Chapter 8: The Federalist Era
advertisement

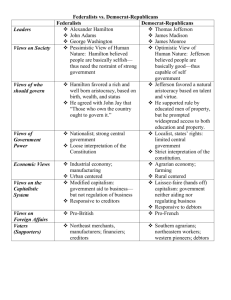
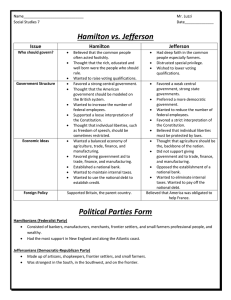
Chapter 8: The Federalist Era MULTIPLE CHOICE 2. As treasury secretary, Hamilton’s goal was to: a. repudiate the national debt. b. reduce the burden of federal taxes. c. create a vibrant, capitalist economy. d. All of the above are true. 4. America’s first vice president was: a. John Adams. b. Aaron Burr. c. Alexander Hamilton. d. Thomas Pinckney. 5. George Washington: a. won thirty-four of sixty-nine electoral votes to become the first president. b. was a reluctant president. c. traveled by coach from his home in New York to Washington, D.C., for his inauguration. d. is correctly represented by all the above statements. 6. Washington’s secretary of state was: a. John Hancock. b. Thomas Jefferson. c. James Madison. d. Edmund Randolph. 8. Alexander Hamilton: a. came from an aristocratic background. b. sought to tie the wealthy class to the government. c. generally favored a weak central government. d. said, “Those who labor in the earth are the chosen people of God.” 10. The question of assumption of the public debt: a. received little debate in Congress. b. was divided along sectional lines, eastern seaboard against western backcountry. c. was the subject of Hamilton’s “Report on Manufactures.” d. was resolved in a compromise involving the location of the national capital. 11. Madison and Jefferson objected to the national bank primarily because: a. they believed in a strict interpretation of the Constitution. b. they felt it was not powerful enough to meet the nation’s needs. c. it would cost the government too much money. d. it would be located in New York rather than Virginia. 12. The Tenth Amendment to the Constitution: a. said that powers not specifically given to the national government remained with the states or with the people. b. guaranteed certain civil rights for African Americans. c. guaranteed free speech and the right of assembly. d. prohibited the national government from interfering in the religious beliefs or practices of any citizen. 14. The emergence of political parties: a. reflected basic philosophical differences between Jefferson and Hamilton. b. was strongly encouraged by President Washington. c. resulted from a division between monarchists and republicans. d. brought the United States to the brink of civil war. 17. Thomas Jefferson: a. supported the vision of an urban, industrial America. b. respected tradition and upheld institutions like the established church. c. had wide-ranging intellectual interests that included science and the arts. d. paid little attention to the needs of small farmers. 18. When Britain and France went to war in 1793, President Washington: a. supported Britain because of its conservative government. b. supported France because of the American alliance with the French. c. expressed neutrality, warning the people of the United States not to aid either side. d. allied with other nations to oppose both Britain and France. 19. Edmond Genêt: a. came to the United States to escape the excesses of the French Revolution. b. encouraged Americans to attack foreign territory on the frontier. c. quickly won the sympathy of Alexander Hamilton and the Federalists. d. is correctly described by all the above statements. 20. As a result of Jay’s Treaty: a. the British agreed to evacuate northwest posts by 1796. b. the border with Canada was adjusted in favor of America. c. all American trade with the British West Indies was legalized. d. duties on most items imported from England were cut in half. 21. The Treaty of Greenville was an agreement between the United States and: a. England. b. France. c. Spain. d. Indians on the northwest frontier. 22. A key factor in encouraging the Whiskey Rebellion was: a. the opposition to drinking alcohol prevalent in the United States at the time. b. a tax placed on the frontier farmers’ most profitable commodity. c. Hamilton’s support of small farmers on the frontier. d. the development of improved rifles, which gave the frontiersmen an advantage over the army. 23. The Whiskey Rebellion ended when: a. Congress removed the tax on whiskey. b. the Federalists agreed to financial assistance for the disgruntled farmers. c. Washington sent an army to put down the revolt. d. a compromise was reached in which the leaders were executed and the tax was gradually lowered. 24. As a result of a treaty with Spain in the 1790s: a. the United States won the right to navigate the Mississippi River and deposit goods at New Orleans. b. Florida passed into the hands of the United States. c. Louisiana passed into the hands of the United States. d. the United States and Spain joined forces against hostile Indians in the Old Southwest. 26. In his farewell address, Washington: a. decried the growing spirit of sectionalism. b. discouraged the formation of political parties. c. urged the United States never to become involved in permanent alliances with foreign nations. d. All of the above statements are true. 30. The vote in Congress to create a national bank revealed: a. a growing sectional division in the young United States. b. a great sense of unity in America. c. the need to develop better banking practices in the United States. d. a hostility toward state banks. 32. The Virginia and Kentucky Resolutions argued that: a. states could decide if laws were unconstitutional. b. taxes imposed by Congress were unconstitutional. c. immigrants should be expelled from the country if they were not loyal to the American cause. d. the “freedom of speech” clause in the Bill of Rights did not apply to purely political rhetoric. 33. The conflict with France that erupted in 1798: a. was over debts still owed to France from the Revolution. b. led to an attempted French invasion. c. was an undeclared naval war. d. resulted in a decisive American victory. 35. In the election of 1800: a. Jefferson campaigned around the country. b. Jefferson was attacked as an atheist and a radical. c. Federalists enthusiastically united behind Adams. d. All of the above are true. 36. Jefferson’s election in 1800: a. continued the Federalist domination of the United States government. b. had to be settled by the House of Representatives. c. occurred because Aaron Burr agreed to withdraw as a candidate for president. d. was almost assured when George Washington announced his support of Jefferson just three weeks before the election.