How Populations Change in Size (Section 8.1)
advertisement

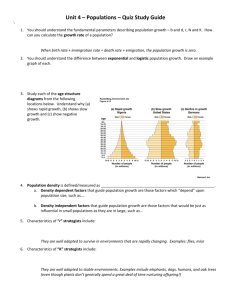
How Populations Change in Size Section 8.1 Objectives: 1. Describe factors affecting population growth. 2. Describe regulation of population size in nature. 3. Describe the relationship between carrying capacity and population size. Two Types of Growth You have just been offered a job that will last one month. You have two salary options. You can either receive $10 a week with a $5 per week raise every week, or you can receive one penny for your first day on the job, and then double the previous day’s pay for each of the remaining 30 days. Calculate your month’s pay for each salary option. Which pay option would pay more? What Is a Population? Definition: all members of a species living in the same place at the same time Examples of populations in your neighborhood: Properties of Populations Size Density 1. 2. Dispersion 3. The number of individuals per unit area or volume EX: number of bass per cubic meter of water in a lake The distribution or arrangement of a population’s individuals within a given space Can be even, clumped, or random Classroom Density activity Classroom Density Activity 12 volunteers Make a 2m x 2m square All 12 students stand in the square. Calculate the DENSITY of that population of students - #students/m2 Expand the square to 4m x 4m. Recalculate the density. Which population has the higher density? WHY? How Does a Population Grow? What would cause an increase in a population? What would cause a decrease in a population? Growth rate A change in the size of a population over a given period of time Growth rate = births – deaths Can be positive, negative, or zero Quick Lab: Population Growth (p.198) – CALCULATORS!!! Year Starting Births Deaths Ending 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Graphing Skills Review 1. 2. 3. 4. Descriptive title Label each axis Even intervals ??? Post-lab Questions What type of growth does the graph indicate: linear growth or exponential growth? Calculate the 10-year growth rate using the formula: Growth rate = Change in population Time Compare this to the growth rate from Year 1 to Year 2. How Fast Can a Population Grow? Reproductive potential The maximum number of offspring that each member of the population can produce Varies WIDELY Higher if an organism produces more offspring at once, reproduce more often, and reproduce earlier in life Exponential growth Growth goes faster and faster EX: 2 dogs give birth to 6 puppies. Each pair then gives birth to 6 puppies. Breck Shampoo Commercials You tell 2 friends, and they tell 2 friends, and so on, and so on, and so on, …… What Limits Population Growth? 1. Carrying capacity: a. the maximum population that an ecosystem can support indefinitely. b. Can be determined by available food, shelter, or breeding sites. c. See Figure 5, p.200 Chapter 8 Population Changes & Carrying Capacity What Limits Population Growth? (cont.) 2. Resource limits – a population cannot consume more of a resource than is available. 3. Competition within a population – a. As a population reaches its carrying capacity, its members must compete with each other for resources. b. They may also compete for dominance or for a territory. Two Types of Population Regulation Density dependent 1. Deaths occur more quickly in crowded populations Causes: limited resources, predation, and disease Density independent 2. Certain number of deaths regardless of density Causes: severe weather and natural disasters Self-Check Quiz 1. How are disease and predation densitydependent? 2. What are some examples of resources that could determine carrying capacity in an ecosystem? Assignment #44 Math Practice (p.201) Section Review (p.202): 1, 3, 6 Answer in complete sentences! For Question #6, read the Ecofact on page 200 and the last paragraph on page 200. Draw a 2circle/oval Venn diagram to compare the two histories.