river revision - The Radyr Geog Blog
advertisement

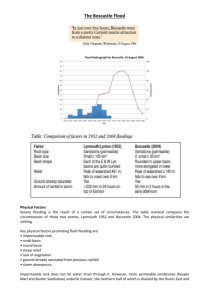
River landscapes and processes Geography GCSE WJEC River Processes Erosion - where parts of the river bed and bank get eroded / removed from the landscape Transportation - where the eroded material is carried from one place to another through the river system Deposition - where the river load becomes too heavy for the river to carry and is dumped down / deposited. A river can erode material from its bed and banks in 4 main ways • Abrasion – Moving water throws particles it is carrying against the bed and banks of the river which dislodges more material • Hydraulic Action - The sheer force of the water pounding into the bed and banks can dislodge material • Attrition - Particles being carried downstream knock against each other, wearing each other down. This results in smaller, rounder particles as you move downstream Can you remember the 4th type? Methods of Erosion • Abrasion – • Hydraulic Action • Attrition • Solution- Methods of Transportation Rivers transport material in 4 main ways •Solution - Some minerals (particularly in limestone areas) dissolve easily in water and are not visible to the naked eye •Suspension – As the speed or velocity of a river increases, it is able to pick up and carry larger and larger particles in its flow. Where particles are carried along in the flow and are not in contact with the river bed, they are said to be travelling in suspension. Methods of Transportation • Saltation - Heavier particles may not be held in the flow all the time but may be bounced along the bed • Traction - The heaviest particles are rolled along the bed. Such particles may only be moved when the river has a large volume of water in it solution The V - Shaped Valley Can you mark the V-shaped valley’s on this photo? • In the UPPER STAGE the river erodes downwards? KEY WORDS Use this sketch to help explain how V shape valleys form Waterfalls and Gorges 1. Draw the stages in the formation of a waterfall 2. Explain in as much detail what is happening at 3 3. What is happening here? (see next slide) ?? Waterfall formation flash Case study: Niagara Falls USA Canada USA Canada Canada Horseshoe 750 meters 52 meters high 20 million visit the falls every year Visitors !!! Hard Resistant Rock - Limestone 52 meters Weak Rock Shale Meanders 1. Can you mark the fastest flow on this? 2. What type of erosion do you think is happening? Also known as the ‘Mature’ stage Meanders 1 (Aerial View) Meanders are formed because the current swings to the outside of a bend and concentrates the erosion there. Deposition occurs on the inside of the bed where there is not enough energy to carry load. EROSION TYPE: Lateral Meanders 2 (Profile View / Cross Section X - Y) EROSION TYPE: Lateral This cross section clearly shows the eddy current (near ’X’) formed by the velocity of the river being concentrated on the outside of the bend. These UNDERCUT the bank causing the formation of a RIVER CLIFF. On the inside (NEAR ‘Y’), a SLIP-OFF-SLOPE is formed where current is too slow to carry any load. Ox- Bow Lakes (Middle Course) What is Meander Migration …. What do you think might happen here? What is Meander Migration Ox-Bow Lake 1 (Aerial View) EROSION TYPE: Lateral Ox-bow lakes are formed when two meander RIVER CLIFFS are being eroded towards each other. These will eventually meet, causing the river to then flow across the bottom of the diagram. Ox-Bow Lake 2 (Aerial View) Can you annotate this photo graph ? Can you annotate this photo graph ? What are Flood Plains and levees? • Levees Floodplain Levees Leeves River Leveés and Raised Beds 1 (Front View) DEPOSITION FEATURE: no erosion in the Lower Course Leveés are formed when rivers flood. The river water overflows the banks of the river and immediately slows down due to friction with the FLOODPLAIN. This drops the larger particles first, building up a raised river bank called a LEVEÉ. Deltas Delta (Aerial View) This deposition feature is one of the largest. When the flowing river hits the non-flowing sea, energy is suddenly lost. This causes all of the load in the river to drop in the river MOUTH. This builds up over time to create a delta – an area of land. The river divides into DISTRIBUTARIES to continue to the sea, which is now some way away from its original meeting point. Can you work out what the river is trying to do by using this diagram? Flooding in Boscastle 16th August 2004 Map of Boscastle. Aerial Photo. MUST: Annotate images and diagrams to show the causes and effects of the Boscastle flood. The Boscastle Drainage Basin The valley sides are steep so … Trees have been cut down above the river. This could make flooding worse because... Settlements have been built upstream. This could mean… Rainfall in this area is The mouth of the high so... river is narrow so… MUST: Annotate images and diagrams to show the causes and effects of the Boscastle flood. The narrow valley can be appreciated when looking upstream from the harbour. MUST: Annotate images and diagrams to show the causes and effects of the Boscastle flood. Causes of the flood: 1. Heavy localised rainfall. 89mm of rain fell in an hour. 2. Saturated ground from previous rainfall. 3. Topography of the land – the landscape upstream of Boscastle acts as a funnel, directing vast volumes of water into the village. The valley sides are steep sided. 4. Narrow river channels in the village itself. MUST: Annotate images and diagrams to show the causes and effects of the Boscastle flood. MUST: Annotate images and diagrams to show the causes and effects of the Boscastle flood. The river reaches bankful stage. Any further water will lead to… The velocity is.. The ground is saturated so any further rain can’t be The discharge is..so.. absorbed The river is discoloured because.. The carrying capacity of the river has increased because.. MUST: Annotate images and diagrams to show the causes and effects of the Boscastle flood. In an operation lasting from mid-afternoon until 2:30 AM, a fleet of seven helicopters rescued about 150 people clinging to trees and the roofs of buildings and cars. Amazingly, no major injuries or loss of life were reported. About 90% of Boscastle’s economy is tourism and about 2/3 of this income usually occurred during the school holidays. MUST: Annotate images and diagrams to show the causes and effects of the Boscastle flood. Impacts of the flood: •Around 115 cars were washed into the sea •Several boats were also lost, •6 buildings were destroyed •Loss of tourist trade •Fall in house prices •B3263 road was blocked by flood waters •businesses destroyed including visitor centre •Economic damage estimated 2006 = £300 million •Seven helicopters rescued about 150 people •No major injuries or loss of life were reported. •About 90% of Boscastle’s economy is tourism based and about 2/3 of this income usually occurred during the school holidays. •House prices fell as houses termed flood risks MUST: Annotate images and diagrams to show the causes and effects of the Boscastle flood. MUST: Annotate images and diagrams to show the causes and effects of the Boscastle flood. How have decision makers responded? A £4.5m scheme to improve flood defences. Boscastle main car park. MUST: Annotate images and diagrams to show the causes and effects of the Boscastle flood. The scheme stretches along the valley, incorporating drainage, sewerage systems and land re-grading. MUST: Annotate images and diagrams to show the causes and effects of the Boscastle flood. The river lies here. Boscastle car park is being raised in height. This will stop the river from bursting it’s banks so easily. MUST: Annotate images and diagrams to show the causes and effects of the Boscastle flood. This drain allows water to run into the lower section of the river quickly. Boscastle flood defences. MUST: Annotate images and diagrams to show the causes and effects of the Boscastle flood. The river channel is being made deeper and wider so that it can accommodate more water. The lower section of the village. MUST: Annotate images and diagrams to show the causes and effects of the Boscastle flood. New sewerage systems are being put in place. The lower section of the village. MUST: Annotate images and diagrams to show the causes and effects of the Boscastle flood. Bridges that hindered the drainage of the floodwater are being replaced by stronger bridges that are less likely to get blocked. Notice attempts to draw in much needed custom. MUST: Annotate images and diagrams to show the causes and effects of the Boscastle flood. So what’s been done to mitigate against flood reoccurrence? MUST: Annotate images and diagrams to show the causes and effects of the Boscastle flood. The bridge has been raised and widened . The narrow river Valency channel has now been widened The river banks have been raised The channel has been deepened MUST: Annotate images and diagrams to show the causes and effects of the Boscastle flood. Whether flooding is prevented remains to be seen... MUST: Annotate images and diagrams to show the causes and effects of the Boscastle flood. PROGRESS CHECK QUESTIONS: Must… Could.. What were the causes of the Boscastle flood? How did people make the Boscastle flood worse? Name 5 effects of the Boscastle flood. Make 2 lists to show long term and short term effects of the Boscastle flood. How can the risk of flooding be reduced? List 4 ways that flooding can be reduced. For each, say how effective the method would be. MUST: Annotate images and diagrams to show the causes and effects of the Boscastle flood. Flood Management Strategies 1) 2) 3) 4) Explain how each method works … give good points & bad points of each strategy Give viewpoints of different groups of people Consider whether the strategy is sustainable Sustainable Planning - Land Use Zoning Preparation - homes and businesses Preparation – well beforehand Preparation - beforehand Preparation River Management – hard engineering e.g. Dams Hard options tend to be more expensive and have a greater impact on the river and the surrounding landscape. They involve engineering (building) a solution to the flood problem. Building dams e.g. Talybont Reservoir River Management – hard engineering Building flood walls / bunds – permanent defences River Management – hard engineering Altering the channel – widening, deepening, straightening - lining in concrete. River Valency Boscastle 2007. Hard Engineering – flood relief channels A channel can be built to divert some of the flood water away from the main channel (like a road bypass) Hard Engineering – flood protection Individual householders can flood proof their home for about £20,000. Businesses use ‘Floodguard’ too A Flood Resilient Home Temporary flood barriers • Geodesign barriers- used in Bewdley 24 times in last 4 years. Take about 6 hours to put up Soft Engineering - afforestation Soft options are more ecologically sensitive. e.g. encourage landowners in Upper Catchment of R Severn to plant more trees Soft Engineering – remove drains Restore blanket bogs on moorlands – remove any farmer’s drains Soft Engineering – natural floodpains Allow floodplains to stay natural – prevent building on floodplains.