The Costs of Taxation
advertisement

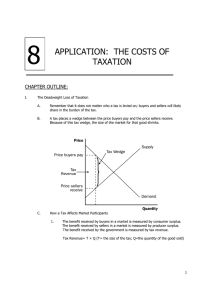
THE COSTS OF TAXATION MR. BARNETT UNIVERSITY HIGH AP MICROECONOMICS DEADWEIGHT LOSS OF TAXATION How a tax affects market participants Drives a wedge between the price that the buyer pays and the price the sellers receives DEADWEIGHT LOSS We can measure the effects of a tax On consumers by examining the change in consumer surplus On suppliers by looking at the change in producer surplus What about he government! Gov’t is 3rd party and receives benefit from tax Gets total revenue of T x Q Taxes help pay for roads, police, firefighters, etc DEADWEIGHT LOSS Welfare without a tax Consumer surplus is equal to: Producer surplus is equal to: Total surplus is equal to: Welfare with a tax Consumer surplus is equal to: Producer surplus is equal to: Tax revenue is equal to: Total surplus is equal to: Changes in Welfare Consumer surplus changes by: Producer surplus changes by: Tax revenue changes by: Total surplus changes by: DEADWEIGHT LOSS Deadweight Loss: The fall in total surplus that results from a market distortion, such as a tax. Taxes cause deadweight losses because they prevent buyers and sellers from benefiting from trade Why does this occur? Because quantity decreases! Many beneficial trades for buyers and sellers will not take place b/c of tax DETERMINANTS OF DEADWEIGHT LOSS • The price elasticities of supply and demand determine size of deadweight loss from a tax • The greater the elasticities of supply and demand, the greater the deadweight loss due to a tax SOCIAL SECURITY TAX & FEDERAL INCOME TAX • Case Study • Taxes on labor earnings • As tax increases, deadweight loss rises more quickly than size of tax • Level of tax revenue will eventually fall LAFFER CURVE SUPPLY SIDE ECONOMICS • Economic theory that says lowering barriers in the market will result in lower prices for consumers with an increased supply of goods and services • Adopted by Reagan as part of Reaganomics • Believed US was on right side of Laffer Curve • Claimed that lower tax rates would result in an increase of government tax revenue • Marginal tax rate reduced from 71% to 31% • Tax revenue did increase from 1980 ($885B) to 1990 ($1.93T) • Controversial