Slide 2 - Fileburst
advertisement

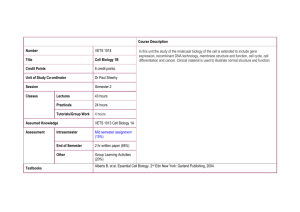
Biological Energy Generating biological free energy by Richard Berry http://www.mrc-mbu.cam.ac.uk/category/slideshows/atpmovies Slide 1: The mechanism by which cells convert energy from light and food into energy stored in ATP is based on membranes; most ATP is made using the free energy of pmf by ATP-synthase. (Movie © Medical Research Council, used by kind permission of John Walker.) “food” e.g. glucose electrons reproduction photons pmf ATP growth transport movement Slide 2: Generating ATP by charging and discharging a membrane capacitor. (Images bottom left and bottom right copyright © 2002 from Molecular Biology of the Cell by Alberts et al. Reproduced by permission of Garland Science/Taylor & Francis Books, Inc.) The mitochondrion Slide 3: Mitochondria. (Images courtesy of Daniel S Friend, taken from Molecular Biology of the Cell by Alberts et al. copyright 2002 Garland Science/Taylor & Francis Books, Inc.) Respiration “food” eg) glucose electrons reproduction photons pmf ATP growth transport movement Burning glucose: ΔG0’ = –1160 kBT Slide 4: “Burning” glucose in respiration. (Image bottom right copyright © 2002 from Molecular Biology of the Cell by Alberts et al. Reproduced by permission of Garland Science/Taylor & Francis Books, Inc.) oxidation of carbohydrate in the citric acid cycle (this fragment of is just a part) provides electrons carbohydrate two high-energy electrons from oxidation of sugar NAD+ H+ + 2e- NAD+ NADH NADHH NAD+ stores energetic electrons (with the help of a proton) to electron transport chain NAD+ H+ + 2eH hydride ion NADH H Slide 5: Key electron transport reactions within the citric acid cycle. (Images adapted from Molecular Biology of the Cell by Alberts et al copyright © 2002. Reproduced by permission of Garland Science/Taylor & Francis Books, Inc.) - 10-7 M H+ 1M NAD+ 1M NADH NAD+ + 2e- + H+ + 10-7M H+ 1atm H2 NADH Standard potential = –0.315 V: reaction proceeds in reverse 2e- + 2H+ H2 Standard potential = 0 V (by definition, this is the reference reaction) Slide 6: Measuring standard redox potentials. (Image copyright © 2002 from Molecular Biology of the Cell by Alberts et al. Reproduced by permission of Garland Science/Taylor & Francis Books, Inc.) overall: 2e- + 2H+ + ½O2 → H2O Slide 7: Electron transport chain – pumping protons. (Image copyright © 2002 from Molecular Biology of the Cell by Alberts et al. Reproduced by permission of Garland Science/Taylor & Francis Books, Inc.) protons move freely through water by hopping through the network of hydrogen bonds protons are readily donated to or accepted from water – electron transfer can be associated with the formation and breakage of a covalent bond to a hydrogen atom transfer of electron through a carrier can be coupled to the pumping of a proton across the membrane Slide 8: Coupling proton pumping to electron transport. (Images copyright © 2002 from Molecular Biology of the Cell by Alberts et al. Reproduced by permission of Garland Science/Taylor & Francis Books, Inc.) “food” e.g. glucose electrons reproduction photons pmf ATP growth transport movement FO H+ or Na+ F1 ATP ADP+ Pi Slide 9: Structure and function of ATP synthase. (Left-hand image reproduced from J.P. Abrahams et al. 1994 Nature 370 621–638 by permission from Macmillan Publishers Ltd, © 1994.) http://www.mrc-mbu.cam.ac.uk/category/slideshows/atpmovies Slide 10: ATP synthase in action. (Movie © Medical Research Council, reproduced by kind permission of John Walker.) http://www.mrc-mbu.cam.ac.uk/category/slideshows/atpmovies Slide 11: Catalytic cycle: ATP synthesis in F1. (Movie © Medical Research Council, reproduced by kind permission of John Walker.) Slide 12: Direct observation of rotation of F1 ATPase. (Image top-left from H Noji et al. 1997 Nature 386 299–302, reproduced by permission of Macmillan, © 1997. Movie bottom-left used by permission of Wolfgang Junge. Image right reproduced from Yasuda, R et al. Cell 93 1117–1124 © 1998 by permission of Elsevier.) Slide 13: Free energy accountancy: overall efficiency of conversion of glucose into ATP. “food” e.g. glucose electrons reproduction photons pmf ATP growth transport movement Slide 14: Light harvesting. Membrane structure of chloroplast Slide 15: Chloroplasts and mitochondria. (Left-hand image courtesy of K. Plaskitt, both images from Alberts et al. Molecular Biology of the Cell, reproduced by permission of Garland Science/Taylor & Francis Books, Inc. © 2002.) Slide 16: Electron transport and proton pumping in chloroplasts. (Image copyright © 2002 from Molecular Biology of the Cell by Alberts et al. Reproduced by permission of Garland Science/Taylor & Francis Books, Inc.) Photosynthetic Respiratory Slide 17: Comparison between respiratory and photosynthetic electron transport. (Left-hand image courtesy of K.N. Ferreira, both images from Alberts et al. 2008 Molecular Biology of the Cell, reproduced by permission of Garland Science/Taylor & Francis Books, Inc. © 2008.)