Lab1.introduction and epithelium(zhou)
advertisement
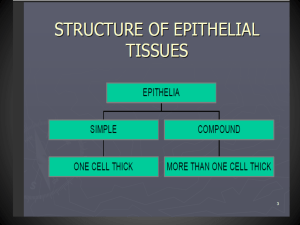
Histology Lab 1 Introduction and Epithelium Jun Zhou(周俊), Ph.D & M.D School of Medicine,Zhejiang University Note: Please come lab on time. Find your seat according your lab number. Your final score is composed of four parts 1) Attendance and picture drawing:10% 2) Quiz: 15% (each quiz 5%) 3) Final lab test: 25% 4) Final written examination: 50% How to pass this course: Final score>60 and Final written exam>50 Lab facilities: 1 Light electron microscope with computer 1 case of slides 1 atlas http://m-learning.zju.edu.cn 1.Students share these facilities 2.Do not take them out the laboratory with you. 3.Put them where they belong to when lab is over. 4.Do not left any rubbish after you. 5.No food in the lab. 6.Lecture and lab slides online: m-learning.zju.edu.cn 2015 Histology and Embryology Contents of Lab 1: 1. Introduction 2. Epithelium 1)Simple squamous epi (small intestine,stomach) 2)Simple cuboidal epi.(thyroid) 3)Simple columnar epi.(small intestine)(drawing) 4)Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epi.(trachea) 5)Stratified squamous epi.(esophagus) 6) Transitional epi.(bladder) 3.Lab report (content of lab , drawing) Tissue Processing 1.Fixation: 10% Formalin 2.Dehydration:graded concentrated ethyl alcohol 3.Clearing:xylene,infiltrate with paraffin solvent. Loss of fat due to ‘clearing’ Tissue Processing 4.Embedding 5.Sectioning Tissue Processing 6.Staining Common Stains: Hematoxylin & Eosin Ross, 5th ed, fig 1.1 Common Stains Hematoxylin and eosin ("H&E") Wright’s stain Relative Sizes in Histology Standard Units of Measure Relative Sizes in Histology Standard Units of Measure micrometer: 10-6 meter nanometer: 10-9 meter Changes in apparent shape, due to orientation of sections Ross, 5th ed, fig 1.11 Changes in apparent shape, due to orientation of sections Netter/Ciba Junqueira fig 1-30 Epithelium Epithelium •No blood vessles, nourishment is by diffusion •Epithelium is innervated •polarization Trachea Classification of Epithelia •Number of cells •Shape of surface cells 1. Simple 1. Squamous 2. Pseudostratified 2. Cuboidal 3. Columnar 3. Stratified 4. Transitional Stomach (NO 25): mesothelium HE ×400 Simple squamous epi. Small intestine (NO 1): endothelium HE × 400 Thyroid (NO 35): HE × 100 Thyroid: HE × 400 Simple cuboidal epi. Small intestine (NO 1): villus HE × 400 (Drawing ) Simple columnar epi., Goblet cells, striated border (microvilli) Trachea Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epi Trachea: HE × 400 Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epi. Esophagus (No.2) Stratified squamous epi. Esophagus: HE × 100 Transitional epithelium distended contracted Bladder Bladder (NO33): HE × 40 Bladder: HE × 100 Transitional epi. Bladder: HE × 400 Transitional epi. The end!