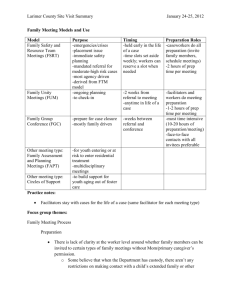
models - University of Delaware
advertisement
Models for Problem-Based Learning Institute for Transforming Undergraduate Education University of Delaware Factors in Choosing a Model Class size Intellectual maturity of students Student motivation Course learning objectives Instructor’s preferences Availability of peer facilitators Common Classroom Models • • • • Medical school Floating Facilitator Peer Facilitator “Hybrid” Medical School Model • • • • Dedicated faculty tutor Groups of 8-10 Very student-centered environment Group discussion is primary class activity A good choice for • Highly motivated, experienced learners • Small, upper-level seminar classes Floating Facilitator Model • Instructor moves from group to group – Asks questions, directs discussions, checks understanding • Group size: 4 • More structured format: greater degree of instructor input into learning issues and resources Floating Facilitator Model Other class activities: – Groups report out – Whole class discussions – (Mini-)lectures A good choice for • Less experienced learners • Classes of all sizes Peer Facilitator Model Advanced undergraduates serve as facilitators – Help monitor group progress and dynamics – Serve as role models for novice learners – Capstone experience for student facilitators A good choice for • Classes of all sizes Dealing with Large Classes Floating facilitator or peer facilitator models are the most appropriate. Requires a more teacher-centered, structured format: instructor directs group activities Group size: 4 Reduce grading burden through group (vs. individual) papers, projects “Hybrid” PBL • Non-exclusive use of problem-driven learning in a class • May include separate lecture segments or other activelearning components • Floating or peer facilitator models common Often used as entry point into PBL in course transformation process A Sampler: ITUE Leaders’ PBL Courses Small Classes (< 30 students) – – – – General Chemistry Introductory Biology, General Physiology Introduction to Biochemistry Biochemical Evolution, Intermediary Metabolism A Sampler: ITUE Leaders’ PBL Courses • Medium-Large Classes (40-120 students) – – – – Problems of the Criminal Judiciary Psychology and the Law Physical Science “Science Semester” for elem. education majors Small Course Characteristics Model Student type (year/major) General Chem (H) Floating facilitator FR Science (not chem) Intro Biology (H) Peer FR/SO facilitators Science, allied health Peer SO/JR General Physiology(H) facilitators Biology % PBL Grp #,(size) Comments 40-50 4-5, (4) Mixed with lecture, demos, other activities 85-90 4-5, (4-6) 6-7 PBL problems per semester 85-90 4-5, (4-6) 6-7 PBL problems per semester Intro to Biochemistry Peer SO facilitators BIOC majors 100 5-8, (4) Uses scientific articles as problems Intermediary Metabolism Floating facilitator SR, GRAD Majors 100 3, (3-6) Progressive disclosure (staged) problems Biochemical Evolution Floating facilitator SR, GRAD Majors 100 3, (3-5) Case study problems Typical PBL Sequence: Gen. Chem. Problems are used to introduce concepts: no prior discussion of concepts in class. Guiding questions are used to focus learning. Groups work in class (texts); meet to finish outside before next class meeting. Groups report out ,typically via overheads. Summaries are prepared from or based on reports. Problem is followed by fuller discussion of related issues, connections to earlier work How Class Time is Used: Gen Chem. Percent of PBL Class Time CHEM 104H 03S 100% 90% 80% 70% 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% 10% 0% 1 4 7 10 13 16 19 22 25 28 31 34 37 40 class number Medium-Large Course Features Model Student type (year/major) FR/SO Prob. Crim. Floating facilitators Majors and Judiciary % PBL Grp.#, (size) Comments 25-33% 25, (4-6) TA’s assist as facilitators Mix w/ lecture, other activities nonmajors Psych and the Law Floating JR/SR facilitators PSYC, CRJU 50% 10, (4) TA’s assist as facilitators Mix w/ lecture, other activities Physical Science Floating All levels facilitators Gen. Ed. course 60% 34, (4) TA’s assist as facilitators Large auditorium/fixed seats “Science Semester” Floating SO facilitators Elem. Ed. 60% 12, (5) Multiple instructors Meets in Gore 208 120 min sessions, 5 days/week Large Physical Science vs Small Physics for Gen. Ed. for Pre-meds • • • • • 120 students auditorium/fixed seats permanent groups, 3-5 problems initiated in large class group discussion, lecture • learning issues addressed in large class and discussion • multiple choice/show work exams • 3 projects related to problems • • • • fewer than 30 students round tables/chairs permanent groups of 4 problems initiated in class • more group oriented discussion than whole class activity or lecture • learning issues addressed mainly in groups • individual and group “show your work” • one large project “Science Semester” An integrated science and teaching methods course for future teachers: combines biology, physical science, geology and science methods •PBL is central focus of 4 curricular units: integrated with active learning and lecture •Session times: 120 min, 5 days/week. •Large class (60) and 3 smaller (20) discussion sections •Multiple instructors as facilitators and discussion leaders Activities in “Science Semester” • Research vessel experience • Assessment strategies: – Group, individual testing – Web pages – PowerPoint presentations to community experts – Letter to editor – Poster presentations – Concept maps – Micro-teaching