Crime and Deviance
advertisement

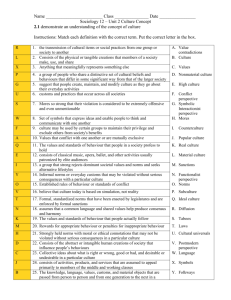
Definitions and links to Psychology. Norms Rules Laws Deviance Crime Delinquency Sanctions Unwritten rules and expectations of society Written expectations in places, with or without sanctions. (ie school/work/transport etc) Formal rules of a country/society, enacted by officials Behaviour that is not the same as the society’s norms and values. Breaking the laws that have been set by society. Behaviour of young people that society does not like, may or may not involve breaking the law. Punishment for breaking laws, both formal (prison etc) and informal (‘tut’) Lombroso Physical appearance Genetic Genes define our behaviour theories Eysenck (1947) The Introvert and the Extrovert. Introverts are shy and quiet while Extroverts are confident and out going. Eysenck believed that extroverts were more likely to commit crime because they would get into situations which may lead to trouble. (ie they are harder to socialise and control) Mental Illness The criminal is mentally ‘sick’ with problems such as Schizophrenia, ADD, Kleptomania, Pyromania etc What does ‘Biological explanation of crime’ mean? What does ‘Psychological explanation of crime’ mean? Kleptomania is the name given to an uncontrollable urge to steal. How would this explain some theft (stealing)? At the time many people believed that Lombroso’s theory argued the best way to deal with criminals was to transport (send) them to Australia, Why do you think this is?