Working Group 1: “Best Use” ARV for Children: Principles
advertisement

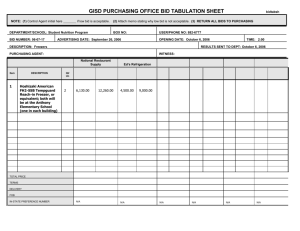
Working Group 1: “Best Use” ARV for Children: Principles • Simplified and standardized guidelines for ARV treatment of HIV-infected children are needed to allow rapid scale-up of treatment in children as well as adults. • Recommendations are targeted at developing countries (not mid-developed or developed countries), taking into account realities in terms of: – Health care infrastructure – Availability of human resources – Socioeconomic context – Currently available drug formulations • Comments are based on use of existing WHO pediatric ARV 1st and 2nd line regimen choices. WHO Recommended First-line ARV Regimen for Children First-Line Regimen Comment d4T or ZDV Plus 3TC Plus NVP or EFZ NNRTI choice: If age <3 yrs or wt <10 kg: NVP If age >3 yrs or wt >10 kg: NVP or EFZ WHO Recommended Second-Line ARV Regimen for Treatment Failure in Children First-Line Regimen Second-Line Regimen d4T or ZDV ABC* Plus Plus 3TC ddI Plus Plus NVP or EFZ Protease inhibitor: LPV/r or NFV, or SQV/r if wt >25 kg Special Considerations for Pediatrics • Drug PK varies by age: – Younger children may need higher doses of drug to achieve same levels as with lower doses in older children. – Yet PK in younger children not available for some of the WHO recommended drugs (e.g., EFV under age 3 years and LPV/r under age 6 months), thus choice of drugs in 1st or 2nd line regimens may differ depending on child’s age – has implications for what drugs and formulations should be acquired by country to allow treatment of children. Special Considerations for Pediatrics • Dosing must be adjusted as child grows. – Need to standardize to allow non-experts to give. – BSA-based dosing involves math calculations and too complex. – “Weight-band” dosing tables would be optimal. – Generally for most drugs in 1st and 2nd line, in terms of weight band dosing, would prefer over- rather than under-dosing, to avoid development of resistance (exception might be for drug with significant toxicity known to be dose-associated, e.g., anemia and ZDV). Special Considerations for Pediatrics • Formulation issues: – Not all tablets/capsules available in low enough doses for children. – However, liquid may need cold chain (e.g., d4T liquid) and be hard to store/administer. – Splitting of adult tablets, while suboptimal, may be only way to provide ART to ill child. – Knowing there is even distribution of drug(s) in tablet important if splitting tablets (some FDC do not have even distribution of drugs in tablets). – Splitting tablets more than once (e.g., in half) felt too inaccurate and not recommended. Special Considerations for Pediatrics • Formulation issues: – Simplified table that has weight bands and the amount of liquid, tablets or capsules (not mg/kg or /m2 dosing instruction) is desirable to allow projecting need for different formulations for children and for ease administration by non-experts (WG started to develop, but need to verify dosing ranges being provided). – Principal would be to try to utilize the adult FDC tablet formulations as much as possible, restricting liquid formulations to infants under 12 kg. Special Considerations for Pediatrics • Formulation issues: – With use adult FDC preparations, be aware of potential under- or over-dosing of individual drug. – For NVP, children in certain weight categories would need FDC plus an additional dose of NVP; NVP also has issue of dose escalation. • Implication: Must have ability to have liquid or tablet formulation of NVP alone available in addition to FDC. Special Considerations for Pediatrics • Formulation problems: – Opening capsules and mixing in liquid or food has been done to administer to children. – However, the stability of such preparations is unknown. • In vitro stability testing is needed of solutions made from capsule powder. – Additionally, bioequivalence testing in adults of such preparations (either mixed in liquid or food) is needed to assure drug is absorbed and dose correct when administered in this manner. – Need for FDC in pediatric doses. Special Considerations for Pediatrics • Monitoring: – Because of concerns related to dosing and formulation problems and interim solutions to split tablets or open capsules until better preparations available: • Will be critical to have operational research done at sentinel sites to determine viral and immune response, • Additionally, important to have at least some monitoring and tracking of clinical (and CD4 if can) response at sites providing treatment to children to assure appropriate response is being seen. “Weight Band” Dosing Charts • Several examples exist, such as Columbia/CDC chart and MSF chart. • All difficult to read as have all drugs and multiple formulations in one big table. • Need to simplify but how best? – Should there be a single table for each combination (eg. a d4T/3TC/NVP chart, an AZT/3TC/NVP chart), divided into first 2 weeks and after escalation? – Would use liquid preparation only when absolutely necessary in young infants with low weight, and move to use of FDC tablets as soon as weight allows. – While table doesn’t have to list actual dose, it is CRITICAL to have dosing calculated and checked when developing table. d4T/3TC/NVP After Dose Escalation Weight band (kg) d4T 3TC NVP 5-6.9 6 mL BID 2 mL BID 4 mL BID 7-9.9 15 mg cap BID 3 mL BID 6 mL BID 10-11.9 15 mg cap BID 4 mL BID ½ NVP tab BID 12-14.9 ½ 30 mg d4T/3TC/NVP tab BID OR ½ 30 mg d4T/3TC tab BID plus ½ NVP tab BID 15-16.9 17-19.9 20-24.9 25-29.9 30-34.9 35-40 ½ 40 mg d4T/3TC/NVP BID plus ½ NVP tab QD OR ½ 40 mg d4T/3TC tab BID plus 1 NVP tab in AM and ½ NVP tab in PM 1 30 mg d4T/3TC/NVP tab BID OR 1 30 mg d4T/3TC tab BID plus 1 NVP tab BID 1 40 mg d4T/3TC/NVP tab BID plus OR 1 40 mg d4T/3TC tab BID plus 1 NVP tab BID d4T/3TC/NVP 1st 2 weeks Weight band (kg) 5-6.9 7-9.9 10-11.9 12-14.9 15-16.9 17-19.9 20-24.9 25-29.9 30-34.9 35-40 d4T 3TC NVP Recommendations • With current formulations we can and should treat children with ARVs today. • Existing success stories examples. – Romania, Botswana, Uganda, S Africa • Development of further simplified guidelines that would allow use of non-physician personnel to provide drugs (model tables). Recommendations • Principles for treatment of children – Infants (<12 kg) can and should be treated as well as older and heavier children. – In order to treat infants <12 kg, necessary to have following ARV: • AZT, ABC, 3TC • NVP • LPV/r – Not recommended for use in <12 kg are d4T liquid, ddI sachet, NFV powder. Recommendations • Principles for treatment of children – Children >12 kg can be treated with adult solid formulations by using weight band-based dosing ranges (at least 5 kg increments). • FDC are preferred • Dual FDC may be better than triple because of potential under-dosing for some drugs like NVP which then require supplementary drug administration • Tablets can be divided in half but not more Recommendations • Development of simplified weight-rangebased dosing table/card may provide a useful tool (see model) – May need to be broken into <12 kg tables and >12 kg tables – Separate table for each of recommended combinations – Front: Schema for dosing (for FDC provide exact ) – Back: “Appropriate” dose range for drugs within weight range – Dose ranges need to be checked d4T/3TC/NVP After Dose Escalation Weight band (kg) d4T 3TC NVP 5-6.9 6 mL BID 2 mL BID 4 mL BID 7-9.9 15 mg cap BID 3 mL BID 6 mL BID 10-11.9 15 mg cap BID 4 mL BID ½ NVP tab BID 12-14.9 ½ 30 mg d4T/3TC/NVP tab BID OR ½ 30 mg d4T/3TC tab BID plus ½ NVP tab BID 15-16.9 17-19.9 20-24.9 25-29.9 30-34.9 35-40 ½ 40 mg d4T/3TC/NVP BID plus ½ NVP tab QD OR ½ 40 mg d4T/3TC tab BID plus 1 NVP tab in AM and ½ NVP tab in PM 1 30 mg d4T/3TC/NVP tab BID OR 1 30 mg d4T/3TC tab BID plus 1 NVP tab BID 1 40 mg d4T/3TC/NVP tab BID plus OR 1 40 mg d4T/3TC tab BID plus 1 NVP tab BID d4T/3TC/NVP 1st 2 weeks Weight band (kg) 5-6.9 7-9.9 10-11.9 12-14.9 15-16.9 17-19.9 20-24.9 25-29.9 30-34.9 35-40 d4T 3TC NVP Critical Needs • Bioequivalence studies of generic drug • Need more PK data younger age group and for certain drugs like NFV • FDC that are scored to allow breaking • FDC that are in pediatric dosing GAPS • Testing and diagnosis, particularly children <18 months. • Adherence – pull together existing tools to provide examples GAPS • Role of non-physician personnel to provide treatment – Promote – Supervision mechanism – “Prevent anarchy”