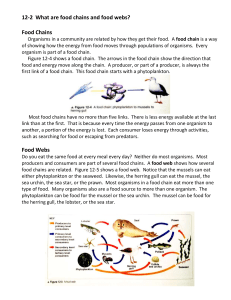
Flow of Energy
advertisement
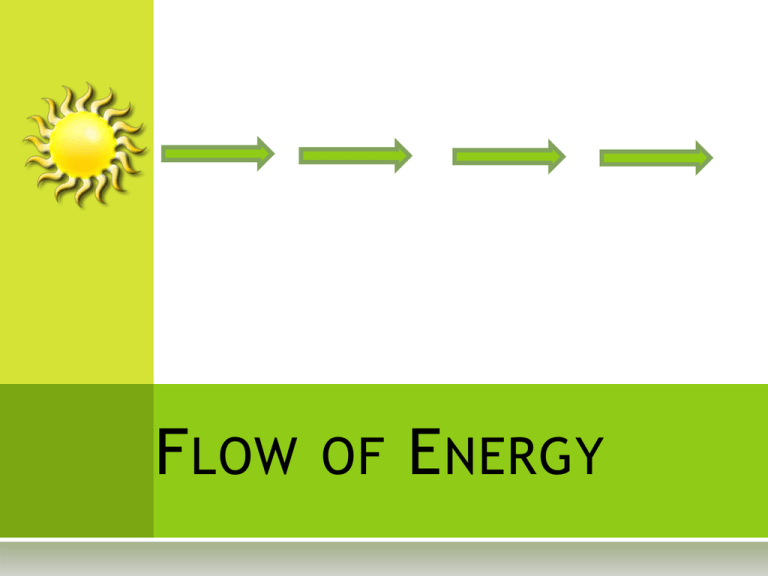
F LOW OF E NERGY S OURCE OF E NERGY Sun = Sol Raise your hand if you included this on your schoolyard diagram. The Sun provides the light and heat energy for most forms of life on Earth. P RODUCERS Producers chemically change solar (light ) energy in the chlorophyll (the green color in the plant) into their food. Plants are producers. F OOD Plants make this food for their own use. They need the energy to survive and thrive. Plants store the food in many places: roots, stems, leaves, and fruits. Plants make food during the process called photosynthesis. P HOTOSYNTHESIS To undergo photosynthesis, plants need: Sunlight Water Carbon dioxide P LANTS U SE THEIR FOOD Plants use food to grow. Plants use stored energy (food) when the resources they need to grow and thrive are unavailable. Plants use food to survive harsh environmental conditions, such as drought or cold winters. C ONSUMERS Consumers are organisms that get their energy by eating either producers (plants) or other consumers (animals). They use this energy to survive, grow, and reproduce . F LOW OF ENERGY Let’s look at some of the diagrams you completed in your science notebook on the first day of this lesson. What do they have in common? F OOD C HAINS When energy is transferred through organisms it is called a food chain. Arrows are used to show the direction the energy is flowing. In the schoolyard, you might see: Remember, nearly every food chain starts with energy from the Sun. E XAMPLE Use the strips of paper to create a food chain for organisms that live in one of the Earth’s ecosystems. It might be the Arctic or the ocean, forest or desert, grassland or jungle. Cut six strips of paper of different sizes, as shown here. Color the widest strip yellow. This will represent the Sun. E XAMPLE Plant Carnivore Write the name of a plant on the second widest strip of paper. On the third widest paper, write the name of an organism that eats the plant. On the fourth widest, write the name of an animal that eats the organism on the second strip. On the fifth and sixth strips, continue the sequence. If you are unable to think of any organisms, name another plant, or a second animal, that may eat one of the organisms listed. F OOD C HAIN Sun Link your food chain together beginning with the Sun. Add the producer and then the consumers (herbivores and carnivores). Use tape to secure the link. Producer Consumer: Herbivore Consumer: Carnivore Consumer: Carnivore C OMPARING FOOD Plankton CHAINS Shrimp Work in groups of four to compare the food chains that were created. What do the food chains have in common with each other? Could any food chains overlap with each other? Small Mullet Flounder Porpoise F OOD W EBS Plankton Shrimp When food chains overlap, a food web is formed. Use the chains in your group to form a food web. Draw the food web in your science notebook. Small Mullet Crab Flounder Trout Porpoise Sea Gull D ECOMPOSERS Decomposers are organisms such as fungi, bacteria, and animals that play a major role in breaking down dead matter and returning nutrients to the soil. They also play a role in the nitrogen cycle. DECOMPOSERS Plankton Shrimp Add some decomposers to your food web. Small Mullet Crab Bacteria Flounder Trout Porpoise Sea Gull Mold T HE MOST IMPORTANT ROLE The most important role an organism (producer, consumer, or decomposer) plays in the ecosystem is ______ because ______. C OMPARE R OLES IN THE E COSYSTEM Producer Decomposer Consumer