Free Body Diagrams
advertisement

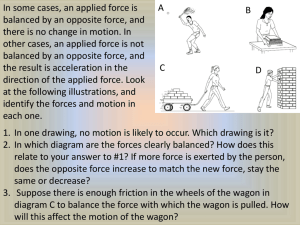
Free body diagrams, acceleration, quiz Friday, November 6, 2015 Friday, 11/6 Unit 4: Forces Respond to the following questions for both pictures. 1. Using your knowledge of inertia, describe how the image demonstrates Newton’s 1st Law of motion. 2. What could you do to change the motion of the bus or the race car? Upcoming dates Friday, 11/6 – quiz Monday, 11/16 – quiz Monday, 11/16 – review due at when the late bell rings Wednesday, 11/ 18 – Unit 4 test W/O 11/23 – Thanksgiving break Friday, 12/11 – 2NW extra credit due Weight vs. Mass Mass is matter (atoms) Weight is the force of gravity acting on mass. Weight is represented by the symbol Fg Fg will always act on an object. How to Calculate force of gravity (weight) Note: when calculating Fg acceleration will always be 9.8 m/s2 Example – calculating weight (Fg) A child pulls a wagon with a mass of 6 kg, ten meters across the grass to the garage. The child applies a 10 N force to overcome 2Ns of friction. Calculate the weight of the wagon. G: m = 6kg E: Fg = (m)(a) U: Fg S: Fg = (6)(9.8) S: 58.8 N Practice calculating weight (Fg) Practice calculating weight (Fg) 245 N 14.7 N 1127 N How to calculate force Note: acceleration will not Be 9.8 m/s2 unless the object Is in free-fall. How to Calculate net force Net Force - answers Newton’s 2nd Law – Practice problem 1 A car has a mass of 550 kg. 1. Find the weight of the car on Earth 2. Find the net force needed to accelerate the car at 12 m/s2. 3. If a net force of 2200 N were to act on the car, what would its acceleration be? Newton’s 2nd Law – Practice problem 2 A sled weighs 2500 N on Earth 1. What is the mass of the sled? 2. What is the mass of the sled on the moon, where g = 1.6 m/s2? 3. What is the weight of the sled on the moon? 4. What net force is needed to accelerate the object at 4.0 m/s2 on the moon? Free body diagram (FBD) Pictorial representation of forces acting on an object. Free body diagram steps Replace the object with a dot. Identify the force pairs acting on the object Identify contact forces acting on the object. 1. 2. 3. • • 4. 5. Remember that only something that is physically touching the object can apply a contact force Possible types of contact forces – push, tension, normal, and friction Add arrows force and label the forces Add any force values that are known Example - FBD A child pulls a wagon with a mass of 6 kg, ten meters across the grass to the garage. The child applies a 10 N force to overcome 2Ns of friction. Calculate the weight of the wagon.