File
advertisement

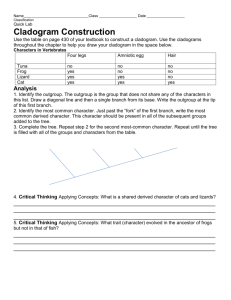
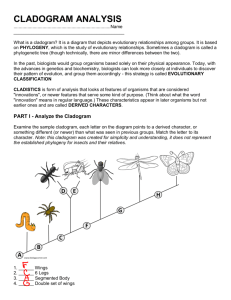
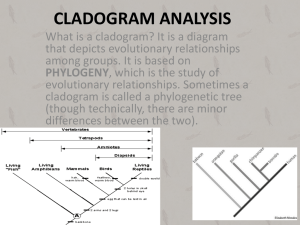
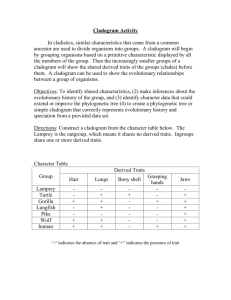
TRUE or FALSE 1. The brontosaurus never existed. 2. Pterodactyls are dinosaurs. 3. Birds descended from pterodactyls. 4. The far side of the moon is the dark side of the moon. 5. The sun affects tides on earth. 6. The sun is on fire. 7. There are nine planets in our solar system. 8. The north star Polaris, is the brightest star in the sky. 9. Stars twinkle at night. 10. Alan Shepard was the first American in space. 11. Sally Ride was the first woman in space. 12. There is no gravity in space. 13. Killer whales are not whales. 14. Goldfish have a memory of only 3 seconds. 15. Adding salt to water lowers its boiling point. 16. Speed and velocity are the same thing. 17. Weight and mass are the same thing. 18. Gravity is not always a downward force. 19. Hens will lay eggs whether or not a rooster is there. 20. A duck’s quack doesn't echo. 21. Bald eagles scream. 22. Birds will not abandon their nests if humans touch them. 23. Birds will abandon their eggs if human touch them. 24. Bats are blind. 25. Houseflies only live for 24 hours. 26. One dog year equals 7 human years. 27. Sunflowers track the sun. 28. Bathwater drains in opposite directions because of the coriolis effect. 29. Glass is actually a liquid. 30. Humans have more than five senses. 31. Different parts of your tongue taste different flavors. 32. Earth’s seasons are caused by the distance from the sun. 33. The equinox is a time of year when earth’s axis is perpendicular to the sun. 34. Lightning never strikes the same place twice. 35. Some meteorites are cold when they strike earth. 36. There is a chemical in some pools that changes color when people urinate in it. 37. The average person swallows eight spiders per year. 38. Alcohol kills brain cells. 39. The blood in your veins is deep red, not blue. 40. Blood turns from blue to red when it contacts the air. 41. Seismologists can accurately predict earthquakes. 42. Centrifugal force keeps liquids in containers as they are spun around. 43. The earth’s core is solid metal. 44. Most diamonds come from coal. 45. Galileo invented the telescope. 46. Watson and Crick discovered DNA. 47. There is no Nobel prize for mathematics. 48. Copernicus was the first person to suggest that the earth orbits the sun. 49. Charles Darwin coined the term “Survival of the Fittest”. 50. Correlation does not imply causation. Terms for Animal Groups A _________________ of crows. A _________________ of chickens. A _________________ of geese. A _________________ of whales. A _________________ of apes. A _________________ of camels. An _________________ of ants. A _________________ of cattle. A _________________ of alligators. A _________________ of seals. A _________________ of caribou. A _________________ of monkeys. A _________________ of cats. A _________________ of buzzards. A _________________ of porcupines. A _________________ of elephants. A _________________ of pigs. A _________________ of ferrets. An _________________ of caterpillars. A _________________ of sardines. A _________________ of quail. A _________________ of rhinoceroses. A _________________ of sharks. A _________________ of pelicans. A _________________ of wolves. A _________________ of raccoons. A _________________ of woodpeckers. A _________________ of rattlesnakes. An _________________ of frogs. A _________________ of fish. A _________________ of grasshoppers. A _________________ of eagles. A _________________ of kangaroos. A _________________ of sardines. A _________________ of leopards. A _________________ of sheep. A _________________ of lions. A _________________ of unicorns. A _________________ of deer. A _________________ of turtles. Dissection Safety Rules 1.) Do not engage in _______________! Common sense should rule here when working with ___________ instruments. 2.) ___________ the specimen to be _________________ securely in the dissecting ________ or tray. Never ________________ while holding the specimen in your _______________ 3.) Wear safety _______________ and a lab _________ in case of chemical spills. 4.) Remove any ______________ lenses so ______________ can not be trapped in your eyes by them. 5.) Point ______________ objects or tools away from yourself and others. 6.) Do not use excess _____________ when working with a sharp instrument such as a ______________. 7.) Use dissecting ______________ instead of a _____________ whenever possible. It tends to ____________ more efficiently for most work and is less ___________________ to use. 8.) Make certain to return your dissection ____________ to their appropriate container. Care for and __________________ of your dissection in accordance with the __________________ given by your instructor. 9.) Obviously one should not __________ or __________ in a laboratory where a ____________________ is occurring. Consequences Horseplay will result in a ________ and a referral to _____________________. * ________________ anything * ________________ of _____________________ * Unauthorized ____________________________ Each time you are told to put your ____________________ back on, you will lose ______________ points on your dissection. If your dissection ___________________ is not properly ________________ after the lab, you will lose __________ points on your dissection CLADOGRAM ANALYSIS What is a cladogram? It is a diagram that depicts evolutionary relationships among groups. It is based on PHYLOGENY, which is the study of evolutionary relationships. Sometimes a cladogram is called a phylogenetic tree (though technically, there are minor differences between the two). In the past, biologists would group organisms based solely on their physical appearance. Today, with the advances in genetics and biochemistry, biologists can look more closely at individuals to discover their pattern of evolution, and group them accordingly - this strategy is called EVOLUTIONARY CLASSIFICATION CLADISTICS is form of analysis that looks at features of organisms that are considered "innovations", or newer features that serve some kind of purpose. (Think about what the word "innovation" means in regular language.) These characteristics appear in later organisms but not earlier ones and are called DERIVED CHARACTERS. PART I - Analyze the Cladogram Examine the sample cladogram, each letter on the diagram points to a derived character, or something different (or newer) than what was seen in previous groups. Match the letter to its character. Note: this cladogram was created for simplicity and understanding, it does not represent the established phylogeny for insects and their relatives. 1. ______ Wings 2. ______ 6 Legs 3. ______ Segmented Body 4. ______ Double set of wings 5. ______ Jumping Legs 6. ______ Crushing mouthparts 7. ______ Legs 8. ______ Curly Antennae PART II - Create Your Own Cladogram To make a cladogram, you must first look at the animals you are studying and establish characteristics that they share and ones that are unique to each group. For the animals on the table, indicate whether the characteristic is present or not. Based on that chart, create a cladogram like the one pictured above. Cells Backbone Slug Catfish Frog Tiger Human DRAWING OF YOUR CLADOGRAM Legs Hair Opposable Thumbs Animal Symmetry and Phyla Animal Phylum Matching Instructions: Draw a line from the Phylum to the organism that matches it. Draw another line from the organism to its description.