Powerpoint
advertisement

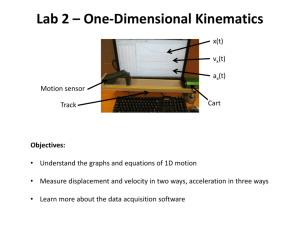
Launch of the HAND Toolkit, Alzhemier’s Victoria Understanding HAND Dr Edwina Wright MD PhD The Burnet Institute World AIDS Conference, Melbourne July 2014 HIV-1 Associated Neurocognitive Disorders: HAND Asymptomatic Neurocognitive Impairment (ANI) Asymptomatic Impairment ≥ 2 domains, ≥ 1SD below the mean for matched controls Mild Neurocognitive Disorder (MND) Mild symptoms but still working and active Impairment: same as ANI HIV-Associated Dementia (HAD) Significant impairment ADLs Impairment ≥ two domains, ≥2SD below the mean for matched controls HAND occurs in ≈ 20% of untreated HIV+ people with CD4+ cells < 200/mm3 1. Updated Research Nosology for HIV-associated Neurocognitive Disorders, Antinori et al, Neurology 2007 Is a diagnosis of Minor Neurocognitive Disorder important? • Associated with increased risk for: – – – – Mortality Job loss Driving ability decline Poor medication adherence in more severe neurocognitive impairment – Risk of HAD www.genomicseducation.ca/. ../health/HIV.asp; (Albert et al, 1995 ; Wilkie et al 1998;Sacktor et al 1996; Mayeux et al 1993; Price et al 1999; Marcotte et al, 1999; Hinkin et al, 2002; Stern et al, 2001; Cherner et al, 2002) HAND: Synopsis Clinical Pathogenesis Caudate, Globus pallidus, Putamen Diagnosis of Exclusion Treatment CART vs no cART or mono/dual therapy improves cognitive function cART with 3 or more drugs with effective CSF penetration appears superior in patients with HAND . Navia et al, Ann Neurol 1986. www.goasiapacific.com. Gonzalez-Scarano et al, Nat Rev Immunol 2005. http://www.med.harvard.edu/AANLIB/ medcine, plosjournals.org. Ferrando et al, AIDS 1998. Price et al, AIDS 1999. Cohen RA, AIDS 2001. Cysique et al, Arch Neurol 2004. Letendre et al, Annals Neurol 2004. Letendre et al, Arch Neurol 2008. Cysique et al, Neurology 2009. Cysique, Waters, Brew. BMC Neurol 2011. Bell, Anthony, Simmons. Current HIV Research, 2006 www.emedicine.com/NEURO/topic447.htm ; www.pulitzer.org/.../ works/africa1.html HAND: Synopsis Clinical Cognitive impairment Forgetfulness, loss of concentration, confusion and slowing ofGlobus thought Caudate, pallidus, Putamen Clinical Diagnosis of Motor symptoms Loss of Exclusion balance, clumsiness, change in handwriting, tremor, unsteady gait Behavioural changes Treatment Apathy, social withdrawal, loss of CART vs no cART or mono/dual interest in hobbies, world events and therapy improves cognitive function their own well-being cART with 3 or more drugs with Some patients effective CSF penetration appears superior in patients with HAND . present with mania Navia et al, Ann Neurol 1986. www.goasiapacific.com. al, Nat Rev Immunol http://www.med.harvard.edu/AANLIB/ medcine, Navia et al, AnnGonzalez-Scarano Neurol 1986 .etTross et al, AIDS2005. 1988. Mijch et al, J Neuropsychiatry plosjournals.org. Ferrando et al, AIDS 1998. Price et al, AIDS 1999. Cohen RA, AIDS 2001. Cysique et al, Arch Neurol 2004. Letendre et al, Annals Neurol 2004. Neurosci 1999.2009. Brew, Oxford Press Letendre et al, Arch Neurol 2008.Clin Cysique et al, Neurology Cysique, Waters, Brew.2001 BMC Neurol 2011. Bell, Anthony, Simmons. Current HIV Research, 2006 www.emedicine.com/NEURO/topic447.htm ; www.pulitzer.org/.../ works/africa1.html HAND: Synopsis Pathogenesis • Lentivirus 3 Pathogenesis Clinical Caudate, Globus pallidus, Putamen • Early CNS infection occurs • PermissiveDiagnosis infectionofmicroglia and Exclusion perivascular macrophages • Non-productive infection astrocytes Treatment • Histopathology: hallmark CART vs no cART or mono/dual encephalitis MNG cells Caudate, Globus pallidus, Putamen therapy improves cognitive function • Topography: deep white matter and cART with 3 or more drugs with basal ganglia effective CSF penetration appears superior in patients with HAND . 1.Navia et al, Ann Neurol 1986. 2. www.goasiapacific.com. 3 Gonzalez-Scarano et al,Nat Rev Immunol 2005. 4. http://www.med.harvard.edu/AANLIB/ 5.medcine, plosjournals.org. 6. Ferrando et al, AIDS 1998. 7. Price et al, AIDS 1999. 8. Cohen RA, AIDS 2001. 9. Cysique et al, Arch Neurol 2004. 10. Letendre et al, Annals Neurol Peluso et al, Virology 1985. Fischer-Smith et al, Am J Pathol 2004;Wiley et al PNAS 1986;Takahashi K, Ann Neurol 1996; McCrossan, Brain 2006. Spudich et al JID, 2004. 11. Letendre et Pathogens al, Arch Neurol 12.etCysique et al, 2009; Neurology 2009. 13. Cysique, Waters, Brew. BMC Neurol 2011. 14. Bell, Anthony, Simmons. Current HIV 2011; Schnell Plos 2011; 2008. Churchill al, Ann Neurol Research, 2006 www.emedicine.com/NEURO/topic447.htm ; www.pulitzer.org/.../ works/africa1.html HAND: Synopsis Clinical/Host/Viral Factors Clinical Pathogenesis3 Caudate, Globus pallidus, Putamen • Degree of immunodeficiency, CD4 nadir, current CD4 Diagnosis of cell count Exclusion • Older age at time of seroconversion • Diabetes: OR 5.34 (1.66-17.7, p<0.01) • Host genotype • • • • • Treatment RH 4.5 (1.36-16.28, p 0.0015) MCP-1-2578G CART low vs-CCR5 no cART or 3.1(1.33-7.6, mono/dual p 0.009) det RH CCL3L1 therapy improves cognitive DARC-46 C/C : time to HADfunction ApoE e4/e4: variable findings cART with or more with TNF308 A 3allele: OR drugs 5.5 (1.8-17.0) effective CSF penetration appears • Others: injecting drug use, female gender superior in patients with HAND • *HIV-1 Clades . Navia et al, Ann Neurol 1986. www.goasiapacific.com. Gonzalez-Scarano et al, Nat Rev Immunol 2005. http://www.med.harvard.edu/AANLIB/ medcine, Cysique, Maruff, Brew, Neurology, 2006. Bhaskaran, Annals Neurology, 2008. Valcour et al, JAIDS 2005. Gonzalez et al, PNAS 2002. Gonzalez et al, Science 2005. He et al , Cell plosjournals.org. Ferrando al, AIDS 1998. et al, AIDS 1999. Cohen RA, AIDS 2001. et Pomara al, ArchetNeurol 2004.Valcour Letendre al, 2008. Annals Neurol 2004. HostetMicrobe 2008. KorderPrice Nat Med 1998. Valcour et al, J Neurovirol 2004. Burt et al,Cysique PNAS 2008. al PNAS 2008. et al,et PNAS Quasney et al, Neurology Letendre et al, Arch Neurol 2008. Cysique et2010. al, Neurology Cysique, Waters, Brew. BMC Neurol 2011. Bell, Anthony, Simmons. Current HIV Research, 2006 2001. Spector et al, AIDS Simioni et al2009. AIDS 2010. Robertson et al, AIDS 2007. Heaton et al, Neurology 2010. www.emedicine.com/NEURO/topic447.htm ; www.pulitzer.org/.../ works/africa1.html HAND: Synopsis HAD is a Diagnosis of Exclusion Exclude important confounds Pathogenesis -Depression, medical illnesses Clinical (diabetes, myocardial infarction, hep C), head trauma, seizures, CVAs Neuropsychological testing Caudate, Globus pallidus, Putamen Diagnosis of Exclusion MRI scan, +/- MRSTreatment (not yet CART vs no cART or mono/dual routinely performed) therapy improves cognitive function Lumbar puncture: HIV viral load and HIV genotype cART with 3 or more drugs with effective CSF penetration appears superior in patients with HAND There is no single or composite biomarker/radiological marker Navia et al, Ann Neurol 1986. www.goasiapacific.com. Gonzalez-Scarano et al, Nat Rev Immunol 2005. http://www.med.harvard.edu/AANLIB/ medcine, for diagnosis HAND plosjournals.org. Ferrando et al,of AIDS 1998. Price et al, AIDS 1999. Cohen RA, AIDS 2001. Cysique et al, Arch Neurol 2004. Letendre et al, Annals Neurol 2004. NAA: n-acetyl aspartate Reflects neuronal metabolism Chemical associated with myelin sheaths HAD Choline Reflects membrane turnover- microglial cells or astrocytes HAD Myoinositol Reflects inflammation and glial cell proliferation HAD Creatine Chemical involved in energy metabolism Letendre etet al, al, ArchNeurology Neurol 2008. Cysique al, Neurology 2009. Cysique,of Waters, Brew. BMC Neurol 2011.Imaging Simmons. Current HIV Research, 2006 Heaton 2010.etSacktor et al, Journal Magnetic Resonance 2005 HeatonBell, etAnthony, al, Neurology 2011 www.emedicine.com/NEURO/topic447.htm ; www.pulitzer.org/.../ works/africa1.html Neuropsychological Testing low income settings • Mini Mental State Exam – Insensitive to MND and HAD • HIV Dementia scale – Limited sensitivity for mild disease (J Neurol Sci. 2007) but reasonable sensitivity and specificity for HAD – Takes 10-15 minutes to administer – Maximum score is 12: a patient with a score ≤ 10 should be evaluated for HAD HAD: Synopsis Treatment of HAND • Treat with cART • >50% patients improve over at least 18 months • Evidence that use of regimens with good CNS penetration is necessary in patients with HAND Clinical Theory: Pathogenesis Regimens with high CNS penetration => lower CSF viral load => Caudate, Globus pallidus, Putamen improved neurocognition 4 of Metric: CNS penetration effectivenessDiagnosis (CPE) Zidovudine score Nevirapine Exclusion Evidence: largely observational studies Indinavir-r 3 2 Abacavir Emtricitabine Lamivudine Stavudine Didanosine Etravirine Didanosine Tenofovir Zalcitabine Atazanavir Atazanavir-r Nelfinavir Ritonavir Saquinavir Saquinavir-r Tipranavir-r Enfuvirtide Delavirdine Efavirenz Darunavir-r Indinavir Lopinavir-r Fosamprenavir-r 1. Cysique et al 2004. 2. Letendre et al, 2008. 3. Cysique et al, 2009. 1 Recent meta-analysis of 16 observational Raltegravir Maraviroc Treatment studies designed to determine benefit vs score no cART or mono/dual ofCART high CPE regimens -6therapy met analysis criteria cognitive function improves -6/6 => high CPE score regimens were associated with cognition or CSF viral load BUT only 2/6 studies were adequately powered cART with 3 or more drugs with effective appears Results one CSF recentpenetration RCT- no benefit high CPE score but study was underpowered superior in patients with HAND Practice: Currently common practice to use high CPE scoring regimens to treat . patients with HAND Navia et al, Ann Neurol 1986. www.goasiapacific.com. Gonzalez-Scarano et al, Nat Rev Immunol 2005. http://www.med.harvard.edu/AANLIB/ medcine, plosjournals.org. Ferrando et al, AIDS 1998. Price et al, AIDS 1999. Cohen RA, AIDS 2001. Cysique et al, Arch Neurol 2004. Letendre et al, Annals Neurol 2004. Tozzi et etal, al,Neurology JAIDS 2001. al, Arch Neurol 2004.2011. Letendre et al, Ann NeurolCurrent 2004.HIV Letendre et 2006 al, Arch Letendre et al, Arch Neurol 2008. Cysique 2009.Cysique Cysique,et Waters, Brew. BMC Neurol Bell, Anthony, Simmons. Research, www.emedicine.com/NEURO/topic447.htmNeurol ; www.pulitzer.org/.../ works/africa1.html 2008. Cysique et al, Neurology 2009. Cysique, Waters, Brew, BMC Neurol 2011. Ellis et al, CID 2014 HAD: Synopsis Clinical Cognitive impairment Psychomotor slowing Behavioural changes Caudate, Globus pallidus, Putamen HAD is one of the leading causes of dementia in young Diagnosis of adultsOOn globally Exclusion Pathogenesis It is one of the few treatable Treatment CART vs no cART ordementias mono/dual therapy improves cognitive function cART with 3 or more drugs with effective CSF penetration appears superior in patients with HAND Navia et al, Ann Neurol 1986. www.goasiapacific.com. Gonzalez-Scarano et al, Nat Rev Immunol 2005. http://www.med.harvard.edu/AANLIB/ medcine, plosjournals.org. Ferrando et al, AIDS 1998. Price et al, AIDS 1999. Cohen RA, AIDS 2001. Cysique et al, Arch Neurol 2004. Letendre et al, Annals Neurol 2004. Letendre et al, Arch Neurol 2008. Cysique et al, Neurology 2009. Cysique, Waters, Brew. BMC Neurol 2011. Bell, Anthony, Simmons. Current HIV Research, 2006 www.emedicine.com/NEURO/topic447.htm ; www.pulitzer.org/.../ works/africa1.html What proportion of HIV+ patients who are fully virologically suppressed may have HAND? ≈30% ANI> MND>> HAD A Why is HAND so prevalent in virologically suppressed populations? HAND • Legacy effect? • Poor CNS HIV control? • Ongoing CNS parenchymal infection +/or inflammation? HAND plus or HAND x • Cardiovascular risk factors? • Neurodegeneration? • Ageing? • cART toxicity? Mothobi and Brew, Curr Opin ID 2012 Summary • HAND occurs in approximately 20% of untreated HIV+ people with < 200 CD4+ cells/mm3 • HAND is the leading cause of dementia in young adults globally • HAND is treatable with HIV antiretroviral agents and the majority of patients make a good recovery • HAND may occur in individuals who are taking antiretroviral therapy and requires appropriate referral and investigation • Other factors including aging and cardiovascular risk factors may influence the neurocognitive health of HIV+ people over time Thank you Picture Credits • • • • • www.genomicseducation.ca/. ../health/HIV.asp www.emedicine.com/NEURO/topic447.html www.pulitzer.org/.../ works/africa1.html www.goasiapacific.com Gonzalez-Scarano et al, Nat Rev Immunol 2005. http://www.med.harvard.edu/AANLIB/ medicine, plosjournals.org • http://www.vectors4all.net/