Africa: Governments
advertisement

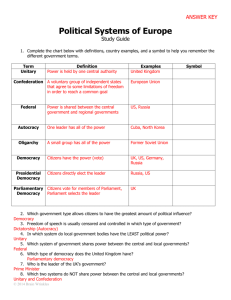
Africa: Governments SS7CG1; SS7CG2 Citizen Participation in Govt. CITIZEN PARTICIPATION • In each country, the people have different rights to participate in the government. – In some countries, any citizen can run for office or vote in elections. – In other countries there are restrictions placed on who can run for office and who can vote. – There are also countries where no citizen can vote and there are no elections. TYPES OF GOVERNMENTS •Autocratic •Oligarchic •Democratic AUTOCRACY • Oldest form of government. • One of the most common forms of government. • Maintain power through inheritance or ruthless use of military and police power. AUTOCRACY • Has a single ruler with unlimited power. • Citizens have no ability to participate in the selection of the ruler or the creation of laws. • Positive: Decisions can be made quickly. • Negative: Needs of the people may be ignored. AUTOCRACIES OF THE WORLD OLIGARCHY • “Rule by a Few” = country is ruled by a small group of people. • Compared to Autocracies, more people are involved in the decision-making process. • Citizens still do not participate in the government. • Leaders get power through military, wealth, religion, or social status. DEMOCRACY • The people are in charge of the government because they can VOTE! • All citizens have the opportunity to be leaders, vote for leaders, and vote for laws. • All citizens participate in the decision-making process. • All groups are represented. • Negative: May be slow moving because all citizens must meet together to discuss and vote on issues. *This is a “Polity Data Series Map” It tries to measure a country’s true democracy in government. It gives scores of -10 to +10. The countries in the lightest pink have the highest democracy score; darker colors have lower scores. HOW GOVERNMENTS DETERMINE CITIZEN PARTICIPATION High Participation Low or No Participation Low or No Participation AUTOCRACY OLIGARCHY DEMOCRACY Parliamentary vs. Presidential Democracy • PARLIAMENTARY: – Legislative and Executive Branches are the same. – Power is in the Parliament. – People elect Parliament; Parliament elects leaders. • PRESIDENTIAL: – Legislative and Executive Branches are separate. – Power is divided between Federal and State governments. – People elect both the Legislative and Executive Branch leadership.