Earth Science: Plate Tectonics
advertisement

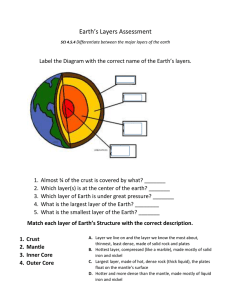
Earth Science: Plate Tectonics How do we see inside the Earth? • Waves • Seismic waves • Seismology – Study & measurement of seismic waves • What do we know that produces seismic waves? Two main types of waves • “P” Waves • “S” waves P-waves “P” or Primary waves – – – – Longitudinal Compress and expand Fastest Travel through all mediums ( solid, liquid and air) “S” Waves • “S” or Secondary waves – – – – Transverse Vibrate up and down / side to side Slower than “P” waves Only travel through solids Layers of the Earth The Crust • • • • • • Surface layer Like an eggshell Thin Brittle Can crack Two regions: – Oceanic (Basalt rock) – Continental (granite rock) • • Crust is less dense than the mantle Like ice on water; the crust floats on the mantle The Mantle The Mantle • • • • • • • Rocky Like the crust Silicon Oxygen Iron, magnesium, calcium are heavier elements Mantle is denser How does the Earth’s crust add to the density of the mantle? • Weight bearing down on the mantle…it compresses the minerals, increasing the pressure and squeezing them into rocks. The Mantle • • • • Higher temperature Why? Increased pressure Decay of radioactive elements Layers of The Mantle • Upper mantle • Lithosphere – Rigid rock upper portion of upper mantle • Asthenosphere – Lies beneath lithosphere and “flows” like plastic – It is solid…silly putty • Lower mantle The Core • Two layers: inner and outer core • 15% Earth’s volume • 30% Earth’s mass • 2x as dense as the Earth’s mantle • Why? • Made of metallic iron • Inner core is VERY hot! • Some places as hot as the surface of the sun! The Inner Core • Solid Iron – How? – Pressure from Earth keeps Iron packed tightly; doesn’t allow it’s atoms to flow The Outer Core • Outer Core – Liquid Iron – Less pressure – Flows and spins as Earth rotates – Creates convection currents – Affects Earth’s surface – Produces electrical charge – Possibly responsible for Earth’s magnetic field Magnetosphere Convection Currents • What are convection currents? • Current of heat flows from core to crust • This sets up a convection current in the mantle Effects of Convection Currents • When the current comes at a weaker part of the crust, for example at a volcano, magma comes above the earth's surface. • This is called plate tectonics. • The movement of these plates goes very slowly. • The bumping of two tectonic plates causes an earthquake. • The convection current along the bottom of the crust causes the moving of the tectonic plates. Continental Drift & Tectonic Plates • Wegner’s Hypothesis on Continental Drift • The World’s continents are in motion • At one time, the continents were joined together as one… • This was known as Pangea • They fit together like a jigsaw puzzle What caused the continents to separate? Continental Drift • Wegner’s theory that proposed the landmass known as Pangea started breaking up • Separated into two parts: Laurasia and Gondwanaland • Wegner’s theory of the separation of Pangea was supported by fossil, biological, climatological and geological evidence Seafloor Spreading • Seafloor is not permanent • Constantly renewing itself • Mid Atlantic Ridge (longest & tallest mountain range in the world, center of the Atlantic Ocean) • Forms islands: Iceland and Azore • There are rifts in the mountains Plate tectonics • Continents move because they are embedded in plates • The plates shuffle or move atop of the Earth’s surface • Plates move in different directions and different speeds from each other • There are nine large plates and several smaller plates Plate Boundaries • Divergent Boundaries • Plates move away from each other • Comes from rock in athenosphere • Partially melted • The rock partially melts = lava • It was magma before it left the surface of the Earth Convergent boundaries • Plates move toward each other Transform fault boundaries • Plates slide past each other Earthquakes • • • • Devastating Stress (force) applied to rock Stress causes strain Eventually the rock cannot bend anymore • It breaks and releases stored energy • The released energy ( Seismic Waves) travel out in all directions Earthquakes cont • The initiating site of the seismic wave: focus • The point at Earth’s surface directly above the focus: epicenter • Measured on a Richter Scale ( the incraments are ten fold in magnitude… Tsunami • Seismic sea wave • Created by an earthquake