y) such that _____ The Coordinate Plane If a and b are real numbers, a vertical line contains all points (x, y) such that _____ x=a Theorem 2 – 4 and y=b a horizontal line contains all points (x, y) such that _____ The Coordinate Plane If a and b are real numbers, a vertical line contains all points (x, y) such that _____ x=a Theorem 2 – 4 and y=b a horizontal line contains all points (x, y) such that _____ y Graph the lines: x = –3 5 4 3 2 1 x -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 -1 -2 -3 -4 -5 2 3 4 5 The Coordinate Plane If a and b are real numbers, a vertical line contains all points (x, y) such that _____ x=a Theorem 2 – 4 and y=b a horizontal line contains all points (x, y) such that _____ y Graph the lines: x = –3 5 4 3 2 1 x -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 -1 -2 -3 -4 -5 2 3 4 5 The Coordinate Plane If a and b are real numbers, a vertical line contains all points (x, y) such that _____ x=a Theorem 2 – 4 and y=b a horizontal line contains all points (x, y) such that _____ y Graph the lines: x = –3 5 4 y=2 3 2 1 x -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 -1 -2 -3 -4 -5 2 3 4 5 The Coordinate Plane If a and b are real numbers, a vertical line contains all points (x, y) such that _____ x=a Theorem 2 – 4 and y=b a horizontal line contains all points (x, y) such that _____ y Graph the lines: x = –3 5 4 y=2 3 2 1 x -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 -1 -2 -3 -4 -5 2 3 4 5 The Coordinate Plane If a and b are real numbers, a vertical line contains all points (x, y) such that _____ x=a Theorem 2 – 4 and y=b a horizontal line contains all points (x, y) such that _____ y Graph the lines: x = –3 5 4 y=2 3 2 1 Graph the point of intersection of these lines. x -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 -1 -2 -3 -4 -5 2 3 4 5 The Coordinate Plane If a and b are real numbers, a vertical line contains all points (x, y) such that _____ x=a Theorem 2 – 4 and y=b a horizontal line contains all points (x, y) such that _____ y Graph the lines: x = –3 y=2 5 4 (–3, 2) 3 2 1 Graph the point of intersection of these lines. x -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 -1 -2 -3 -4 -5 2 3 4 5 The Coordinate Plane