Victorian Curriculum F*10 History Primary School Presentation
advertisement

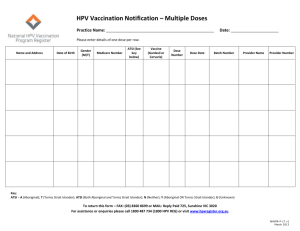
Victorian Curriculum History F–6 Familiarisation Gerry Martin Acting Curriculum Manager History and Civics and Citizenship Key features • Structured as a learning continuum that enable teachers to identify the current levels of achievement and then plan for progression • Includes 11 levels for English and Mathematics and bands (5 or 6) for all other Learning Areas and Capabilities • Levels A-D supporting students with disabilities • Cross-curriculum priorities (Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander histories and culture, Asia and Australia’s engagement with Asia, and Sustainability) are embedded in the Learning Areas and Capabilities, not represented as additional or separate curriculum • 4 rather than 7 capabilities included in the curriculum. Additional 3 general capabilities in the Australian Curriculum are Literacy, Numeracy and ICT. Teachers will develop students’ learning of literacy, numeracy and ICT across the curriculum. These capabilities are incorporated in the learning areas and do not require separate treatment. Overview The History curriculum is written for Levels F – 10. The Humanities include four disciplines Economics and Business Geography Civics and Citizenship History The Humanities Key changes • Historical methods and procedures are strengthened and explicit in both strands • Two strands o Historical Concepts and Skills o Historical Knowledge • Removal of duplication and pedagogy o Historical questions and research (Australian Curriculum) now sits in the Critical and Creative Thinking Capability- Questions and Possibilities o Explanation and communication- is the product of student historical thinking Key changes • 11 levels changed to five bands o 2 level bands e.g. Level 3-4 o Achievement Standard at each two level band o Consistent with other learning areas o Strengthen curriculum coherence o Greater flexibility for schools in how to organise the delivery of the history curriculum History Structure Key Changes • F–2 consolidated from three contexts to two to remove duplication and repetition. Renamed as Personal Histories and Community Histories • Levels 3-4 Community and Remembrance has been renamed Community, Remembrance and Celebrations • Richer material has been included to strengthen the historical content. Level 3-4: o One significant narrative, myths or celebration from the past (VCHHK075) Strand: Historical Concepts and Skills Key Changes: • Historical Skills strand has been renamed Historical Concepts and Skills. • Historical perspectives and historical interpretations are sub-strand descriptors under the skill ‘Use historical sources as evidence’ • Clear progression of concepts and skills F–10 • Concepts are explicitly emphasised in the strand Historical Knowledge • Located at the beginning of each level to emphasise the discipline of history. • These are explained in the Learning in History Strand: Historical Concepts and Skills determining historical significance sequencing chronology using historical sources as evidence analysing cause and effect identifying continuity and change Progression of concepts and skills Identify Continuity and Change F-2: Identify examples of continuity and change… 5-6: Identify and describe patterns of continuity and change… 3-4: Identify and describe continuity and change over time… 9-10: Identify and evaluate patterns of continuity and change… 7-8: Identify and describe patterns of continuity and change in society and daily life… Scope and Sequence Progression of Historical Concepts and Skills Achievement Standards at two level bands Strand: Historical Knowledge Levels Historical Concepts and skills are explicit. 3 and 4 First contacts The diversity and longevity of Australia’s first peoples and the significant ways Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples are connected to Country and Place (land, sea, waterways and skies) and the effects on their daily lives (VCHHK078) The journey(s) of a significant world navigator, explorer or trader up to the late eighteenth century, including their contacts with and effects on other societies(VCHHK079) Stories of the First Fleet, including causes and reasons for the journey, who travelled to Australia, and their experiences and perspectives following arrival(VCHHK080) The nature of contact between Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples and others, for example, the Macassans and the Europeans, and the effects of these interactions (VCHHK081) Victorian Curriculum Website Lets explore Capabilities It is a whole-school decision on how the capabilities are to be taught. Learning Areas do not have to integrate all the capabilities into all of their curriculum. Whole-school planning is fundamental. Example 1 Levels 3 and 4 Historical Concepts and Skills Strand • • • Identify the origin and content features of primary sources when describing the significance of people, places and events Describe perspectives of people from the past Identify and explain the causes and effects of European settlement and exploration Historical Knowledge Historical Concepts and Skills Critical and Creative Thinking Historical Knowledge Strand • The nature of contact between Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples and others, for example, the Macassans and the Europeans, and the effects of these interactions • Questions and possibilities • Reasoning Example 1 Levels 3 and 4 • • Focus Question: What was the effects of contact between Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples and early traders, explorers and settlers? Activity: 3-2-1 Bridge 3 thoughts/ideas 2 questions you have 1 example from the source Repeat for each source Bridge: Explain how your response to each source connects and changes from your initial response. Harvard Project Zero. (2009). 3-2-1 Bridge. Available: http://www.visiblethinkingpz.org Liardet, W. F. E. (1875) A corroboree on Emerald Hill in 1840, Available at: http://digital.slv.vic.gov.au Schramm, Alexander (1850) A scene in South Australia Available at: Art Gallery of South Australia, http://www.artgallery.sa.gov.au Mundy, Godfrey (1852) Mounted Police and Blacks' depicts the killing of Aboriginals at Slaughterhouse Creek by British troop Available at the Australian War Memorial Locating information Curriculum Resources and Support Support Phase 1: Professional learning for principals/curriculum leaders Phase 2: School-based planning Phase 3: Professional learning in specialist areas Curriculum planning • Is not the responsibility of the individual teacher – it is a team effort • Recognises that we are educating the whole child across many years of schooling curriculum is designed as a continuum of learning • Without the “what” students should learn, pedagogy is a process without purpose • Deep familiarity with the curriculum is essential Curriculum Planning Curriculum Mapping Templates Timelines Implementation of the new Victorian Curriculum can commence in individual schools as soon as they choose, with all schools required to implement the new curriculum from the start of 2017. In other words, schools will have the remainder of 2015 and all of 2016 to prepare for full implementation in 2017. 2015-16 • • AusVELS curriculum • available AusVELS website • archived December 2016 From 2015 Victorian Curriculum available Full implementation from 2017 Assessment “ .. the fundamental purpose of assessment is to establish where learners are in their learning at the time of assessment.” Reforming Educational Assessment: Imperatives, principles and challenges Masters, G. ACER 2013 Supporting learning • The most important single factor influencing learning is what the learner already knows. Ascertain this and teach him accordingly (Ausubel 1968) • Vygotsky (1978) referred to the ‘zone of proximal development’ the region of ‘just manageable difficulties’ where students can succeed but often only with the support of others for example through scaffolding activities. • … learning is enhanced when teachers pay attention to the knowledge and beliefs that learners bring to the learning task and use this knowledge as a starting point for new instruction (Bransford et al 2000) Summary • Discipline of History is strengthened • Duplication and repetition eliminated • Greater clarity • Consistent and explicit use of historical concepts • Clear progression Strand • Historical Concepts and Skills • Disciplinary concepts and skills are explicit • Progression of concepts and skills Strand • Historical Knowledge contexts • Historical concepts are explicit within the knowledge content descriptors • Achievement Standards • Progression of concepts and Achievement skills Standard Contact Gerry Martin Acting Curriculum Manger History and Civics and Citizenship Telephone: 61 3 9032 1694 Mobile: 04 3911 3496 e-mail: martin.gerard.f@edumail.vic.gov.au Additional contact details VCAA websites Victorian Curriculum http://victoriancurriculum.vcaa.vic.edu.au/ Curriculum Planning Resources: http://curriculumplanning.vcaa.vic.edu.au/home Contacts Sharon Foster Manager Victorian Curriculum Phone: (03) 9032 1680 Email: foster.sharon.a@edumail.vic.gov.au