Power corrupts, and absolute power corrupts absolutely.
advertisement

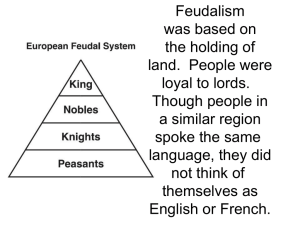
Absolutism Enduring Understanding: How people view an action determines how they will respond to that action. Conceptual Unit Question: How much power should one person or institution have? Power tends to corrupt, absolute power corrupts absolutely. Great men are almost always bad men.“ ~Lord Acton, 1887 Absolutism in Context During the Middle Ages the Church was looked to as the power and authority. During the Renaissance the Church was still powerful but there was shift toward secularism. Absolutism in Context The Reformation brought a complete break with the Catholic Church for much of the population of Europe. As church power diminished there was an increase in the power of a central monarch who was an absolute ruler. What is Absolutism? Political system in which total power is vested in a single individual usually a monarch (king or queen). The opposite of a constitutional government like the United States. Distinguished from democracy by the unlimited power claimed for one ruler. Power of a Monarch In the seventeenth century people looked to the monarch for political stability Absolute monarchs could make laws, levy taxes, administer justice, control the state’s officials, and determine foreign policy. No Rights for People Citizens had no say in matters of government. There were no written Constitutions or Bills of Rights Most people did not have any political rights at all. Absolutism-Vocabulary Monarch-a king or queen who rules a state or territory, usually for life and by hereditary right Arbitrary- rule based solely on personal wishes, feelings, or perceptions, rather than on objective facts, reasons, or principles Dynasty- a family that rules based on the idea that divine right is passed down from one generation to the next. Do you have rights? What are some rights you have and how are these rights guaranteed by law? Who Pays? Where did the money come from that supported the king or queen? TAXES!! Where Did Their Power Come From? Where did the king or queen’s power come from? GOD! Rule by Divine Right The political idea that a monarch received their power directly from God and were responsible only to God for their actions. This allowed monarchs to go unchallenged by their subjects. Absolute Monarchs We Will Learn About Louis XIV of France-Palace of Versailles as a symbol of royal power Peter the Great of Russia-City of St Petersburg and the westernization of Russia End PPT French Wars of Religion The French religious wars of the sixteenth century pitted Protestant Calvinists against Catholics. From 1560 to 1650, wars, including the devastating Thirty Years’ War, and economic and social crises plagued Europe. European monarchs sought economic and political stability through absolutism and the divine right of kings French Wars of Religion Causes Calvinism and Catholicism were becoming militant Aggressive tactics were being used to get converts There was a Catholic monarch, but the nobles were mainly Protestant Many Nobles were becoming Huguenots Age of Absolutism ENDURING UNDERSTANDINGS: Students will understand: The variety of ways monarchs held and exercised power People are not born equal Leaders have the right to control their citizenry The relationship of religion and political authority When a ruler’s power goes unchecked great changes will occur The personal beliefs of a leader greatly influence his/her course of action Characteristics of absolute monarchies Power in most European states was concentrated in the monarch: Centralization of power Concept of rule by divine right Gradually religious toleration emerged, along with democratic thought