Unit 1 PPT on History and Approaches of Psychology
advertisement

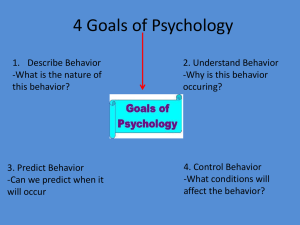
DO FIRST 1. Put either your homework or your demerit card on your desk 2. Have out ONLY a pencil and a red pen when the bell rings. 3. You will have 6 minutes for the reading quiz (surprise!) QUIZ PROCEDURES 1. Get the quiz from your table’s folder. 2. Dominate the quiz, keeping your answers covered at all times, or I will recycle your work. 3. Pass your quizzes to the right, and write “graded by: ________” at the top. 4. Mark the answers right or wrong. 5. Circle the number they got CORRECT at the top of the quiz. 6. Return quiz to folder for teacher to pick up. 5 TRADITIONS 1. Structuralism 2. Functionalism 3. Behaviorism 4. Gestalt Psychology 5. Psychoanalysis Who were the major players? What were their core beliefs? What were they asking? What are some key terms? 4 BEHAVIORISM Wait wait wait… If we can’t SEE the conscious mind, how the HECK are we supposed to study it? What’s that you say? By DIRECTLY OBSERVING BEHAVIOR??? Sounds familiar… Class? Behaviorists are asking: • How does one acquire behavior? • How is that behavior changed in response to outside influences? I. IVAN PAVLOV Pavlov’s Dog JOHN B. WATSON 7 B. F. SKINNER 8 5 Traditions – TEACH YOUR NEIGHBOR! 1. Structuralism 2. Functionalism 3. Behaviorism 4. Gestalt Psychology 5. Psychoanalysis Who were the major players? What were their core beliefs? What were they asking? What are some key terms? 9 5 TRADITIONS 1. Structuralism 2. Functionalism 3. Behaviorism 4. Gestalt Psychology 5. Psychoanalysis Who were the major players? What were their core beliefs? What were they asking? What are some key terms? 10 GESTALT PSYCHOLOGY Asked the question: • How can we study the conscious mind holistically?? 11 MAX WERTHEIMER (1880-1943) 5 Traditions – TEACH YOUR NEIGHBOR! 1. Structuralism 2. Functionalism 3. Behaviorism 4. Gestalt Psychology 5. Psychoanalysis Who were the major players? What were their core beliefs? What were they asking? What are some key terms? 13 5 TRADITIONS 1. Structuralism 2. Functionalism 3. Behaviorism 4. Gestalt Psychology 5. Psychoanalysis Who were the major players? What were their core beliefs? What were they asking? What are some key terms? 14 PSYCHOANALYSIS The unconscious mind is what drives your behavior Who was the founder? SIGMUND FREUD 5 TRADITIONS 1. Structuralism 2. Functionalism 3. Gestalt Psychology 4. Psychoanalysis 5. Behaviorism Who were the major players? What were their core beliefs? What were they asking? What are some key terms? 17 EXIT TICKET Using your notes, independently answer the following questions 1. Why was Wilhelm Wundt a Trailblazer? 2. Who coined the term “Structuralism”? 3. Who influenced most of William James’ psychological theories? 4. What goes “Gestalt” mean in German? 5. Who introduced new ideas about the unconscious mind? 18 DO FIRST 1. Get out your Ψ notes (aka, the usual) 2. At the top of your notes for today, respond to the following prompt. You have until 12:03. 1. Have you ever “lost it”, and done something that was completely out of character? Something that really surprised you? Write about that experience, and write as many reasons as you can think of for why you did it. 2. If you’ve never had that experience, write about someone you know who has. OBJECTIVES 1. SWBAT Compare and contrast 7 of the current perspectives in psychology: • • • • • • • Behaviorist Humanist Psychodynamic Biological Cognitive Socio-cultural Evolutionary 2. SWBAT Experience the complexity of determining causes of behavior. 3. SWBAT Understand how psychology’s “Levels of Analysis” are used to explain human behavior. THE CASE OF ANDREA YATES June 20, 2001: After her husband left for work, Andrea Yates, a Houston mother, methodically drowned her five children in the family bathtub. Yates filled the bathtub with water and called her children in, one by one, and forcibly drowned them. She started with the three youngest boys, beginning with Paul, placing his dead body atop the bed covered with a sheet. Last to die was the oldest, seven-year-old Noah, whom she later confessed put up the toughest fight. She told police that she drowned the children to save them from burning in hell. A jury rejected her insanity defense, and she was sentenced to serve her life in a psychiatric prison. You’re the Psychologist… Ask yourself… What do you believe to be the causes of Andrea Yates’ murder of her own children?? THE EVIDENCE Mood disorders run in families, and Andrea’s was no exception. A sister and two brother were also on antidepressants. A lack of the neurotransmitter serotonin is correlated with depression. Andrea had previously been diagnosed with post-partum depression with psychosis, and had been taken off her antipsychotic medication (people who are psychotic are described as having breaks from reality) about a month before her children’s deaths. Her husband even claimed to have begged doctors to put her back on Haldol, a medicine used to treat people who hear voices or have delusional thoughts. THE EVIDENCE Despite our individualistic Western culture, remnants of our hunter-gatherer lifestyle still remain. For example, research shows that when a mother (human or animal) believes that her children are in danger, she will defy the limits of normal behavior and ability to save them. THE EVIDENCE Yates’ family history is full of mental disorders such as bipolar disorder and major depressive disorder. Although Andrea had a fairly normal adolescent life, her exposure to family members with mental illness in her early childhood could have impacted her significantly. THE EVIDENCE Since Western culture is so individualistic, the Yates’ extended families weren’t around to help. She learned that it was her responsibility to take care of her family by herself, and if she couldn’t handle it, she needed to figure out what to do by herself. She also may have learned earlier in her life that the best way to deal with problems is to just make them go away. If it worked for her in the past, why wouldn’t it work in the future? THE EVIDENCE Andrea Yates also had a defect in her private mental functioning—the way she thought about and perceived her life. She has low self-esteem. At the time she killed her children, she believed that she was possessed and that the sign of Satan (666) was marked on her scalp. She told the police that her children “weren’t developing correctly” and that drowning them was the only way to save them. THE EVIDENCE Andrea Yates’ needs for love and acceptance were not met in her husband. Sources say that he wasn’t socially or emotionally supportive. He claimed to have never even changed a diaper. He left her home alone with 5 children when he was clearly aware that she couldn’t even take care of herself. After their fourth child, the doctors had strongly urged against further children, but he clearly didn’t listen and impregnated her with a fifth. THE EVIDENCE Finally, the religious environment that the Yates family was in was very extreme. They attended the church of a sharptongued, volatile preacher, who spoke with fervor about the wickedness of Eve and of all women, and insisted that if a mother did not bring up her children in the ways of Jesus, she and her children were bound for Hell. Andrea Yates was captivated and convinced, and she would later reference some of the preacher’s statements when she testified in court. You’re the Psychologist… Ask yourself… What do you believe to be the causes of Andrea Yates’ murder of her own children?? Directions: 1. Sit with the groups you’ve been numbered into. 2. Using your notes, BECOME A PSYCHOLOGIST of your assigned perspective. 3. On your cardstock, write how your perspective would attribute Yates’ behavior. Use evidence from the text. You’re the Psychologist… Ask yourself… What do you believe to be the causes of Andrea Yates’ murder of her own children?? FOR EXAMPLE: “As a psychologist of the ___________ perspective, I believe that Andrea Yates’ behavior can be attributed to ________________________. This is evidenced by __________________________________.” DO FIRST The half sheet of paper asks you to consider why people display pro-social behavior, or helping behavior. Basically, what causes people to be nice to each other? Determine what contemporary perspective is associated with each explanation. When you’re finished, review your notes REVIEW: HOW DO WE GET A COMPLETE PICTURE OF THE CAUSES OF BEHAVIOR? Mrs. Ries! Don’t forget to ring the bell for Victor’s insight! By using levels of analysis! TO REVIEW… WHAT IS PSYCHOLOGY? Psychology is the scientific study of behavior and mental processes. “Psychology” has its roots in the Greek words of “psyche,” or soul/mind, and “-ology,” or a field of study.” GESTALT PSYCHOLOGY GESTALT PSYCHOLOGY WHY DO PSYCHOLOGY? Is war our biological destiny? How does the brain work? What should we eat? Are men necessary? Women? Can robots become conscious? Why do we sleep? How smart are animals? Can drugs make us smart? Does the paranormal exist? PSYCHOLOGIST VS. PSYCHIATRIST VS. PSYCHOANALYST 3 WAYS OF DOING PSYCHOLOGY 1. Experimental Psychologists: 3 WAYS OF DOING PSYCHOLOGY 2. Teachers of Psychology: 3 WAYS OF DOING PSYCHOLOGY 3. Applied Psychology: PRACTICE QUIZ! PRACTICE QUIZ PROCEDURES 1. Put up testing folders. 2. Dominate the quiz, keeping your answers covered at all times, or I will recycle your work. 3. Once time is up, work with a partner to find the correct answers. 4. Mark any question you got wrong, and take notes on your misunderstandings. Ask for help! 5. When time is up, put your quizzes in your table folder for teacher to pick up FLASHCARDS Students will complete a flashcard for each key term and key person for each unit, according to the following specifications: FLASHCARDS OPTIONAL (but highly recommended): A picture or mnemonic device to help you remember the term. Can be on either side. HOMEWORK • • • • Study for Quiz Bring pre-sharpened colored pencils Bring composition notebook for psychology journal Do Ch. 1 flashcards.