Ex. 47 PowerPoint
advertisement

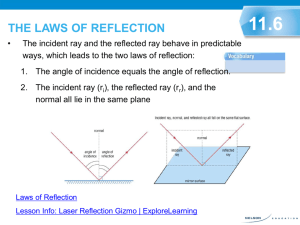
High School by SSL Technologies Physics Ex-47 THE LAW OF REFLECTION When light strikes a surface and is reflected, it changes direction. The direction it takes depends upon the angle it strikes the surface. As illustrated below, a ray of light going towards a surface is called an incident ray while a ray of light which is reflected away from a source is called a reflected ray. The law of reflection says that the angle of the incident ray with the normal equals the angle of the reflected ray (also with the normal). Click Physics Ex-47 By definition, the angle which the incident ray makes with the normal is called the angle of incidence while the angle which the reflected ray makes with the normal is called the angle of reflection. Note that the incident ray, the reflected ray, and the normal are all on the same plane. Remember : The angle of incidence (i) is the angle formed by the incident ray and the normal (not the reflecting surface). The angle of reflection (r) is the angle between the reflected ray and the normal. Click Physics Ex-47 The law of reflection, therefore, simply states that when a ray of light is reflected from a surface, it is reflected in such a direction that the incident angle equals the reflected angle. Using the law of reflection, we can determine the location of images formed by plane mirrors. Click Physics Ex-47 An object is placed in front of a plane mirror. Such as right here! Normal Find the location and characteristics of the image. We can now draw the image. There are two steps in finding the image of a plane mirror. Where the two reflected raysits meet In Objects locating consist an image, of anwe infinite take number one point ofon points. the object and find Normal Since point we are not given the location of theof object, is the imageobject. point the object point. corresponding (location) on the image And each point we hascan an infinite number of rays radiating outwards. select any arbitrary location. Object As shown above, we usually take the (extreme) top point and find Back of mirror Images also consist of an infinite number of points. its corresponding point on the image object. Step-1 Step-2 Each point on the object has a corresponding point on the image. Draw incident ray slightly upwards towards Draw anan incident ray slightly downwards towardsthe themirror. Then draw its then reflected accordance mirror, drawray its in reflected ray. with the law of reflection. Click Physics Ex-47 Virtual images are formed by extended rays. Real images are formed by reflected rays. Click Physics Ex-47 Physics Ex-47 Given a plane mirror and the position of an observer’s eye, determine the field of vision. Mirror angle of incidence = angle of reflection Normal Normal Step-1 Step-2 angle of incidence = angle of reflection Eye There are two steps ineye finding the field of Draw Draw aa ray ray from from the the eye toto the one other endend ofvision. the of the mirror. mirror. This Thisisisthe thereflected reflectedray. ray. Then, Then,inin accordance accordancewith with the thelaw lawofofreflection, reflection,draw drawthe theincident incident ray. ray. Field of vision (Any point within this area will be reflected to the observer’s eye as an image point.) Click Physics Ex-47 P' Image point Image distance Mirror Given a plane mirror, a point object (P) and the position of an observer’s eye, determine whether or not the observer can see object point P. Next, since the image distance equals the object distance, =point, Image distance Object To find the location ofthe theimage image point, wealong start the by drawing a line. line Perpendicular to mirror weObject mark offdistance P‘, extended To determine whether or notline the observer can see the given distance perpendicular to the mirror and not extend it beyond the object, mirror. Look! The does intersect the mirror. we first locate the image of the object. Conclusion: observerANSWER cannot see the image. Object point Next, we draw a line from thewe image to theline observer (eye). Finally, drawpoint a straight from the P The observer cannot see the image. observer’s eye to the image point. If the line intersects the mirror, the observer can see the image. Eye If the line does not intersect theline mirror, then the observer If this intersects the mirror, cannot see the image. the observer can see the image. If this line does not intersect the mirror, the observer cannot see the image. Click P' Physics Ex-47 Image point Given a plane mirror, a point object (P) and the position of an observer’s eye, determine whether or not the observer can see object P. Image distance Mirror ANSWER observer the image. To determine whether or not the The observer can seecannot the givensee object, We now draw a straight line from the Tolocate find the we first thelocation image of the image object.point, we start by drawing a line observer’s eye=toImage image point. perpendicular toObject the mirror and extend itthe beyond the mirror. distance distance Next, we draw a line from the image point to the observer’s eye. Look! The line does not intersect the mirror. Object If this line intersects the mirror, distance Perpendicular tocan mirror If the line intersects thethe mirror, the observer observer can see the image. the see image. Thus, observer cannot seethe the image. If the line does not intersect Ifthe mirror, then not the intersect observerthe cannot this line does mirror, see the image. the observer cannot see the image. Eye P Object point Click Question-1 Physics Ex-47 State the Law of Reflection. The angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. Click Physics Ex-47 Question-2 The diagram below represents an object in front of a plane mirror. Object Note : Diagram not drawn to scale. a) Draw the image. b) How high is the image? 4 cm c) How far is the image from the object? 20 cm Click Question-3 Physics Ex-47 Explain why there is only a lateral (left-right) reversal when we look at ourselves in a plane mirror. Because when we turn towards a mirror, we do so by turning about the Y-axis (left-right) and not about the X-axis (top-bottom). Click Question-4 Physics Ex-47 The diagram below illustrates the image of an object produced by a plane mirror. Label the incident ray, the reflected ray and the extended ray. Reflected ray Incident ray Extended ray Click Physics Ex-47 Question-5 Explain how real images are formed and how virtual images are formed. Real images are formed by the intersection of reflected rays, virtual images are formed by the intersection of extended rays. NOTE As long as there is at least one extended ray, the image is said to be virtual. Click Question-6 Physics Ex-47 Stefania is 1.5 m tall. Prove that the shortest mirror necessary for Stefania to see her full height is 75 cm (half her height). Divide Stefania’s height into two parts, from her eyes to the top of her head and from her eyes to the bottom of her feet. Half Stefania’s height Thus, in order for a person to see their full height in a plane mirror, the minimum mirror required is a mirror half their height. Click Question-7 Physics Ex-47 A beam of light is reflected from a plane mirror such that the angle between the incident ray and reflected ray is 50o. Draw the beam and calculate the angle of incidence? . Click Question-8 Physics Ex-47 Two mirrors, M1 and M2, are at 90o to each other. As illustrated, a beam of light strikes mirror M1 with an angle of incidence of 60o and is reflected by mirror M2. Complete the diagram and find the angle of incidence of the ray reflected by mirror M2. Angle of incidence of mirror M2 Click Question-9 Physics Ex-47 Two plane mirrors, M1 and M2, are at 60o to each other as illustrated in the diagram below. A beam of light strikes mirror M1 with an angle of incidence of 40o. Complete the diagram and determine the angle of reflection of the beam reflected from mirror M2 ? Angle of reflection of mirror M2 Click Click Question-10 Physics Ex-47 Two mirrors are parallel to each other as illustrated in the diagram below. A beam of light strikes the beginning of one mirror at an angle of incidence of 35o. Complete the diagram and find the number of times the beam is reflected before it emerges from the two mirrors? . Click Physics Ex-247 Question-11 What is the angle of reflection for the ray diagram illustrated below? Angle of reflection Angle of incidence A) 1 B) 2 C) 3 D) 4 REMINDER All angles are measured from the “normal”. Click Physics Ex-47 Question-12 Stefania wants to install a rear view mirror on her bike. She has a choice of choosing a plane or a convex mirror as illustrated below. Which mirror should Stefania choose in order to obtain the maximum filed of view? Observer Answer: Stefania should choose the convex mirror in order to obtain the maximum field of view. Observer Click Physics Ex-47 Question-13 The following set up consists of a light source, an obstacle, six different locations (labeled 1 to 6) and a target. Note thatthe only at location 5 can To determine correct location, At which one of the locations can you place a plane mirror we draw unobstructed lines both We now divide angle between the two draw twothe lines each point. so that the light source we is reflected to the from target? toline theto source anda to the target. lines at location 5 with bisector. One the light source and This If another required, using anormal protractor, we can bisector will be the the mirror. line the target. If both Thus, weto must placeto the mirror measure the at angle of incidence or lines aredraw unobstructed, 5. is the Finally, we thelocation mirror that perpendicular to the angle of reflection. point where we place the mirror. the normal (bisector). No No No No No Yes Mirror Click Physics Ex-47 Question-14 The set up below consists of an object and its shadow cast on a screen by a point light source. This problem illustrates the fact that light travels in a straight line, technically known as rectilinear propagation . Determine the position of the light source. A) Point-A B) Point-B C) Point-C Draw a line from the top of the shadow to the top of the object and then extend the line to the light source. D) Point-D Click SSLTechnologies.com/science