Genetics and behaviour
advertisement

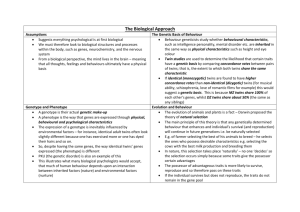
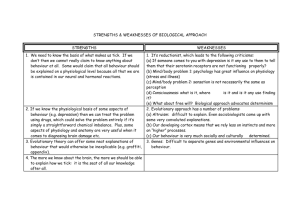
2.2 Biological level of analysis Genetics and behaviour Learning Outcomes • First four are the same as in 2.1 • New are: • Discuss the extent to which genetics influence behaviour • Examine one evolutionary explanation of behaviour • Discuss ethical considerations in research into genetic influences on behaviour The developing child http://www.learner.org/vod/vod_window.html? pid=1502 This program traces the nature vs. nurture debate, revealing how developmental psychologists study the contributions of both heredity and environment to child development. With Dr. Renee Baillargeon of the University of Illinois and Dr. Judy De Loache of the University of Illinois Is biology destiny? Case Study 1. “A boy without a penis” handout 2. Money study on p. 37 same study • Read and comment • What is your response? Behavioural genetics • Deals with understanding how both genetics and the environment contribute to individual variations in human behaviour • What is inherited may be one of the building blocks for such complex behaviours Behavioural genetics • Psychologists argue that an individual may have a genetic predisposition towards a certain behaviour; however, without the appropriate environmental stimuli, this behaviour will not be manifested • An example of this is: the origin of depression The diathesis-stress model • Is used to explain the origin of depression • This model argues that depression may be a result of the interaction of a “genetic vulnerability” and traumatic environmental stimuli in early childhood. • Not everyone who experiences a traumatic childhood or has someone in the family who becomes depressed, will be depressed, therefore there in no single cause-and-effect relationship between genes and behaviour Genes • Humans have 24 distinct chromosomes, with app.. 20 000- 25 000 genes • Human genome project: mapping the genetic make-up of the human species by identifying those genes • http://www.ornl.gov/sci/techresources/Huma n_Genome/home.shtml Genetic research • Is to a large extent based on correlational studies What is that? Twin studies, family studies and adoption studies • To study the possible correlation of genetic heritance and behaviour • But why? Twin studies • There are two types of twins: monozygotic (MZ) and dizygotic (DZ) • Monozygotic twins: are genetically identical due to one fertilized egg that splits into two. These twins are of the same sex, and look very much alike Twin studies Dizygotic twins are from two eggs. • DZ twins are not any closer genetically than brothers and sisters, that is, they will have 50% of their genes in common. • They don’t have to be of the same sex. Twin studies • The hypothesis is that the higher the genetic relationship, the more similar the individuals should be if the particular behavior being studied is inherited. • The correlation found is called the concordance rate Family studies • A more representative sample of the general population. • A child inherits half of its genes from the father and half from the mother • Sibling will share 50% with each other • Grandparents will share 25% with their grandparents • First cousins will share 12,5% with each other Family studies • These different degrees of genetic relatedness are compared with behaviour. • For example: if one study intelligence and believe that IQ has a lot to do with the genes, there should be a strong correlation in IQ between children and their mother and fathers, but a weak correlation in IQ with their second cousins and if any with strangers Adoption studies • Adopted or foster children generally share none of their genes with their adoptive parents, but 50% with their biological mother and father. Adoption studies • Therefore, if the heritability of a behaviour is high, the environment should have little part to play • And the adopted children should correlate more strongly with the behaviour (e.g. IQ) of their biological mother and father than their adoptive parent. Adoption studies • Critique against using this method: • Not representative of the general population • Adoption agencies tend to use selective placement when finding homes (as similar as possible) Is Madonna a similar family? To sum up • These methods help the researchers to determine the extent of genetic influence • There is a clear correlation between several behaviours and genetic heritance • We are going to examine Intelligence