Cisco Packet Tracer - Victor Tikhonov website
advertisement

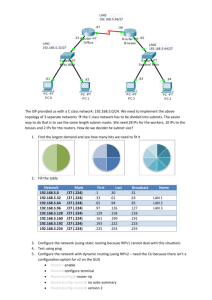
1 Lab-1-Packet Tracer: Cisco Router Configuring Tab.1− Packet Tracer routing table Router# - console invitation ip route – command to show route table 10.0.0.0 ÷ 10.0.0.7 – inter router connections Gateway of last resort (шлюз последней надежды) 10.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 8 subnets C – connected directly O – OSPF Fast Ethernet 1/0 ÷ Fast Ethernet 7/0 – interface numbers via 10.0.0.1 – gateway address [110/2] – AD/in-hop metrics 00.48.29 – h/m/s – time of last modifying Tab.2− The 4-th octet of the Network Addresses 4-th octet: Binary Digit Number 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Decimal Value Weight NW1 NW2 NW3 NW4 NW5 NW6 NW7 NW8 NW0 1 2 4 8 16 32 64 128 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 16 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 32 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 48 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 64 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 80 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 96 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 112 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 NW0-Ad=192.168.0.0/25 SW1 PC1 SW2 NW1 NW5 1 192.168.1.2 R1 2 2 3 R4 SW4 NW6 3 R3 2 1 PC2 192.168.18. 2 3 Core network NW8 1 R2 3 NW2 NW7 2 1 SW3 NW4 NW3 PC3 PC4 192.168.1.34 192.168.1.50 Fig.1− Network topology Tab.3− Network design table Tab.1− Packet Tracer routing table ID NW1 NW2 NW3 NW4 NW5 NW6 NW7 NW8 R1-1 R1-2 R1-3 R2-1 R2-2 R2-3 R3-1 R3-2 R3-3 R4-1 R4-2 R4-3 NW0 Fa9/0 Fa0/0 Fa1/0 Fa9/0 Fa0/0 Fa1/0 Fa9/0 Fa0/0 Fa1/0 Fa9/0 Fa0/0 Fa1/0 IP Address 192.168.1.0 192.168.1.16 192.168.1.32 192.168.1.48 192.168.1.64 192.168.1.80 192.168.1.96 192.168.1.112 192.168.1.1 192.168.1.65 192.168.1.113 192.168.1.17 192.168.1.66 192.168.1.81 192.168.1.33 192.168.1.97 192.168.1.82 192.168.1.49 192.168.1.98 192.168.1.114 192.168.1.0 /Mask /28 −“− −“− −“− −“− −“− −“− −“− −“− −“− −“− −“− −“− −“− −“− −“− −“− −“− −“− −“− /25 A/Mask 255.255.255.240 −“− −“− −“− −“− −“− −“− −“− −“− −“− −“− −“− −“− −“− −“− −“− −“− −“− −“− −“− 255.255.255.128 Host Interface Addresses 192.168.1.2−192.168.1.14 192.168.1.18−192.168.1.30 192.168.1.34−192.168.1.46 192.168.1.50−192.168.1.62 − − − − − − − − − − − − − − − − − Broadcast Address 192.168.1.15 192.168.1.31 192.168.1.47 192.168.1.63 192.168.1.79 192.168.1.95 192.168.1.111 192.168.1.127 − − − − − − − − − − − − 192.168.1.127 3 Configuring the network routers scenario Router>enable Router#configure terminal Router(config)#router rip Router(config-router)#network 192.168.1.0 Router(config-router)#network …………… Router(config-router)#network …………… Router(config-router)#version 2 (use RIP2) Router(config-router)#exit (exit of the RIP configuring mode) Router(config)#exit (exit of the configuring console) Enter Router#write memory (save settings in memory) Building configuration... [OK] R1 Routing Table: Enter Router> enable Router#show ip route Gateway of last resort is not set 192.168.1.0/28 is subnetted, 8 subnets C 192.168.1.0 is directly connected, FastEthernet9/0 R 192.168.1.16 [120/1] via 192.168.1.66, 00:00:23, FastEthernet0/0 R 192.168.1.32 [120/2] via 192.168.1.66, 00:00:23, FastEthernet0/0 R 192.168.1.48 [120/3] via 192.168.1.66, 00:00:23, FastEthernet0/0 C 192.168.1.64 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0 R 192.168.1.80 [120/1] via 192.168.1.66, 00:00:23, FastEthernet0/0 R 192.168.1.96 [120/2] via 192.168.1.66, 00:00:23, FastEthernet0/0 C 192.168.1.112 is directly connected, FastEthernet1/0 Router# Pinging Test Focuse PC1 – run – PC2 – run – PC3 – run – PC4 – run – ping 192.168.1.18, ping 192.168.1.__ , ping 192.168.1.__ , ping 192.168.1.__ , ping 192.168.1. 34, ping 192.168.1. __, ping 192.168.1. __, ping 192.168.1. __, ping 192.168.1.50 ping 192.168.1.__ ping 192.168.1.__ ping 192.168.1.__ 4 Lab.1 Job 1. Start the PT application: Cisco Packet Tracer 2. Examine the lower left corner menu box: Routers, End Devices Switches, WAN emulation Hubs, Custom made devices Connections Multiuser connection 3. Construct the network comprising 4 routers (Generic type), 4 switches (Generic type), 4 personal computers (Generic type). Be aware!!! 3.1 Use connections of “Copper Cross-over” type (continuous line) to connect any two routers. Instead, Use connections of “Copper Straight-Through” type (dropped line) to connect any routers to the PC. 3.2. Routers have default solely two interfaces, though you are to complete any router with additional interface. To do that: − click the chosen router; − push the right edge of the window until the router circuit breaker is visible; − switch off the router circuit breaker; − choose the copper fast Ethernet interface (PT-Router NM-1CFE); − drug chosen interface into the free lot of the router rack unit; − switch on the router circuit breaker again. 4. Preinstall in static mode (manually) all the router interfaces: − click the chosen router config; − choose the interface (e.g. Fast Ethernet0/0, Fast Ethernet0/1, Fast Ethernet0/9); − input IP-address and Masks in accordance to the Table 1 (e.g. 192.168.1.1, 255.255.255.240); − make port status “on”; − repeat all the previous steps for all the router interfaces and all the routers. 5. Preinstall in static mode (manually) all the PC interfaces: − click the chosen PC config; Fast Ethernet0; − input IP-address and Masks in accordance to the Table 1 (e.g. 192.168.1.2, 255.255.255.240); − make port status “on”; − input Gateway IP-address in accordance to the Table 1: − click the chosen PC config; Settings (e.g. 192.168.1.1); − repeat all the previous steps for all the PCs. 6. Configure all the routers (apply RIP and Join all the neighbor networks using the command line interface CLI): − click the chosen Router (e.g. for the R1) CLI: Router>enable Router#configure terminal Router(config)#router rip Router(config-router)#network 192.168.1.0 Router(config-router)#network 192.168.1.64 Router(config-router)#network 192.168.1.112 Router(config-router)#version 2 (use RIP2) Router(config-router)#exit (exit of the RIP configuring mode) Router(config)#exit (exit of the configuring console) Enter Router#write memory (save settings in memory) Building configuration... [OK] 7. Apply Ping Test for all the PCs (e.g. for the PC1) to verify your network Focuse PC1 – run – ping 192.168.1.18, ping 192.168.1. 34, 8. Present your results to your master and get Lab1 credit. ping 192.168.1.50