Economics 111.3 Winter 14

TEXT: Michael Parkin and Bade Robin (2013) Microeconomics:
Canada in the Global Environment, Eights Edition with
MyEconLab
GRAPHS IN ECONOMICS
Coordinate System
40
30
20
10
0
B
(1, 20)
A
(4, 5)
1 2 3 4 5
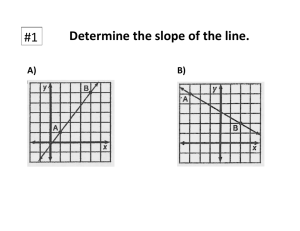
The slope of a relationship is the change in the value of the variable measured on the yaxis divided by the change in the value of the variable measured on the x-axis.
We use the Greek letter
(capital delta) to represent
“change in.”
So
y means the change in the value of the variable measured on the y-axis and
x means the change in the value of the variable measured on the x-axis .
Slope equals
y/
x.
The Slope of a Straight Line
Variables That Are Unrelated
Equation of a straight-line (linear) relationship
Y = a + bX
Position of line: determined by the yaxis (vertical) intercept
$6
5
4
3
2
1
0
Nonlinear Curve
10 20 30
Quantity
40
Slope at a Point
•
The slope of a curved line at a point is equal to the slope of a straight line that is the tangent to that point.
Slope Across an Arc
•
The average slope of a curved line across an arc is equal to the slope of a straight line that joins the endpoints of the arc.
Inverse and Direct
Relationships
Inverse relationship:
When X goes up, Y goes down
When X goes down, Y goes up
X
Direct relationship:
When X goes up, Y goes up
When X goes down, Y goes down
X
Y Y
Variables Moving in the
Same Direction
Variables Moving in
Opposite Directions
The Importance of Scales
$14,000
13,000
12,000
11,000
10,000
1992 1994 1996
(a) Income over time (1)
$18,000
16,000
14,000
12,000
10,000
1992 1994 1996
(b) Income over time (2)
Variables That Have a
Maximum or a Minimum
Maximum Point
Maximum
Slope = 0
A
Minimum Point
Slope = 0
B
Minimum
Types of variables
•
There are two types of variables - independent and dependent.
•
Independent variable (the cause variable, controlled variable, manipulated variable, explanatory variable) is a variable that stands alone and is not changed by the other variables the model in question measures.
•
Dependent variable (outcome variable, response variable, measured variable, explained variable) is a variable that depends on other variables in a model