Principles of Marketing
advertisement

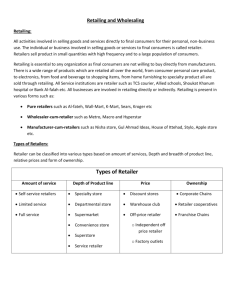
Principles of Marketing Lecture-30 Summary of Lecture-29 Producer Marketing activities Intermediaries Demand End users Demand Push Strategy Marketing activities Producer Demand Intermediaries Demand End users Pull Strategy Marketing Logistics and Supply Chain Management Functions of Logistics Systems Costs Minimize Costs of Attaining Logistics Objectives Order Processing Submitted Processed Shipped Logistics Transportation Water, Truck, Rail, Pipeline & Air Functions Warehousing Storage Distribution Inventory When to order How much to order Just-in-time Today’s Topics Retailing and Wholesaling Retailing Retailing is the process by which goods and services are sold to consumers for their personal use. Retailers provide many benefits such as: –providing an assortment of merchandise under one roof, –allowing access to goods customers might never see, –providing interesting environments in which to spend our leisure time. Retailing can be done in stores (store retailing) or out of a store (nonstore retailing) such as: –Direct mail, –Catalogs, –Telephone, –Home shopping shows, –Internet. “...all activities involved in selling, renting, and providing goods and services to ultimate consumers for personal, family or household use.” -Berkowitz et al Classification of Retailing Amount of Service Self-Service, Limited-Service and Full-Service Retailer Product Line Length and Breadth of the Product Assortment Relative Prices Pricing Structure that is Used by the Retailer Retail Organizations Independent, Corporate, or Contractual Ownership Organization Amount of Service Self-Service Retailer Limited-Service Retailers Provide Few or No Services to Shoppers Provide Only a Limited Number of Services to Shoppers Full-Service Retailers Retailers that Provide a Full Range of Services to Shoppers Product Line Specialty Stores Narrow Product Line, Deep Assortment Department Stores Wide Variety of Product Lines i.e. Clothing, Home Furnishings Supermarkets Wide Variety of Food, Laundry, & Household Products Convenience Stores Limited Line of High-Turnover Convenience Goods Superstores Large Assortment of Routinely Purchased Food & Nonfood Products Discount Stores Standard Merchandise at Lower Prices Off-Price Retailers Changing Collection of Higher-Quality Goods at a Reduced Price Warehouse Clubs Limited Selection of Brand-Name Grocery Items, Appliances Relative Prices Discount Stores “Off-Priced” Retailers Catalog Showrooms Retail Organization Corporate Chains Retailers wanting economies of scale Corporate Chains Franchise Operation s Retailers wanting economies of scale Corporate Chains Franchise Operations Retailers wanting economies of scale Voluntary Chains Cooperative Chains The Wheel of Retailing High Margin High Price High Status Young Store Brand New Store Older Store Low Margin Low Price Low Status Nonstore Retailing Mail Order •Catalogs - from clothing to computers •Direct Mail - brochure offering a product or service at one point in time. Direct Selling •Door-to-Door Sales - declining in U.S. •Parties & Networks - presentations •Telemarketing - over the phone Automatic Vending •Best suited to inexpensive merchandise and food and beverages. Direct Response Television •Home Shopping Networks - TV channels that sell products Retailer’s Product Assortment and Services Decisions Product Assortment Decisions • Width and Depth of Assortment • Quality of Products • Product Differentiation Strategies Services Mix Key Tool of Nonprice Competition for Setting One Store Apart From Another. Store’s Atmosphere • Physical Layout • “Feel” That Suits the Target Market and Moves Customers to Buy Factors Influencing Store Atmosphere Employee Type and Density Merchandise Type and Density Most Influential Factors on Store Atmosphere Fixture Type and Density Sound Odors Visual Factors Retailer Marketing Decisions Retailer Strategy Target Market Retail Store Positioning Retailer Marketing Mix Product and Service Assortment Prices Promotion Place (Location) Strategic Issues in Retailing Location Product Assortment Customer Service Atmospherics Pricing Promotion Wholesaling What is Wholesaling? All the activities involved in selling goods and services to those buying for resale or business use. Wholesaler - those firms engaged primarily in wholesaling activity. Services Provided by Wholesaling Intermediaries Buying Selling Storing Transporting Providing Makret Information Financing Risk Taking Customer Expectations for Wholesaling Easy Inquiry and Order Error-Free Invoicing Accuracy Reliable Delivery On-time Delivery Post-Sales Support Easy Claims Handling Suppliers’ Logistics Systems Types of Wholesalers Merchant Wholesaler Independently Owned Business that Takes Title to the Merchandise it Handles. Brokers/ Agents They Don’t Take Title to the Goods, and They Perform Only a Few Functions. Manufacturers’ Sales Branches and Offices Wholesaling by Sellers or Buyers Themselves Rather Than Through Independent Wholesalers. Wholesaler Marketing Decisions Wholesaler Strategy Wholesaler Marketing Mix Product and Service Assortment Target Market Prices Retail Store Positioning Promotion Place (Location) So…. Compete on value (not just price.) Save customers time and energy. Make shopping fun. End of Place part….. Enough for today. . . Summary Retailing and Wholesaling Classification of Retailing Amount of Service Self-Service, Limited-Service and Full-Service Retailer Product Line Length and Breadth of the Product Assortment Relative Prices Pricing Structure that is Used by the Retailer Retail Organizations Independent, Corporate, or Contractual Ownership Organization Nonstore Retailing Mail Order •Catalogs - from clothing to computers •Direct Mail - brochure offering a product or service at one point in time. Direct Selling •Door-to-Door Sales - declining in U.S. •Parties & Networks - presentations •Telemarketing - over the phone Automatic Vending •Best suited to inexpensive merchandise and food and beverages. Direct Response Television •Home Shopping Networks - TV channels that sell products Wholesaling Types of Wholesalers Merchant Wholesaler Independently Owned Business that Takes Title to the Merchandise it Handles. Brokers/ Agents They Don’t Take Title to the Goods, and They Perform Only a Few Functions. Manufacturers’ Sales Branches and Offices Wholesaling by Sellers or Buyers Themselves Rather Than Through Independent Wholesalers. Next…. Review rd 3 P (Place) Principles of Marketing Lecture-30