Lab - Human Population Growth (Answer Key)
advertisement

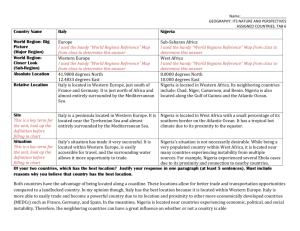
Laboratory: Human Population Growth Mrs. Côté Answer Key Enviro. Science 120 Pre Lab Work: Before beginning this laboratory, answer the following questions on your own piece of paper in your notebook: 1. Define the following terms: a. growth rate – describes how fast a population is increasing or decreasing and is dependent upon the birth rate and death rate b. birthrate – is the number of infants born in a given year/1000 people in the population c. death rate – is the number of people who die in a given year/1000 individuals in the population d. zero population growth – when the population is in equilibrium or the number of births and deaths are equal e. developed country – countries that highly developed economy and advanced technology f. developing country – countries that are considered to have low standard of living, and undeveloped industrially g. demographic transition – refers to the transition from high birth and death rates to low birth and death rates 2. What is a population explosion? How quickly is our population growing each year? What about each day? A population explosion is when a population lacks limited resources so is able to grow out of control. The human population is grows about 80 million a year and 219, 178 each day. 3. How is the growth rate of the human population calculated? Growth rate = birth rate – death rate 4. What causes a negative population growth? What causes a positive population growth? Negative population growth occurs when the birth rate is less than the death rate Positive population growth occurs when the birth rate exceeds the death rate 5. Why do the two graphs appear to have a different shape? The population growth rate was much slower in the earlier years. The J-curve shows exponential population growth and the graphs are not drawn to the same scale. 6. Using a piece of paper, create the following charts: Country USA Birthrate (%) 2.06 Death rate (%) 0.51 Population Growth 2005 0.92 Population Growth 2050 -0.06 Demographic Transition 1.55 Relative Place in Transition 5 Sketch graph showing Blue & Pink Line China 1.62 0.3 0.6 -0.98 1.32 6 Egypt 2.83 0.41 2 1.32 2.42 2 India 2.35 0.39 1.56 0.76 1.96 4 Italy 1.28 0.72 0.35 -1.33 0.56 7 Mexico 2.43 0.25 1.41 0.96 2.18 3 Nigeria 4.78 0.26 2.46 3.58 4.52 1 Analysis: Write the answers to these questions on your piece of paper. 1. Referring to the data, at what time in history does the data indicate a negative population growth? Which do you think played a greater role in the population decline – a change in birth rate or a change in death rate? What do you think might have caused this change? Between 1300 and 1400 there is a decrease in population. The death rate probably increased. This change was caused by the plague in Europe called Black Death. 2. When did the world’s population begin to increase rapidly? The most dramatic increase has occurred in the last half of the 20th century. 3. Graph B shows the growth in population over a 50 year period. Estimate the population when you are 50 years old. Between 8 and 9 billion as long as the current rate continues. 4. At the current growth rate, how many days did it take for the world population to recover from each of the following disasters? a. Approximately 200, 000 people killed by a cyclone in Bangladesh (1991) 200,000 ÷ 219,178 = < 1 day b. Three million deaths caused by a famine in India (1969-70) 3,000,000 ÷ 219,178 = 13.7 days c. The 21,000,000 deaths caused by an influenza epidemic in 1918 21,000,000 ÷ 219,178 = 95 days 5. List two social factors that contribute to each country’s relative place in transition. USA – capitalist country, industrialized and developed China – very developed, highly Egypt – becoming developed, less education/availability to birth control India – becoming more developed, technology growing Italy – currently a developed country Mexico – becoming more developed, more technology Nigeria – becoming developed, less education/availability to birth control 6. How do you suppose living conditions differ between the country ranked first with the highest demographic transition and the country ranked last with the lowest demographic transition? How would living conditions in these two countries affect both birth and death rates? Explain. The country ranked first (Nigeria) is an undeveloped country that is beginning to develop at a fast rate where the last ranked country (Italy) is a developed country that is slowing down in its development. Nigeria is a much more difficult and underprivileged country to Italy. In Italy they would have more technology and education regarding sickness and birth control causing it to have lower death rates and birth rates where in Nigeria they would not have as much use of birth control; however their lack of medicine technology may cause more deaths. 7. How does the shape of the population lines in each graph differ as you look from developed (highest ranked) to least developed (lowest ranked) differ? Explain why you believe they are different? As you go down in the ranks the graph of the population becomes less exponential right to the point where the 7th ranked country is becoming a negative growth rate. 8. How has technology affected the growth of the human population? Cite specific examples. Technology has increased the growth rate. Medical technology extends the life span and increases the birth rate. Advances in weather forecasting reduce the loss of life from major storms. Although some people die in automobile accidents, adding seat belts and air bags has reduced the death rate. The ability to transport the sick and injured to hospitals quickly and the medical technology available for treatment increase the survival rate. Vaccines have reduced the incidence of disease, and, in the case of smallpox, completely eradicated the disease. Technology has increased our ability to produce food and reduce the death rate due to starvation. Students will think of other ways that technology has contributed to an increase in growth rate. 9. How do highly populated countries such as India and China reduce or regulate population levels through legislation and policy? Populations have been controlled through limited numbers of children per person, family planning organizations, contraceptive courses and availability, and forced sterilizations. 10. Many scientists agree that without limits to population growth, we will destroy the planet. But some people think that the human population differs from other populations because humans can use technology. Do you think the human population is reaching the earth’s carrying capacity? Explain. Opinion answer – varied: No one really knows how many people the earth can support — the earth’s carrying capacity. Most scientists believe that the concept of carrying capacity does apply to the human population. Although the world population has not reached the carrying capacity of the planet, some parts of the world have exceeded their ability to produce food needed to sustain the population. Technology has improved our ability to provide food and other natural resources such as fossil fuels. But many scientists believe that we are providing for 6 billion people with resources that will be needed by future generations. The growth in the production of food has slowed and is not keeping pace with the growth in the population, but it is too early to tell if we are reaching the limits of the “ecosystem” to provide, or if new technology will come to the rescue. 11. Describe the relationships between the growth of the human population and the following environmental factors. a. Forests - loss due to increased demand for wood products and fuel; development of forests for housing, roadways and farming. Link to biodiversity (see description below). b. Prime farmland - disappears as land is developed to provide housing, shopping centers and roadways. c. Toxic chemicals - increase as more pesticides are used to ensure the harvest and storage of food; increase with greater demand for consumer products. d. Climate - is getting warmer as increased combustion and higher carbon dioxide emissions enhance the greenhouse effect (global warming). Link to flooding (see preceding description). e. Energy - increased need for energy leads to increased impacts from mining of coal, transportation of oil, cutting of wood and use of land for solar collectors or wind farms.