Document

GSACEP core man LECTURE series:
Airway management
Lauren Oliveira, DO
LT, MC, USN
Updated: 01MAR2013
Disclaimer
Views and opinions expressed do not necessarily reflect those of GS-ACEP,
The Department of Defense, the U.S.
Government, the North American
Continent, the Western Hemisphere, or
Mother Earth.
Objectives
Anatomy/Physiology
Airway Assessment
Airway Management
Equipment and Medications
Skills Practice
Anatomy
Upper Airway
Anatomy
Lower Airway
Anatomy
Anatomy
physiology
Ventilation
Inhaling and exhaling
Oxygenation
Adding oxygen to the body system
physiology
Oxygen in
Hemoglobin on the RBCs carry O2 to the tissues
Carbon dioxide out
Airway assessment
Look, listen, feel (noisy is bad)
Rate/Quality
Breathing fast?
Working hard?
Shallow breaths?
Chest rising?
Airway assessment: Monitor
Pulse oximetry
The “oxygenation” vital sign
>94%
Capnography (End Tidal CO2)
The “ventilation” vital sign
35-45mmHg
Airway assessment
Predicting a difficult Bag Valve Mask (BVM)
Old
No teeth
Beard
Airway assessment
Predicting a difficult intubation
Limited neck mobility
Large tongue
Facial trauma
Malampati score
Airway management
One person in charge
Assess, intervene, monitor
Airway management
Position
Ear-to-sternal notch
Universal ventilation and intubation position
Independent of age and size
Airway management
Position
Head Tilt/Chin Lift
Jaw Thrust
(Maintains C-spine precautions)
Airway management
Unconscious/no gag reflex intubate
Confused/combative patients are hypoxic until proven otherwise
Airway management
Cricoid pressure (Sellick maneuver) no longer recommended
Aspiration still can occur
Makes it difficult to ventilate…complete AW occlusion in 11%
Detrimental effects on view and blocks tube passage
MRI studies show esophageal occlusion not reliable
Airway management
However, external manipulation of the thyroid cartilage by the person intubating is helpful to improve view
Equipment and medications
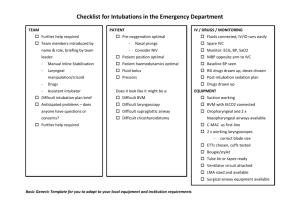
SOAP ‘EM
S uction
O xygen (BVM ready and pre-oxygenate)
A irway adjuncts (OPA, NPA)
P osition
E nd Tidal CO2 (Capnography or colormetric device)
M eds & Monitors
Equipment
Suction
Oxygen Delivery
Nasal cannula, simple mask, non-rebreather
5-12L/min
Must be at least 10L/min
Equipment
Bag Valve Mask (BVM)
Connect to oxygen
Squeeze against hand to verify positive pressure
Equipment
Airway Adjuncts
Nasopharyngeal airway
Okay in an awake patient
Measure nose to ear lobe
Equipment
Airway Adjuncts
Oropharyngeal airway
Only in a comatose patient (will gag)
Measure corner of mouth to ear lobe
Equipment: Advanced airway
Endotracheal tube (ETT) and laryngoscope
Laryngoscope Blade
(here is a Miller)
Laryngoscope
Handle
Tape to secure tube
Syringe to inflate the cuff
ETT and Stylet
Equipment: advanced airway
LMA (Laryngeal Mask Airway)
Equipment: advanced airway
King LT
Equipment: advanced airway
Bougie
Equipment: advanced airway
Direct vs Video laryngoscopy
Equipment: advanced airway
Direct laryngoscopy
Equipment: advanced airway
Direct vs Video laryngoscopy
Equipment: advanced airway
Cricothyroidotomy
1. Vertical incision through skin w/ scalpel
Equipment: advanced airway
Cricothyroidotomy
2. Horizontal incision through cricothyroid membrane
Equipment: advanced airway
Cricothyroidotomy
4. Slide 6-0 ETT over bougie, remove bougie and secure tube
3. Bougie into opening
Equipment: advanced airway
Cricothyroidotomy
5. Confirm placement
Gold= Golden
Breath sounds
Equipment: medications
1 st = Sedate
Etomidate
Ketamine
Midazolam (or other benzodiazepine)
2 nd = Paralyze
Succinylcholine
Rocuronium
Vecuronium
SkillS practice…Go!
Intubation set up
O2, BVM, suction, pulse ox, laryngoscope, tube(s), stylet, syringe, CO2
Medications
Paralytics
Sedatives
Rescue devices
Cricothyroidotomy
Skills practice