Chapter 1 Gateway 2 - GE-sec3
advertisement

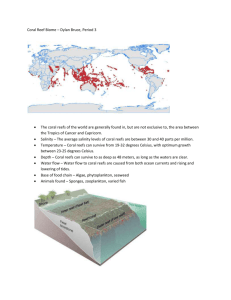
CHAPTER 1 COASTS Should Coastal Environments Matter? CHAPTER 1 COASTS Should Coastal Environments Matter? In this Chapter, you will explore three key questions: 1.How and why are coastal environments different and dynamic? 2.Why are coastal areas valuable? 3.How can we manage coastal areas in a sustainable manner? CHECK-IN: The Coral Triangle The Coral Triangle spans an area of 6 million square kilometres . It consists of countries such as Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Papua New Guinea, Timor Leste and the Solomon Islands. 76 per cent of the world’s coral species, 6 out of 7 of the world’s marine turtle species, and at least 2,228 reef fish species live in this area. Why is the Coral Triangle important? The Coral Triangle region is unique not only because of its wildlife and marine and coastal ecosystems, but also for the benefits the local communities and governments can gain from the area. Consider this: •120 million people are directly sustained by the marine and coastal resources of the Coral Triangle •US$2.4 billion is the amount that fisheries in Southeast Asia make from making use of the coral reef ecosystem •US$12 billion is the size of the Coral Triangle nature-based tourism industry CHAPTER 1 COASTS Should Coastal Environments Matter? Gateway 2: Why are coastal areas valuable? a. b. c. How do coastal ecosystems provide services to people? How do people make use of coastal ecosystems for their own benefit? What is the value of mangrove & coral reef ecosystems? What are the pressures on them? What are coastal ecosystems? Previously you learnt about… Different and dynamic coastal environments and coastal processes which shape coastal landforms. Within these coastal environments are plant and animal communities which interact with each other and make up the coastal ecosystem. Types of coastal ecosystems Mangroves Coral reef a. How do coastal ecosystems provide services to people? Services Natural resources (products) Regulate/Stabilise shoreline Cultural services Supporting other ecosystems a. How do coastal ecosystems provide services to people? Provisioning services (natural products) Fish • Source of seafood • Source of income Water • Sheltered harbours for boats/trading vessels • Converted into electrical energy Wave energy Mangrove wood Corals • Used build boats & houses • Converted to charcoal • Converted into ornaments • Used to make cement a. How do coastal ecosystems provide services to people? Regulating services •Watch: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9jni98YDvf8 •How do you think mangroves help the people living behind it? a. How do coastal ecosystems provide services to people? Regulating services •Stabilisation of shoreline: – coral reef and mangroves as a natural barrier reduces wave energy impact on shoreline / reduces shoreline erosion •Coastal flood prevention: – wide beaches, sand dunes and wetlands disperse water / act as a barrier / can contain large amount of water •Protection from natural hazards (storms, typhoons, tsunamis): – mangroves absorb wave energy and buffer the impact of storms a. How do coastal ecosystems provide services to people? A Cultural services B C a. How do coastal ecosystems provide services to people? Supporting services •They support other ecosystems so that their value to people increases Mangroves Beach Habitat, nursery, breeding ground Habitat, nursery, breeding ground Root network offers protection Source of food CHAPTER 1 COASTS Should Coastal Environments Matter? Gateway 2: Why are coastal areas valuable? a. b. c. How do coastal ecosystems provide services to people? How do people make use of coastal ecosystems for their own benefit? What is the value of mangrove & coral reef ecosystems? What are the pressures on them? b. How do people make use of coastal ecosystems for their own benefit? b. How do people make use of coastal ecosystems for their own benefit? • Fish farming takes place in cages and ponds close to coasts • What do the top 6 aquaculture producers have in common? b. How do people make use of coastal ecosystems for their own benefit? Ca Mau, Vietnam – shrimp production • Coastal mangroves which are waterlogged are favourable for shrimp production – therefore cleared for shrimp farms – What are the effects of this action? • Mud and concrete ponds have replaced the mangrove shrimp ponds • New alternative: organic shrimp farming must grow in mangrove forest & in a balanced ecosystem b. How do people make use of coastal ecosystems for their own benefit? • Coastal area used to build houses • Water as a means of transport • Kukup, Malaysia – stilt house communities b. How do people make use of coastal ecosystems for their own benefit? Kukup, Malaysia •Stilt house communities – Air Masin, a village within Kukup with a community of 180 stilt houses – Two modes of transport: boats (used by local fisherman) and scheduled ferry services (used by visitors) b. How do people make use of coastal ecosystems for their own benefit? • What are some recreational and tourism activities and amenities that can be found along the coastline? b. How do people make use of coastal ecosystems for their own benefit? Sentosa, Singapore – a resort island •Holds two golf courses, a marina (for boats and yachts), a residential area, and an integrated resort CHAPTER 1 COASTS Should Coastal Environments Matter? Gateway 2: Why are coastal areas valuable? a. b. c. How do coastal ecosystems provide services to people? How do people make use of coastal ecosystems for their own benefit? What is the value of mangrove & coral reef ecosystems? What are the pressures on them? c. What is the value of mangrove & coral reef ecosystems? What are the pressures on them? • What are coral reefs / mangroves? • Where are coral reefs / mangroves found? (distribution) • What environmental conditions are essential for their growth? • What is the value of coral reefs / mangroves? • How are coral reefs / mangroves threatened? (pressures on them) c. What is the value of mangrove & coral reef ecosystems? What are the pressures on them? • What are coral reefs / mangroves? Coral reefs Mangroves c. What is the value of mangrove & coral reef ecosystems? What are the pressures on them? • What are coral reefs / mangroves? Coral reefs Mangroves Made up of millions of polyps which leave limestone skeletons when they die Provide microscopic algae with nutrients and CO2 Salt-tolerant tropical / subtropical plants Found below sea level / on seabed Found on sheltered coasts / tidal mud Habitat to many plants and animals c. What is the value of mangrove & coral reef ecosystems? What are the pressures on them? • What are coral reefs / mangroves? • Where are coral reefs / mangroves found? (distribution) • What environmental conditions are essential for their growth? • What is the value of coral reefs / mangroves? • How are coral reefs / mangroves threatened? (pressures on them) c. What is the value of mangrove & coral reef ecosystems? What are the pressures on them? • Where are coral reefs / mangroves found (distribution)? What is the distribution of coral reefs around the world? 5.40% 2.50% Asia and Pacific region Africa 7.10% 7.50% Europe 77.50% Latin America and Caribbean North America c. What is the value of mangrove & coral reef ecosystems? What are the pressures on them? • Where are coral reefs / mangroves found (distribution)? What is the distribution of mangroves around the world? c. What is the value of mangrove & coral reef ecosystems? What are the pressures on them? • Where are coral reefs / mangroves found (distribution)? Coral reef Between Tropic of Cancer and Tropic of Capricorn Mangroves Along coasts of countries between Tropic of Cancer and Tropic of Capricorn Concentrated in Southeast Asia Tropical coastlines: Malay Peninsula, Borneo, northern Australia c. What is the value of mangrove & coral reef ecosystems? What are the pressures on them? • What are coral reefs / mangroves? • Where are coral reefs / mangroves found? (distribution) • What environmental conditions are essential for their growth? • What is the value of coral reefs / mangroves? • How are coral reefs / mangroves threatened? (pressures on them) c. What is the value of mangrove & coral reef ecosystems? What are the pressures on them? • What environmental conditions are essential for their growth? • What is the main reason for coral loss? • What does microscopic algae do for the coral? • What factor is essential/vital for coral reef to survive? • Watch:http://www.youtube.com/watch?=liG_ZV 289VM c. What is the value of mangrove & coral reef ecosystems? What are the pressures on them? • What environmental conditions are essential for their growth? Coral reef Mangroves Wave action – destructive waves destroy corals Low energy waves Sediments suffocate corals Adaptive mangrove features – aerial and strong roots Saline environment – high salt content Average salinity Clear water to allow sunlight to Muddy waterlogged land penetrate / low turbidity to reduce murkiness Temperature must be ideal c. What is the value of mangrove & coral reef ecosystems? What are the pressures on them? • What are coral reefs / mangroves? • Where are coral reefs / mangroves found? (distribution) • What environmental conditions are essential for their growth? • What is the value of coral reefs / mangroves? • How are coral reefs / mangroves threatened? (pressures on them) c. What is the value of mangrove & coral reef ecosystems? What are the pressures on them? • What is the value of coral reefs / mangroves? • Why do fishermen clear mangroves? • Why is it important to restore the mangroves for the community highlighted in the video? http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5n8wF_H N6m0&feature=results_video&playnext=1&lis t=PL8816A31ED654E195 c. What is the value of mangrove & coral reef ecosystems? What are the pressures on them? • What is the value of coral reefs / mangroves? Coral reef Mangroves Habitat to many species of marine life Filters sediments washed down by rivers onto coasts Protect land mass from coastal erosion from storms and typhoons Protect coastal areas from erosion by storm waves Nearby land areas developed as tourist attractions Breeding ground and habitat for a range of marine creatures Corals used as souvenirs Wood for fuel and construction c. What is the value of mangrove & coral reef ecosystems? What are the pressures on them? • What are coral reefs / mangroves? • Where are coral reefs / mangroves found? (distribution) • What environmental conditions are essential for their growth? • What is the value of coral reefs / mangroves? • How are coral reefs / mangroves threatened? (pressures on them) c. What is the value of mangrove & coral reef ecosystems? What are the pressures on them? • How are coral reefs / mangroves threatened (pressures on them)? • Human activities • Natural processes What are some causes of destruction of coral reefs? c. What is the value of mangrove & coral reef ecosystems? What are the pressures on them? • How are coral reefs / mangroves threatened (pressures on them)? What are some causes of destruction of mangrove forests? c. What is the value of mangrove & coral reef ecosystems? What are the pressures on them? • How are coral reefs / mangroves threatened (pressures on them)? What are some causes of destruction of mangrove forests? Tropical Mangroves under Threat in Thailand Mangrove forests are currently among the most threatened habitats in the world and are disappearing at an accelerated rate. The exposed portions of mangrove roots are highly susceptible to clogging by crude oil and other pollutants. Organic wastes (sewage), toxic minerals (heavy metals), organic chemicals (pesticides and herbicides) suffocate the underwater sections of mangrove. These poisons also become concentrate within the cellular structure of the plants. Over time, these environmental stresses can kill large numbers of mangrove trees. In addition, the charcoal and timber industries have also severely impacted mangrove forests, as well as the developing tourism industry and other coastal developments. Finally, the rapidly expanding shrimp aquaculture industry poses a threat to the world's remaining mangroves. It has been estimated that thousands of hectares of mangrove forests have been cleared to make room for artificial shrimp ponds. c. What is the value of mangrove & coral reef ecosystems? What are the pressures on them? • How are coral reefs / mangroves threatened (pressures on them)? What are some causes of destruction of mangrove forests? Tropical Mangroves under Threat in Thailand Mangrove forests are currently among the most threatened habitats in the world and are disappearing at an accelerated rate. The exposed portions of mangrove roots are highly susceptible to clogging by crude oil and other pollutants. Organic wastes (sewage), toxic minerals (heavy metals), organic chemicals (pesticides and herbicides) suffocate the underwater sections of mangrove. These poisons also become concentrate within the cellular structure of the plants. Over time, these environmental stresses can kill large numbers of mangrove trees. In addition, the charcoal and timber industries have also severely impacted mangrove forests, as well as the developing tourism industry and other coastal developments. Finally, the rapidly expanding shrimp aquaculture industry poses a threat to the world's remaining mangroves. It has been estimated that thousands of hectares of mangrove forests have been cleared to make room for artificial shrimp ponds. CHAPTER 1 COASTS Should Coastal Environments Matter? Gateway 2: Why are coastal areas valuable? a. b. c. How do coastal ecosystems provide services to people? How do people make use of coastal ecosystems for their own benefit? What is the value of mangrove & coral reef ecosystems? What are the pressures on them?