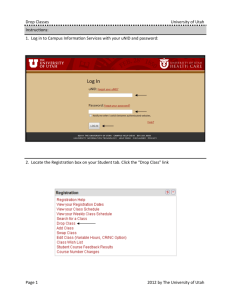
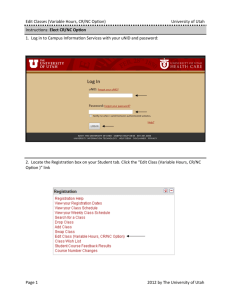
Review for Chapter 7 - Mount Logan Middle School
advertisement

Utah in the Modern Age This is a no gum class. Please dispose of it properly! Take out all of your papers from Utah Studies. Take out the ‘End of the Cold War’ and any other papers you have, then work on your study guide. If you are 100% finished with your study guide (including every question, all parts of the vocabulary, and the essays), show it to me. If I agree that you are done with everything, then you can work on any other missing/incomplete assignments. The Cold War inspired musicians just like WWII, the war in Vietnam, and other conflicts did before. In the 1980s, many songs reflected fears of nuclear war, the desire for peace and anger at the governments/leaders of the U.S. and U.S.S.R. for not being able to resolve the conflict. Where should your backpack be? This is a no gum class. Please dispose of it properly! Take out all of your papers from Utah Studies. If you are 100% finished with your study guide (including every question, all parts of the vocabulary, and the essays), show it to me. If I agree that you are done with everything, then you can work on any other missing/incomplete assignments. The 1980s saw the beginning of ‘pop’ music, songs that are designed to be ‘popular’. They are criticized as being too simple in style and lyrics, but typically sell well because of their fun sound. During the ‘80s, Rock and Roll took interesting turns with the development of Punk, Heavy Metal and Hair Bands. Latin music became a permanent fixture of the music charts, and Rap and Hip Hop were first heard on the airwaves. Where should your backpack be? This is a no gum class. Please dispose of it properly! Pick up your study guides from the front table. Review for the test. Put your turquoise checkout paper in your box. With the Internet becoming available to almost everyone, access to music also skyrocketed. During the 1990s, people diversified their musical genres with downloading services like Napster, the forerunner of Pandora and Spotify. Where should your backpack be? 1. Check your grades. 2. How did World War II affect the people and industries of Utah? 3. Why do immigrants come to Utah today, and what challenges do they face? 4. How is Utah being affected by major events happening today? History Objective – We will prepare for the exam by reviewing the study guide. Language Objective – We will listen to, give answers and write the important details from the activity. Behavior Objective – Participation & Work Ethic: We will listen to each questions, answer the ones given to us, and write the important details in our notes. 33. How has the economic recession changed Utah’s economy? Although Utah has had a stronger economy than many states during the recession of 2008-2012, many jobs were lost, many people had to move away from Utah, and gov. spending on education and many other important programs, etc. decreased. 32. How has/did the wars in Afghanistan and Iraq affected Utah? Soldiers from Hill Air Force Base and Utah reserve soldiers have been called up for duty many times. Utah, like the rest of the country, has been affected by the cost in lives and money from these wars. It is estimated that the U.S. has spent 2-6 trillion dollars on the wars and related costs. Over 5000 soldiers have died and more than 50,000 have been wounded in the conflict. 31. Explain the origins of the War on Terrorism. The U.S. has had conflicts with countries in the Middle East for 30 years, and problems between the Middle East and Western countries (Europe & U.S.) can be traced back hundreds of years. Some, like Iran, don’t trust the U.S. because of coups staged in the ’70s and ‘80s. Many Islamic militia fighters (Bin Laden) were trained by the U.S. to fight the U.S.S.R but turned against the U.S. when American forces did not leave Saudi Arabia, etc. U.S. support of Israel has also been a source of conflict. 2) 3) 30. How did the U.S. defeat the U.S.S.R. in the Cold War? The U.S. spent 1.5 trillion $ to arm the U.S. and our allies. The U.S.S.R tried to keep up while still taking care of their people, and their country went bankrupt as a result of the massive spending. The Soviets’ agreement to give basic human rights to all of their people encouraged thousands to protest and eventually try to break away from the U.S.S.R. The leader of the Soviet Union, Mikhail Gorbachev, believed that people should not be forced to stay in the U.S.S.R. and allowed countries like Poland, East Germany, etc. to have sovereignty for the first time since WWII. 29. What are some of the things an immigrant needs to accomplish in order to become a citizen? -18 years old -lawful resident of the U.S. for at least 5 years -read, write, and speak English -show knowledge of U.S. history and government -believe in the U.S. Constitution -like the U.S. -pass an interview and test -swear an oath of loyalty to the U.S. 28. What are some ways immigrants preserve their cultural identity? -celebrate traditional holidays/festivals -meet with other residents who share their culture -keep practicing their home language, culture, customs -share their culture with their community 27. What issues do immigrants face in adapting to life in Utah? They need to learn about the language, money, how to shop for things they need, get a job, find housing, fit in with their community, etc. 26. Why are immigrants still coming to Utah? What country has the largest numbers of immigrants come from in recent years? -To join family already here, to find work or better jobs, get away from war, get an education, escape persecution in their home counties. -Mexico 25. Describe the excitement in Utah over the 2002 Olympics and how the Olympics affected the state. The Olympics were the most complex event Utah has ever organized. People across the state volunteered to help with the games, worked at the venues, watched the games on TV or went to the events. It brought a lot of positive publicity to the state which boosted tourism, promoted job growth, and promoted a positive image of Utah and more. 24. Describe the transformations that have occurred in the Computer Age. Technology became an everyday part of people’s world. Almost everyday we use TVs, cars, computers, mp3 players, cell phones, etc to make our lives easier, but also add complications from always being ‘plugged in’. 23. What role did Utah play in helping the first man to land on the moon? Utah companies like Thiokol, Sperry Rand, and Hercules built rocket boosters and propulsion systems. 22. Compare the way ethnic groups and whites were treated before and after the Civil Rights Law of 1964 was passed? Many minorities were segregated from the white population, often they were kept from voting, and faced discrimination in employment and everyday life. The Civil Rights Law made it illegal to discriminate against people because of their race, religion, gender, etc. helping everyone to be treated fairly. 21. Who was Martin Luther King, Jr. and what did he do in this chapter? He was an important leader of the Civil Rights movement who lead peaceful protests across the U.S. to promote racial equality. He visited Utah to encourage civil rights laws to be passed here. 20. Describe the Civil Rights movement and Utah’s involvement in it. Like many states, Utah had laws in the past that allowed racial discrimination like segregation. Utah passed laws in the ‘40s and ‘50s to outlaw discrimination voting, public places, etc. 19. How did the war (in Vietnam) affect the people of Utah and the United States? Utahns were divided about the war. Many supported the war, while others protested it. Many refugees from Vietnam, Laos and Cambodia settled in Utah. The U.S. was demoralized about the end of the war in the ‘70s. 18. Describe how the war began and the events that took place during it. Vietnam began as a civil war between the communists in North V. and people in the South. The U.S., China , and the U.S.S.R. supplied weapons to either sides of the conflict. 3 million Vietnamese were killed, their country devastated, and over 50,000 U.S. soldiers died in the war. 17. What effect did this [the freeway system] have on the growth of new communities? The freeways made it easier to travel across the country and lead to the growth of suburban communities. These communities combined the benefits of cities with a more rural setting. Suburban growth allowed many families to have more space and privacy, but promoted segregation, poverty, and other problems in cities. It also lead to people leading less efficient, consumer lifestyles. 16. How did the country improve transportation after WWII? The government spent vast amounts of money to create the interstate Freeway system, a system of national airports (like SLC international), improve roads, ports, and international trade. 15. What happened to Moab’s mining industry at this time? Uranium mining became a leading industry in Moab for twenty years, providing enough money for the area to promote tourism to areas like Arches when the government no longer needed as much uranium. 14. Describe the events that led to the war in Korea and the war itself. Korea was divided at the end of WWII into North Korea, which was communist, and South Korea, which was pro-capitalism. With the support of the U.S.S.R N. Korea invaded S. Korea. The United Nations, especially the U.S., fought to free Korea. The war ended in a cease fire. 13. Who was Philo Farnsworth and what did he do in this chapter? 12. Describe the invention of the television and how it affected people’s lives. 11. How did the Cold War boost Utah’s defense industry? 9. Describe some of the major events of the Cold War. (7-10) 9. What was the Cold War and who were the opposing sides in it? 8. Describe how the war ended in Europe and the Pacific. Europe 8. Describe how the war ended in Europe and the Pacific. Pacific 7. What was life like in camps like Topaz? The The 6. Why were Japanese Americans relocated to camps during the war? Wartime hysteria (fear) and prejudice lead many to think that Japanese Americans could be spies working to subvert the U.S.’s war effort. This proved to be false, and Japanese Americans returned to find that most of their possession, homes, and businesses had been lost, destroyed or occupied costing these families millions of dollars. 5. How did the Navajo Code Talkers help the U.S. win the war? 4. Why was Utah a good resource to help the government during the war? 3. Describe the causes and some of the major events of the war. (7-10 causes/events) 2. Why did the Japanese bomb Pearl Harbor? The U.S. was worried that Japan was becoming too powerful so they restricted trade (especially oil) with Japan. The U.S. also did this to stop/protest the Japanese invasion of other Asian countries like China. 1. How did the United States become involved in the war? Pearl Harbor, Hawaii was attacked by Japanese forces. The U.S. had already agreed to help end the war in Europe if they were drawn into the conflict so the U.S. put most of its efforts into winning the war in Europe while also fighting in the Pacific. Check for gum under your desk and clean it if you find it. Otherwise your class will lose the privilege. Get out your papers for chapter 13. Put them in this order then staple them: Study guide – top Blue Grey Pink - bottom Pick up your folder from the PTC bins back in the northeast corner of the room. (Some students took them home at Conferences.) Work on any incomplete questions. Don’t worry about doing the essay right now unless it is the only thing you have left to do. Where should your backpack be? Take the Chapter 13 test. You can take it 3 times, and it will show you any questions you got wrong so you can fix them next time. Check your grades on the ipad and turn in any missing work to the late box. Pick up your plastic and paper folders from the back of the room. Take home any assignments you want to keep, recycle the rest. Turn in your plastic and paper folders to the correct pile at the front of the room. You make take home your PTC folder. Pick up and fill out your check out paper. If there is time, you can take the extra credit states test. 1. How did Utahns keep up with the changes that happened in the later half of the 1900s? 2. How did World War II affect the people and industries of Utah? 3. Why do immigrants come to Utah today, and what challenges do they face? 4. How is Utah being affected by major events happening today?