Projectile Motion Homework: Physics Problems & Virtual Lab
advertisement
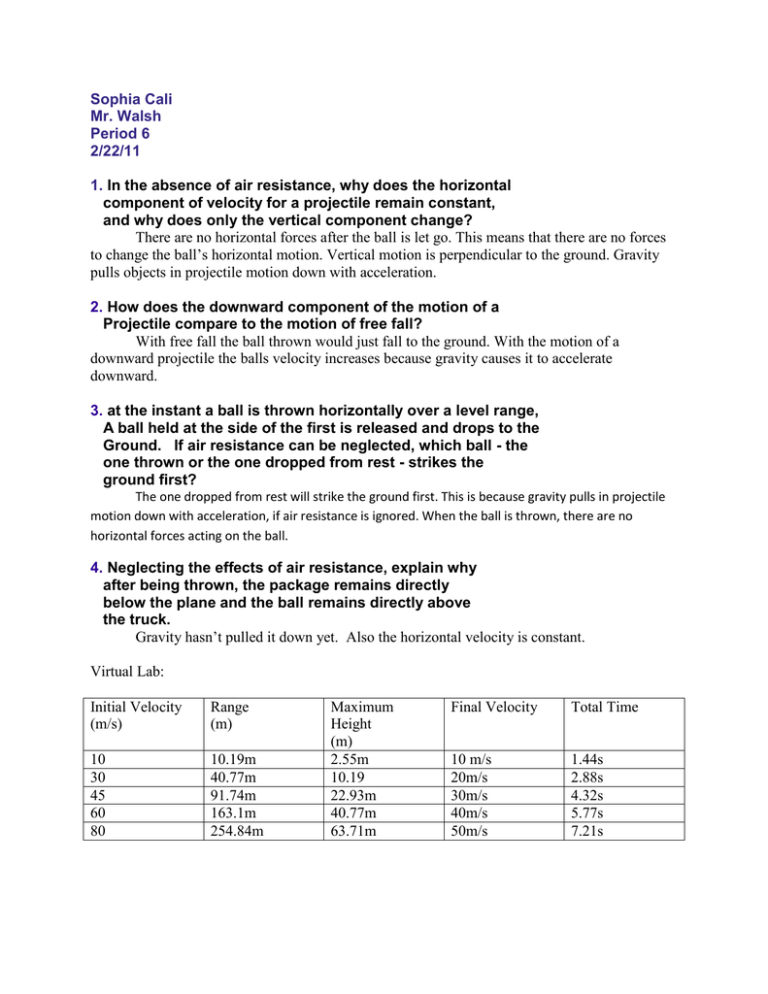
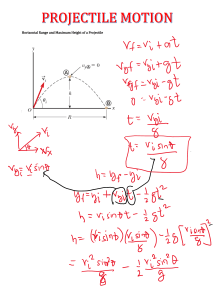
Sophia Cali Mr. Walsh Period 6 2/22/11 1. In the absence of air resistance, why does the horizontal component of velocity for a projectile remain constant, and why does only the vertical component change? There are no horizontal forces after the ball is let go. This means that there are no forces to change the ball’s horizontal motion. Vertical motion is perpendicular to the ground. Gravity pulls objects in projectile motion down with acceleration. 2. How does the downward component of the motion of a Projectile compare to the motion of free fall? With free fall the ball thrown would just fall to the ground. With the motion of a downward projectile the balls velocity increases because gravity causes it to accelerate downward. 3. at the instant a ball is thrown horizontally over a level range, A ball held at the side of the first is released and drops to the Ground. If air resistance can be neglected, which ball - the one thrown or the one dropped from rest - strikes the ground first? The one dropped from rest will strike the ground first. This is because gravity pulls in projectile motion down with acceleration, if air resistance is ignored. When the ball is thrown, there are no horizontal forces acting on the ball. 4. Neglecting the effects of air resistance, explain why after being thrown, the package remains directly below the plane and the ball remains directly above the truck. Gravity hasn’t pulled it down yet. Also the horizontal velocity is constant. Virtual Lab: Initial Velocity (m/s) Range (m) 10 30 45 60 80 10.19m 40.77m 91.74m 163.1m 254.84m Maximum Height (m) 2.55m 10.19 22.93m 40.77m 63.71m Final Velocity Total Time 10 m/s 20m/s 30m/s 40m/s 50m/s 1.44s 2.88s 4.32s 5.77s 7.21s