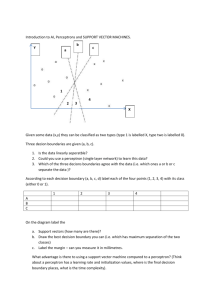
APHG Political Geography suumative assessment
advertisement

APHG Learning Targets Political Geography: Pre-Test • 1. Geopolitics is best described as: • A Study of relationships among politics, geography, economics, demography especially in respect to foreign policy. • B Study of politics in countries around the world • C Political parties in countries on a global scale • D All • E None 2. A state • A Boundary of a group of people with common cultural characteristics • B An area with boundaries and sovereignty • C boundaries coincide with the cultural boundaries of a particular group • D None • E All 3. A Nation • A Boundary of a group of people with common cultural characteristics • B An area with boundaries and sovereignty • C boundaries coincide with the cultural boundaries of a particular group • D All • E None 4. A Nation-State • A Boundary of a group of people with common cultural characteristics • B An area with boundaries and sovereignty • C boundaries coincide with the cultural boundaries of a particular group • D All • E None 5. A commonwealth • A The working of two or more countries to increase wealth • B A territory that has established a mutual agreement with another state to benefit both parties • C A conflict that arises when two or more countries vie for control of a territory • D All • E None 6. A Territorial dispute • A The working of two or more countries to increase wealth • B A territory that has established a mutual agreement with another state to benefit both parties • C A conflict that arises when two or more countries vie for control of a territory • D All • E None 7. Sovereignty • A States ability to regulate their own internal and external affairs. • B The head of state such as a king, president, etc. • C A state taking control of another state • D All • E None 8. The Kurds • A Group of people without their own state in Spain • B A Group of people without their own state in the Middle East • C A Group of people without their own state in Europe • D All • E none 9. The Basques • A Group of people without their own state in Spain • B A Group of people without their own state in the Middle East • C A Group of people without their own state in Asia • D All • E none 10. The Palestinians • A Group of people without their own state in Africa • B A Group of people without their own state in the Middle East • C A Group of people without their own state in China • D All • E none 11. Geometric Boundaries • A Boundaries determined by natural features • B Boundaries determined by cultural factors such as language, religion or ethnicity • C Boundaries determined by longitude and latitude • D All • E None 12. Physical Boundaries • A Boundaries determined by natural features • B Boundaries determined by cultural factors such as language, religion or ethnicity • C Boundaries determined by longitude and latitude • D All • E none 13. Ethnographic Boundaries • A Boundaries determined by natural features • B Boundaries determined by cultural factors such as language, religion or ethnicity • C Boundaries determined by longitude and latitude • D All • E none 14. Ethnic Conflict • A Disagreements that usually result in military action or violence of one race of people against another. • B A Disagreements that usually result in military action or violence of one ethnic group of people against another ethnic group.. • C A Disagreements that usually result in military action or violence of one religion of people against another religion. • D All • E None 15. Religious Conflict • A Disagreements that usually result in military action or violence of one race of people against another. • B A Disagreements that usually result in military action or violence of one ethnic group of people against another ethnic group.. • C A Disagreements that usually result in military action or violence of one religion of people against another religion. • D All • E None 16. Balkanization • A. Adding territory to an already existing state. • B The break up of an area into smaller independent units usually with some degree of hostility. • C A union of many states for achievement of a common goal or purpose • D All • E none 17. Annexation • A. Adding territory to an already existing state. • B The break up of an area into smaller independent units usually with some degree of hostility. • C A union of many states for achievement of a common goal or purpose • D All • E none 18. Definitional Boundary Dispute • A A question about the use of a boundary not the boundary itself. • B A dispute about a specific issue involving a boundary, not the boundary itself • C A dispute about language that defines a boundary. • D All • E none 19 . Locational boundary Dispute • A A question about the site of boundary itself. • B A dispute about a specific issue involving a boundary, not the boundary itself • C A dispute about definition that defines a boundary. • D All • E none 20. Operational Boundary Dispute • A A question about the use of a boundary not the boundary itself. • B A dispute about a specific issue involving a boundary, not the boundary itself • C A dispute about definition that defines a boundary. • D All • E none 21. Allocational Boundary Dispute • A A question about the use of a boundary not the boundary itself. • B A dispute about a specific issue involving a boundary, usually over contro lof natural resources, not the boundary itself • C A dispute about definition that defines a boundary. • D all • E None 22. UNCLOS • A United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea • B United Nations Convention on the Law of the Skies • C United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sub-Continents • D All • E none 23. International Law of the Sea • A Treaty among nations established by the UN • B Regulates how ships operate on the high seas • C Establishes a 12 mile territory sea limit and a 200 mile exclusive economic zone for countries • D All • E none 24. Exclusive Economic Zone • A 200 mile zone off a states coast • B State has control over what goes on within 200 mile of their coast • C Established by the UNCLOS • D All • E None 25. Median-Line Principle • A A method of resolving boundary disputes • B Principal upon which colonialization is justified • C Process of drawing congressional districts • D All • E none 26. Global Commons applies to? • • • • • A North America B Asia C Antarctica D All E none 27. Antecedent Boundaries • A Example: Native American borders of tribes hunting grounds • B Example: the border between East and West Berlin • C Example: border imposed by a super power on a territory • D All • E None 28. Subsequent Boundaries • A Example: Native American borders of tribes hunting grounds • B Example: the border between East and West Berlin • C Example: borders established on Native American hunting grounds by settlers • D All • E None 29. Superimposed Boundaries • A Example: Native American borders of tribes hunting grounds • B Example: the border between East and West Berlin • C Example: border imposed by a super power on a territory • D All • E None 30. Relic Boundaries • • • • • A Example: Native American borders of tribes hunting grounds B Example: the border between East and West Berlin C Example: border imposed by a super power on a territory D All E None 31. Reunification • • • • • A Example: East Germany and West Germany B Example: North and South Vietnam C Example: the Union and Confederacy in USA D All E none 32. Boundary Evolution • A The technical wording of treaty that defines where a boundary should be located • B. A cartographer drawing a boundary on a map • C The process of natural selection of a boundary • D All • E None 33. Delimitation • A The technical wording of treaty that defines where a boundary should be located • B. The transition or translation of a boundary that results in a cartographer drawing a boundary on a map • C The process of natural selection of a boundary • D All • E None 34. Colonialism • A Control of territory for the primary benefit of the mother country • B Control of territory for the primary benefit of the colony • C Control of territory for the primary benefit of a third country • D All • E none 35. Organic Theory • A Uses to justify European colonies in Americas and Africa • B Control of central Europe and West Asia controls the world • C Control of the area surrounding central Europe and West Asia controls the world • D All • E None 36. Self-Determination • A. The power of the people to vote on issues • B The power of the people to establish their own government • C The right of women to vote • D All • E none 37. Suffrage • A. The power of the people to vote on issues • B The power of the people to establish their own government • C The right of women to vote • D All • E none 38. Women’s Enfranchisement • A. The power of the people to vote on issues • B The power of the people to establish their own government • C The right of women to vote • D All • E None 39 . Land Empire • A. A settlement designed to stay a long time in an area and over time send resources back to the home country • B Sea power is used to control and area so resources can be sent back to the home country • C Conquest by force of an area to send resources back to the home country • D All • E none 40. Sea Empire • A. A settlement designed to stay a long time in an area and over time send resources back to the home country • B Sea power is used to control and area so resources can be sent back to the home country • C Conquest by force of an area to send resources back to the home country • D I do not know 41. Settlement Empire • A. A settlement designed to stay a long time in an area and over time send resources back to the home country • B Sea power is used to control and area so resources can be sent back to the home country • C Conquest by force of an area to send resources back to the home country • D All • E None 42. Forward Capital example • • • • • A Washington DC B Brasilia C Mexico City D All E none 43. Microstates Example • • • • • • A Vatican City B Poland C Luxembourg D All E none 44. Ministates example • • • • • A Vatican City B Poland C Luxembourg D All E none 45. Territorial Morphology • • • • • A The death of a state B The shape of a state C The state of a state D All E none 46. Compact Country example • • • • • A Vatican City B Poland C Luxembourg D All E none 47. Elongated Country Example • • • • • A Chile B Argentina C Italy D All E none 48. Fragmented Country • A Usually a state with multiple islands such as the Philippines • B A state with deep political divisions • C Example: the USA • D All • E none 49. Exclave example • • • • • A Alaska B Florida C California D Al E None 50. Perforated Country • A States has another state entirely inside its borders • B A states major holes in it • C A separate state • D All • E none 51. Enclave • • • • • A Same as a landlocked country B State surrounded by water C Religious state D All E none 52. Landlocked Country • • • • • A Same as an Enclave B State surrounded by water C Religious state D All E none 53. Prorupted Country • A State has part of its territory sticking out from its mainland like Florida in the USA • B A state with many volcanoes • C A state with a large number of professionals • D All • E none 54. Embassies • A Secondary office that deal with economic issues and granting visas to enter a country. • B The official representative of one country to another. • C Sovereign territory of one country in another, usually a compound or group of buildings, to represent countries interests on another country • D. All • E None 55. Ambassadors • A Secondary office that deal with economic issues and granting visas to enter a country. • B The official representative of one country to another. • C Sovereign territory of one country in another, usually a compound or group of buildings, to represent countries interests on another country • D. All • E none 56. Consulates • A Secondary office that deal with economic issues and granting visas to enter a country. • B The official representative of one country to another. • C Sovereign territory of one country in another, usually a compound or group of buildings, to represent countries interests on another country • D. All • E none 57. Satellite States • A States with a lot of satellites • B States controlled by another state for defensive purposes • C States that orbit another state • D All • E none 58. Iron Curtain • • • • • A The division between East and West Europe B Established by the USSR C Part of the Iron Curtain cut through Berline D All E none 59. Buffer State • A States with a lot of satellites • B States controlled by another state for defensive purposes, similar to a satellite state • C States that orbit another state • D All • E none 60. Heartland Theory • A Uses to justify European colonies in Americas and Africa • B Control of central Europe and West Asia controls the world • C Control of the area surrounding central USA and North America controls the world • D All • E None 61. Rimland Theory • A Uses to justify European colonies in Americas and Africa • B Control of central Europe and West Asia controls the world • C Control of the area surrounding central Europe and West Asia controls the world • D All • E None 62. Domino Theory • A Popular after WWII • B A theory on the spread of communism • C Dominates US foreign policy from the 1950s through the 1980s • D All • E none 63. Irredentism • A Policy of disrupting a state such that a new government is put in place more favorable to another state. • B USA employed this policy in Central America for many years • C The Shah of Iran was put in place by the Usa through this policy • D All • E none 64. Centrifugal Forces • • • • • A Forces that tend to pull a state apart B Forces that tend to hold a state together C Forces of minorities D All E none 65. Centripetal • • • • • A Forces that tend to pull a state apart B Forces that tend to hold a state together C Forces of minorities D All E none 66. National Iconography examples • • • • • A Flag B Anthem C Monuments D All E none 67. Theocracies • • • • • A Religious states B States based on a theory C Secular states D All E none 68. Reapportionment • A Reallocation of US House of Representatives based on changes in population. • B Regeneration of a states constitutional division of power • C Regurgitation of the bill of rights in a more palatable form • D All • E None 69. Gerrymandering • A The drawing of congressional district to favor one political party, racial or ethnic group • B The benefits that senor citizens are entitled to • C Division of powers of government • D All • E none 70 Census • • • • • A required by the constitution B Conducted every 10 years C Used to allocate Congressional seats D All E none 71. Census data is shared with other government agencies., • A True • B False 72. Only citizens are counted in the census. • A true • B false 73. Homeless people are not counted in the census. • A True • B False 74. It is a crime for a census worker to reveal census information • A True • B False 75. House of Representatives is based on? • • • • • A Size of a state B Population C Combination of Size and population D All E none